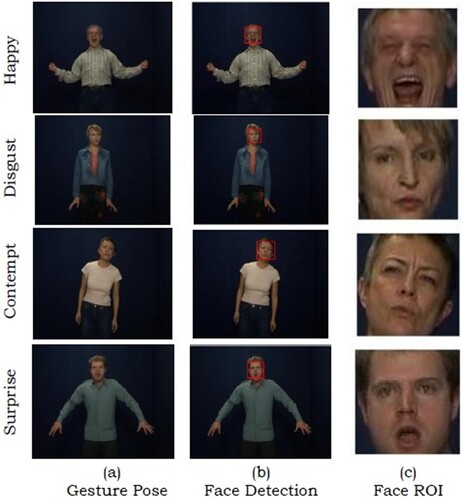
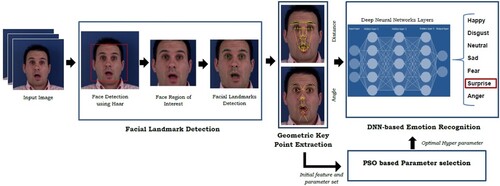
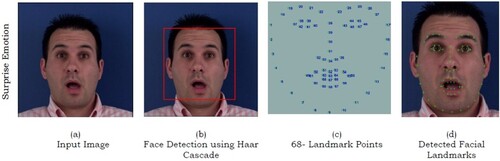
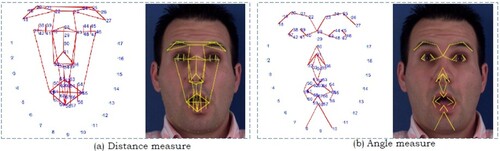
Figures & data
Table 1. Prior work on Facial emotion recognition.
Table 2. Facial Landmark coordinates for feature extraction.
Table
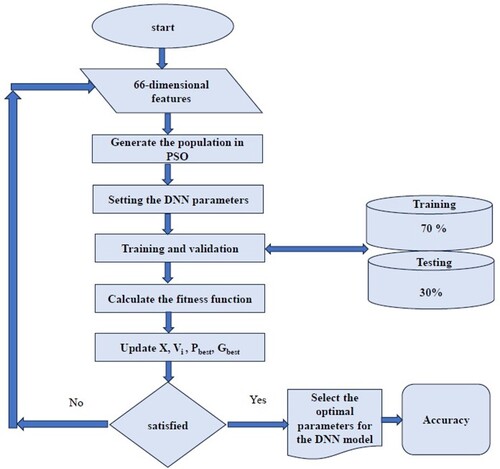
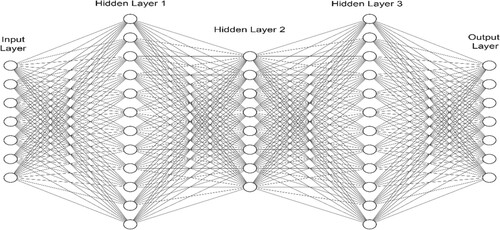
Table 3. Hyperparameter setting for training the DNN using the PSO Algorithm.
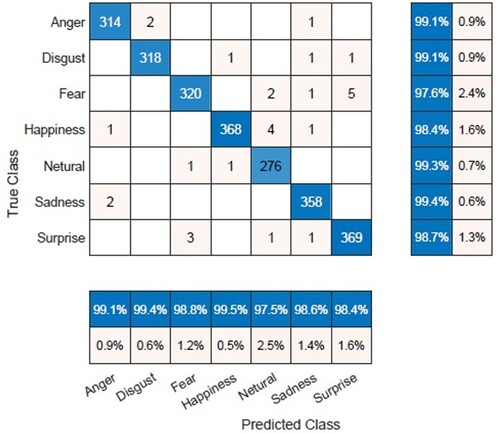
Table 4. Performance measure of seven basic emotions.
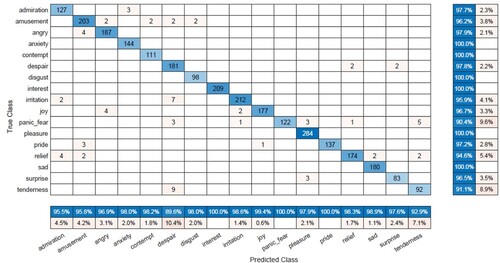
Table 5. Performance measure of micro-coded emotions.
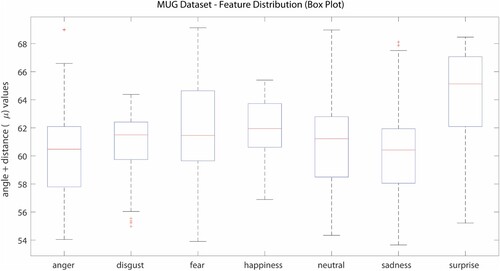
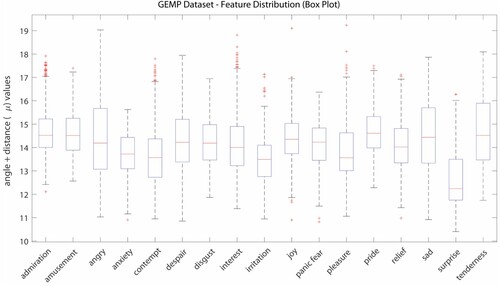
Figure 12. (a) and (b) Model Performance for the MUG Dataset, (c) and (d) Model Performance for the GEMEP Dataset.
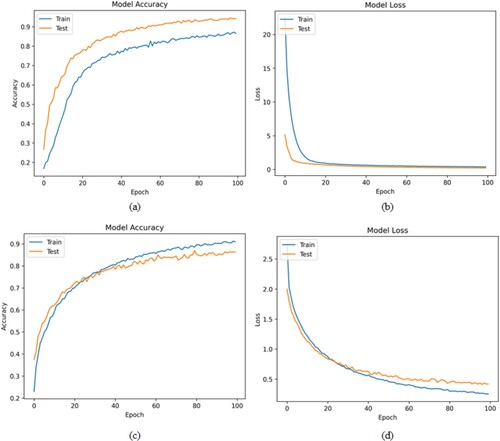
Table 6. Cutting-edge results achieved in the emotional datasets.