Figures & data
Figure 1. Correlation between NSAID anti-inflammatory/analgesic potency ratio in experimental models and clinical analgesic activity in a model of post-surgical dental pain. Graphical elaboration from CashmanCitation56.
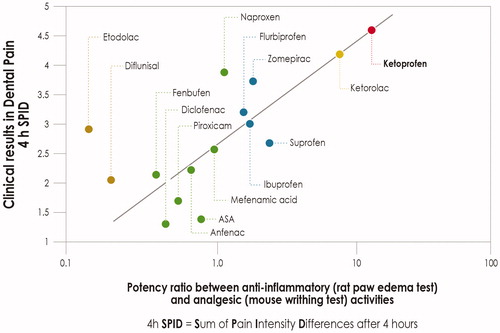
Table 1. Summary of the pharmacodynamic features of the opiod agonists, usually combined with non-opioid analgesics.
Table 2. Summary of the pharmacokinetic features of the opiod agonists, usually combined with non-opioid analgesics.
Figure 2. Clinical study in a dental pain model showing the best analgesic efficacy of the dexketoprofen-tramadol combination in a 1:3 ratio. Percentage of patients showing response (≥ 50% max TOTPAR) over 6 h post-dose (Primary end-point). Maximum TOTPAR corresponds to the theoretical maximum possible time-weighted sum of the PAR scores, measured on a 5-point VRS (0 = none to 4 = complete). Graphical elaboration from Moore et al.Citation48
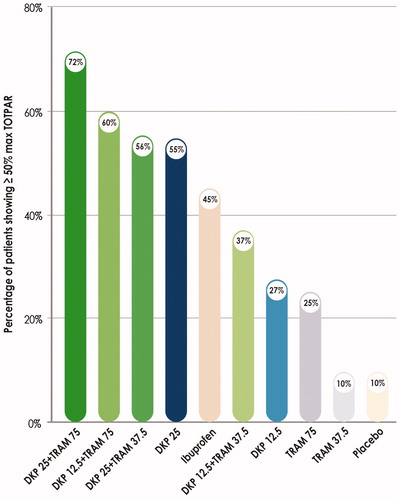
Figure 3. Fixed-dose combination dexketoprofen/tramadol mechanism of action. Different modes of action contribute to dexketoprofen/tramadol analgesic FDC efficacy. A synergy between central analgesic action, peripheral analgesic effect, and anti-inflammatory activity underlies the multimodal analgesia provided by the fixed-dose combination dexketoprofen/tramadol. 5-HT: 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin); AA: arachidonic acid; COX: cyclo-oxygenase; GABA: γ-amino-butyric acid; MOR: μ-opioid receptor; NA: noradrenaline; PG: prostaglandin.
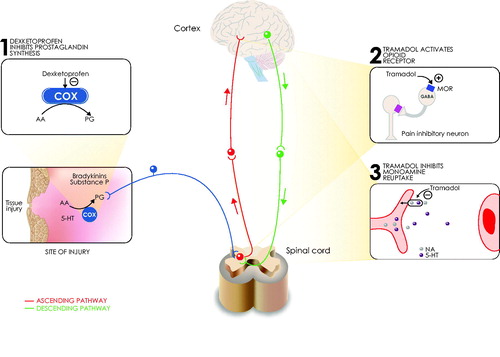
Table 3. Percentage of pain intensity (PI) responders (achievement of mean pain intensity VAS <40 mm) at rest over the first 8 h and percentage of patients using rescue medication (RM) over 24 h, during the multiple dose phase in clinical trials with DKP/TRAM FDC.
