Figures & data
Table 1. Tapinarof cream 1% compared with treatments for atopic dermatitis approved by the US FDA since 2000: Regulatory restrictions, warnings, and common adverse events.
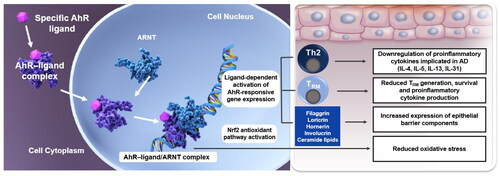
Figure 1. Ligand-specific binding and activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in the treatment of atopic dermatitis (Citation36,Citation38–44). Ligand-specific binding and activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor downregulates proinflammatory cytokines, reduces oxidative stress, upregulates expression of skin barrier components and inhibits the generation, persistence, and cytokine production of resident memory T cells in the skin. Some of the proposed downstream effects of tapinarof in AD are distinct from its mechanism of action in psoriasis. The proposed mechanism of action of tapinarof in psoriasis is described by Bissonnette et al. (Citation36). AhR: aryl hydrocarbon receptor; ARNT: aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator; DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid. Th2: T helper 2 cell; TRM: resident memory T cell.