Figures & data
Table 1. Baseline demographics and clinical characteristics.
Figure 1. Proportion of patients achieving ACR20 by subgroup. ACR20: ≥20% improvement in American College of Rheumatology criteria; BMI: body mass index; CI: confidence interval; csDMARD: conventional synthetic disease-modifying, anti-rheumatic drug; Dx: diagnosis; hsCRP: high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; PsA: psoriatic arthritis; PBO: placebo; RZB: risankizumab.
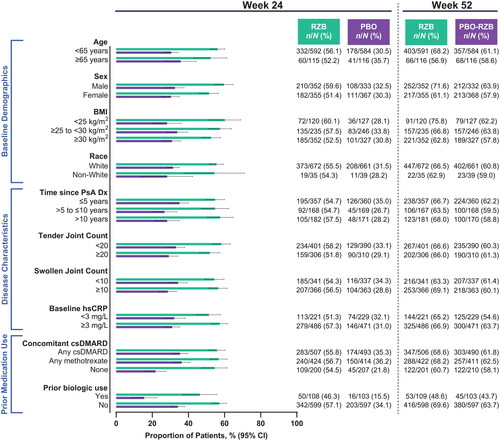
Figure 2. Proportion of patients achieving ACR50 by subgroup. ACR50: ≥50% improvement in American College of Rheumatology criteria; BMI: body mass index; CI: confidence interval; csDMARD: conventional synthetic disease-modifying, anti-rheumatic drug; Dx: diagnosis; hsCRP: high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; PsA: psoriatic arthritis; PBO: placebo; RZB: risankizumab.
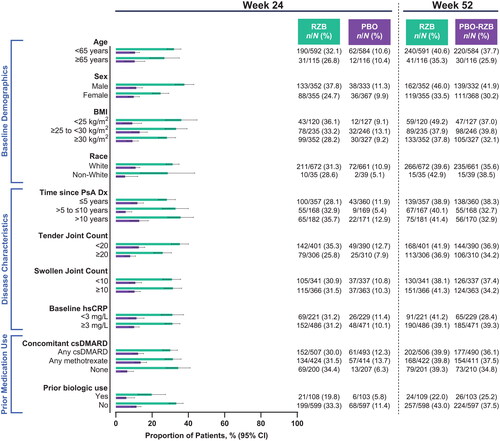
Figure 3. Proportion of patients achieving ACR70 by subgroup. ACR70: ≥70% improvement in American College of Rheumatology criteria; BMI: body mass index; CI: confidence interval; csDMARD: conventional synthetic disease-modifying, anti-rheumatic drug; Dx: diagnosis; hsCRP: high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; PsA: psoriatic arthritis; PBO: placebo; RZB: risankizumab.
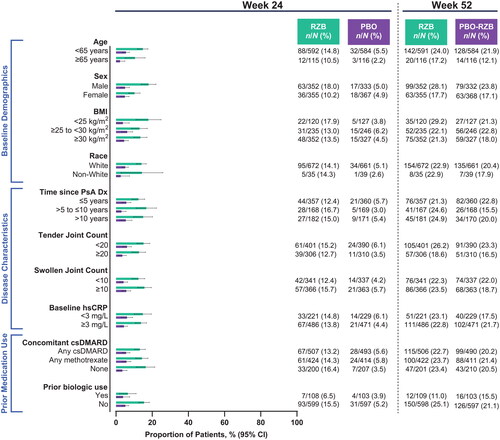
Figure 4. Proportion of patients achieving PASI90 by subgroup. Patients included in the PASI90 analysis had BSA ≥3% at baseline. BSA: body surface area; BMI: body mass index; CI: confidence interval; csDMARD: conventional synthetic disease-modifying, anti-rheumatic drug; Dx: diagnosis; hsCRP: high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; PASI90: ≥90% improvement in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index; PsA: psoriatic arthritis; PBO: placebo; RZB: risankizumab.
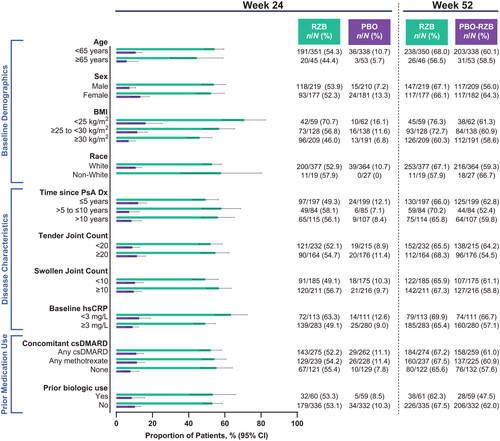
Figure 5. Proportion of patients achieving MDA by subgroup. BMI: body mass index; CI: confidence interval; csDMARD: conventional synthetic disease-modifying, anti-rheumatic drug; Dx: diagnosis; hsCRP: high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; MDA: minimal disease activity; PsA: psoriatic arthritis; PBO: placebo; RZB: risankizumab.
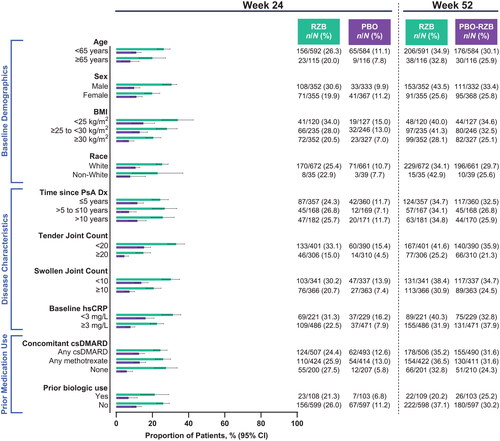
Figure 6. Proportion of patients achieving DAPSA LDA by subgroup. BMI: body mass index; CI: confidence interval; csDMARD: conventional synthetic disease-modifying, anti-rheumatic drug; DAPSA LDA: Disease Activity in Psoriatic Arthritis Low Disease Activity score of 5–14; Dx: diagnosis; hsCRP: high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; PsA: psoriatic arthritis; PBO: placebo; RZB: risankizumab.
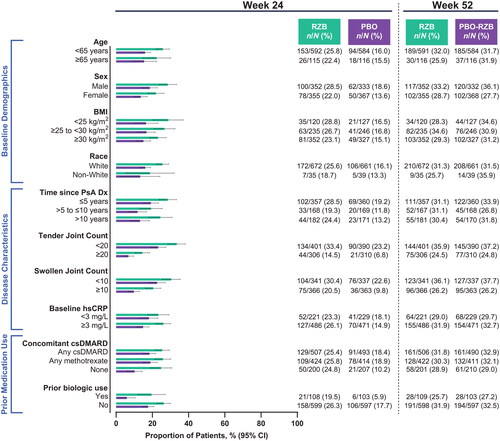
Figure 7. Proportion of patients achieving a minimal clinically important difference in pain by subgroup. A minimal clinically important difference in pain was defined as ≥10 mm decrease (on a 100-mm visual analog scale) among patients with baseline pain ≥10 mm. BMI: body mass index; csDMARD: conventional synthetic disease-modifying, anti-rheumatic drug; CI: confidence interval; Dx: diagnosis; hsCRP: high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; PsA: psoriatic arthritis; PBO: placebo; RZB: risankizumab.
Supplemental Material
Download PDF (141.6 KB)Data availability statement
AbbVie is committed to responsible data sharing regarding the clinical trials we sponsor. This includes access to anonymized individual and trial-level data (analysis data sets), as well as other information (e.g., protocols, clinical study reports, or analysis plans), as long as the trials are not part of an ongoing or planned regulatory submission. This includes requests for clinical trial data for unlicensed products and indications. These clinical trial data can be requested by any qualified researchers who engage in rigorous, independent scientific research, and will be provided following review and approval of a research proposal and statistical analysis plan and execution of a data sharing agreement. Data requests can be submitted at any time after approval in the United States and Europe and after acceptance of this manuscript for publication. These data will be accessible for 12 months, with possible extensions considered. For more information on the process or to submit a request, visit the following link: https://vivli.org/ourmember/abbvie/ then select ‘Home’.

