Figures & data
Figure 1. Twenty-five key questions categorized to guide future areas of AOPs in radiation research and policy work.

Figure 2. Hypothetical example of how radiation exposures conditions (acute or chronic) can lead to a common molecular initiating event of deposition of energy (DOE) to multiple different key events (KEs) depending on the radiation exposure parameters. Not all KEs are sufficient to progress to adverse outcome (AO). Red X represents a no-go to the AO, the blue zig zag represents multiple KEs. For the purposes of this example low dose and low dose-rate refers to <100 mGy/<0.1 mGy/min and high dose and high dose-rate refers to >1Gy/>0.01 Gy/min.
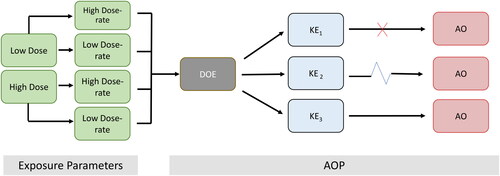
Table 1. Focus areas for future advancements of AOPs.
