Figures & data
Figure 1. Reliability network of a system with components from n varieties, (a) logically arranged in series; (b) logically arranged in parallel.
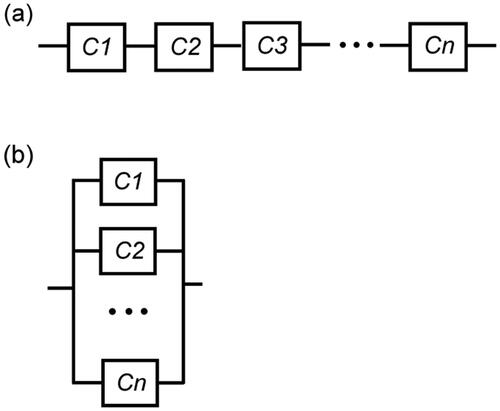
Figure 2. (a) Reliability network of a series-parallel system with components from n varieties; (b) reliability network of a series-parallel system involving components of 3 varieties.
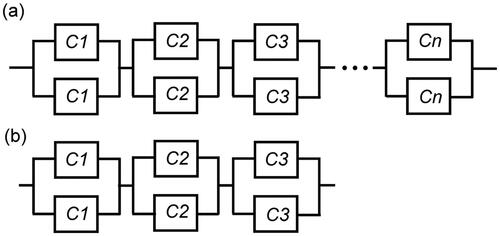
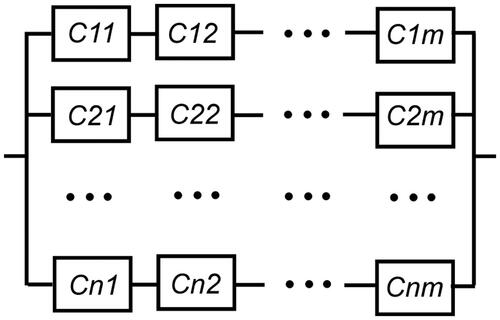
Figure 3. (a) Reliability network of a series-parallel system with components from n varieties and m redundancies in each section; (b) reliability network of a series-parallel system with components from 3 varieties and 3 redundancies in each section.
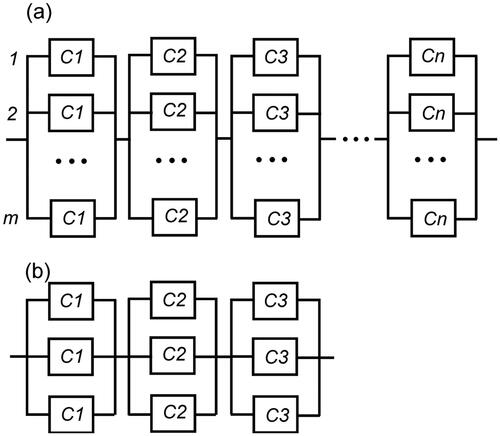
Figure 4. Reliability network of a parallel-series system with n parallel branches each including components from m varieties.