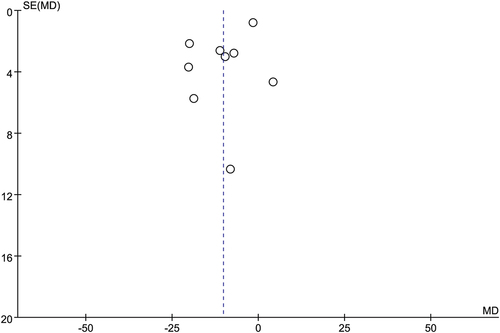
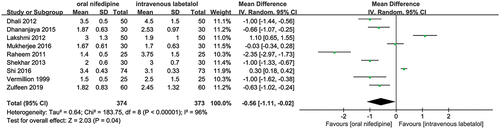
Figures & data
Figure 1. Flow diagram of retrieval and selection of study. CENTRAL, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials; CNKI, China National Knowledge Infrastructure.
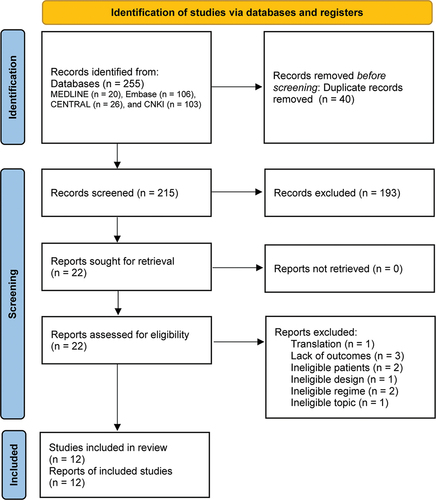
Table 1. Characteristics of the included studies (n = 12).
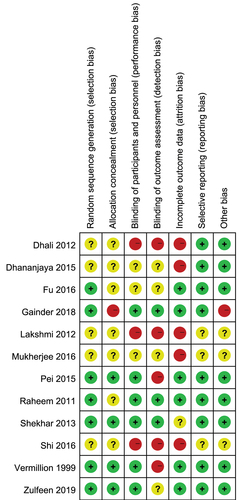
Figure 2. Risk of bias summary. Low risk of bias (green hexagons), unclear risk of bias (white hexagons), and high risk of bias (red hexagons).
Supplemental Material
Download Zip (1.1 MB)Data availability statement
No datasets were generated for this study