Figures & data
Table 1.. Plant species, family, common name, and lot or sample number for single (one species) and blended (two or more species) essential oils used in this study.
Figure 1 Correlation between INT and OD measurements in determining the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 14 essential oils against Staphylococcus aureus. (A) and Candida albicans. (B).
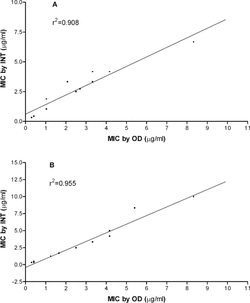
Table 2.. Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 14 essential oils against Staphylococcus aureus. as determined by the metabolic dye (INT) and % inhibition (OD).
Table 3.. Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 14 essential oils against Candida albicans. as determined by the metabolic dye (INT) and % inhibition (OD).
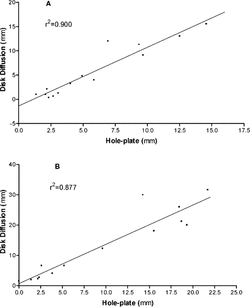
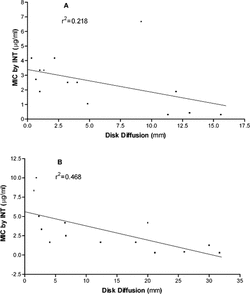
Table 4.. Zones of inhibition for diffusion assays against Staphylococcus aureus. and Candida albicans..