Figures & data
Figure 2. MR results of immune cell signatures with a causal relationship to COPD. From the inner to outer circles, they represent the p-value of weighted mode, simple mode, weighted median, MR-Egger, and inverse-variance weighted methods, respectively. The shades of color reflect the magnitude of the pvalue.
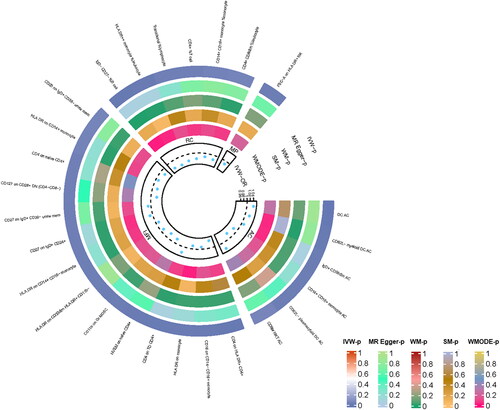
Figure 4. Scatter plots of the MR analyses for the association of immune cell signatures and the risk of COPD.
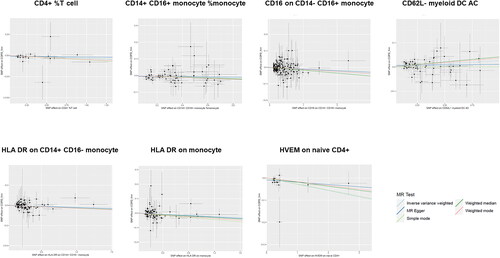
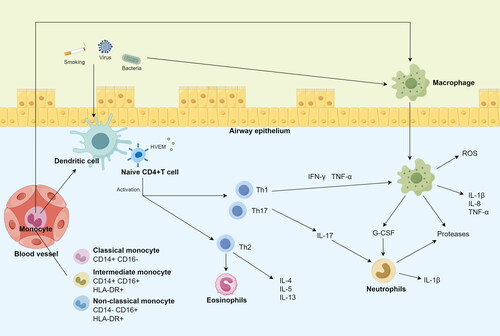
Table 1. The functions of these seven immune cells.
Supplemental Material
Download Zip (11 MB)Data availability
The data that supports the findings of this study are available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author.