Figures & data
Figure 1. Akkermansia muciniphila is involved in mucin production by goblet cells independent on type 2 immunity.
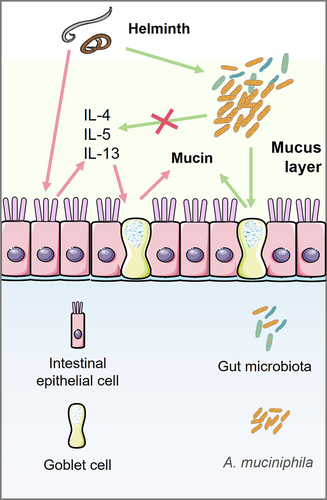
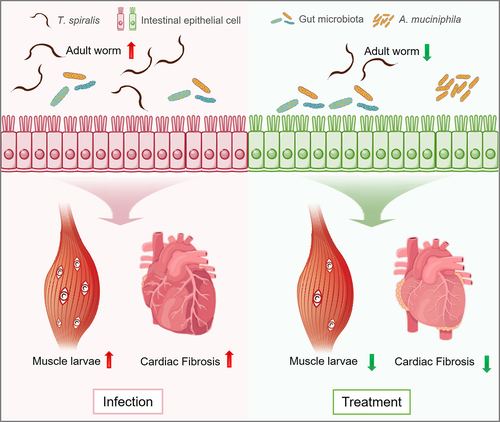
Figure 2. Akkermansia muciniphila plays a role in protection against Trichinella spiralis infection.
Data availability statement
All data are included in the manuscript.
