Figures & data
Table 1. Resistance and virulence genes in three K. pneumoniae strains and mutations in the coding region of strains KP29499 and KP30086 using KP29105 as reference.
Figure 1. Genomic profiles of these 3 clinical K. pneumoniae strains KP29105, KP29499 and KP30086. (a) Circular maps of plasmids in these 3 strains (b) Major structural features of the multi-resistance plasmids in the 3 K. pneumoniae isolates. pKP29499–2 integrated an IncR type plasmid after an insertion sequence IS6 of pKP29105–2, and blaCTX-M-15 becomes blaCTX-M-71 by single amino acid substitution. Whereas pKP30086–2 had a large fragment deletion compared with pKP29499–2, and the blaCTX-M gene was located in this fragment (figure 1B). Boxed arrows indicate the positions of open reading frames (ORFs) and their directions of transcription. ORFs encoding resistance genes are portrayed by red arrows. Green arrows indicate insertion sequences. Gray areas denote more than 95% DNA identity between sequences. (c) Resistance genes in the 3 clinical K. pneumoniae strains. Asterisks represent genes with mutations.
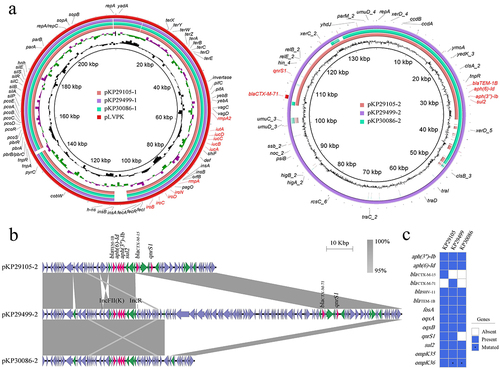
Table 2. Antibiotic resistance characteristics (MICs, mg/L) of 3 clinical K. pneumoniae isolates and the transconjugant, transformants and mutants.
Table 3. Antibiotic resistance characteristics (MICs, mg/L) of K. pneumoniae strain KP29499 to ceftazidime, ceftazidime-avibactam, meropenem and ceftriaxone.
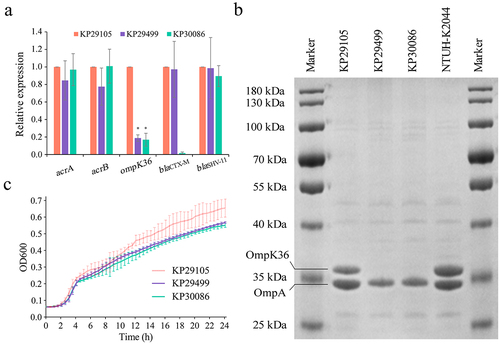
Figure 2. Porin profiles and growth curves of K. pneumoniae strains KP29105, KP29499 and KP30086. (a) Relative expression at the transcriptional level of genes ompK35, ompK36 and blaCTX-M. Data were normalized to the expression levels of gene rpoB. K. pneumoniae NTUH-K2044 and KP29105 were set as the basic expression for porins and CTX-M, respectively. (b) SDS-PAGE (sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) of outer membrane proteins. K. pneumoniae NTUH-K2044 was used as reference. (c) Growth curves of the K. pneumoniae isolates. Three independent experiments were carried out. The significance level was as follows: *p < 0.05.
Data Availability statement
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary materials.
