Figures & data
Figure 1. MLL regulates transcription of RhoGDI1 to regulate the levels of Rho GTPases. (a) MLL HMT complex is involved in the active transcription of RhoGDI1. RhoGDI1 acts as a chaperone for the small Rho GTPases, RhoA, Rac1 and CDC42, ensuring their stability in the cell. These Rho GTPases regulate the cell shape, cell migration and actin cytoskeleton formation. (b) Inhibition of MLL using RNAi or small molecule inhibitors in cells reduces the transcription of RhoGDI1, which further affects the stability and function of small GTPases and results in the abnormal cell shape and cell migration, most likely as a consequence of reduced actin cytoskeleton.
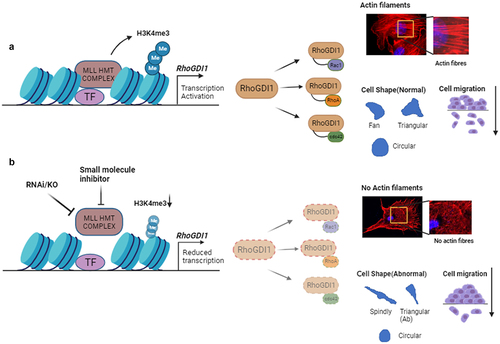
Figure 2. MLL fusion partners from Rho GTPase signalling pathway – many Rho GTPase regulators like GAPs and GEFs as well as other proteins functioning in Rho GTPase signalling act as fusion partners for MLL as depicted in the table. They may dysregulate the cell cytoskeleton by changing the expression or perturbing functions of genes that play important role in actin, microtubule and intermediate filament regulation.
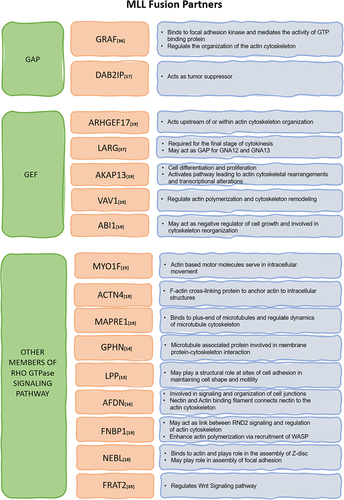
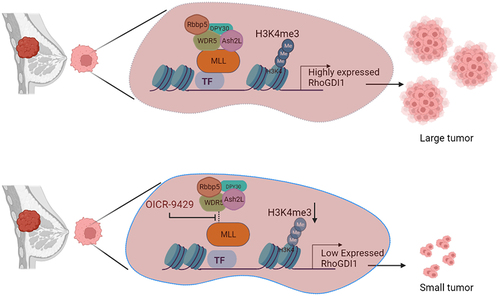
Figure 3. Inhibition of MLL can reduce tumours in xenografts. MDA-MB-231 cells are triple-negative breast cancer cells with high RhoGDI1 expression, which promotes tumour formation. MLL with its core-complex proteins promotes the transcription of RhoGDI1 by methylating the RhoGDI1 promoter. Treatment with OICR-9429, a non-peptide inhibitor of MLL-WDR5 interaction, reduces the activity of MLL at RHOGDI1 promoter, thus reducing the expression of RhoGDI1 gene. This results in tumour regression. Thus, inhibition of MLL can be used as a potential therapeutic in tumours showing high expression of RhoGDI1.
Data availability statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analysed in this study.
