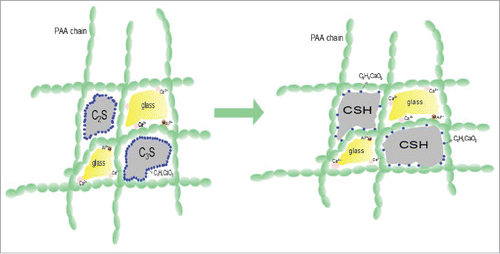
Figures & data
Table 1. Initial and final setting times for wollastonite modified cements.
Table 2. Initial and final setting times for MTA modified cements.
Figure 3. Compressive strength of GIC with wollastonite and MTA. Test groups with the same superscript letter are not significantly different at P < 0.05 level (one-way ANOVA, LSD's test).
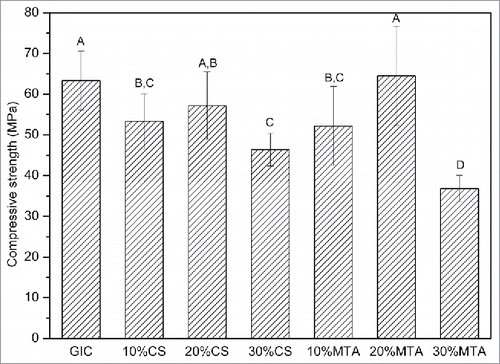
Figure 4. pH changes of solution over a period of 7days. GIC with (A) Wollastonite in SBF (B) Wollastonite in water (C) MTA in SBF (D) MTA in water.
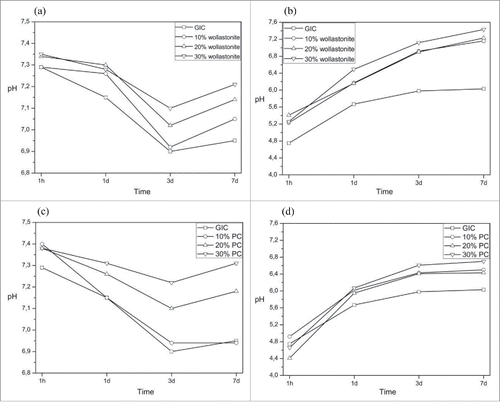
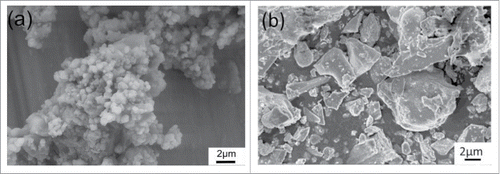
Figure 5. SEM images of the cements with wollastonite after soaking in SBF solution. (A) GIC after 1h, (B) GIC after 7 d, (C) 10% wollastonite after 1 h (D) 10% wollastonite after 7 d, (E) 20% wollastonite after 1h, (F) 20% wollastonite after 7 d, (g) 30% wollastonite after 1h, (h) 30% wollastonite after 7 d.
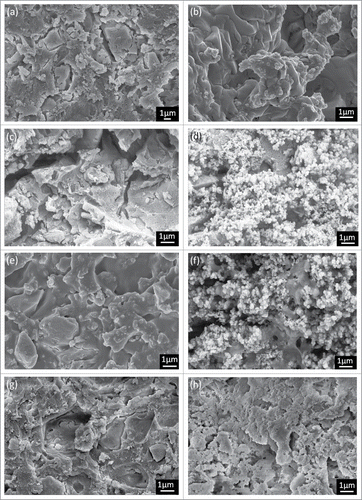
Figure 6. SEM images of the cements with MTA after soaking in SBF solution. (A) 10% MTA after 1 h (B) 10% MTA after 7 d, (C) 20% MTA after 1 h, (D) 20% MTA after 7 d, (E) 30% MTA after 1 h, (F) 30% MTA after 7 d.
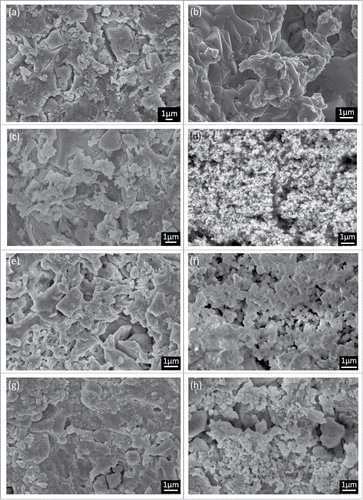
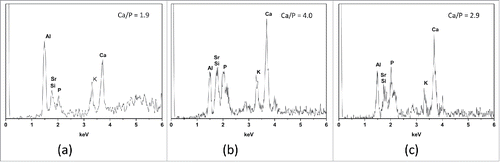
Figure 7. EDX analysis: (A) GIC (B) 20% wollastonite (C) 20% MTA. The specimen was immerged in the SBF for 7 d at 37°C.
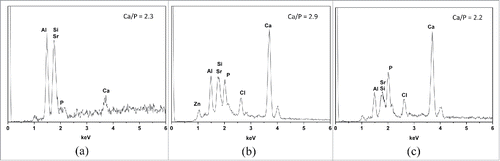
Table 3. Initial and final setting times for wollastonite and MTA modified commercial luting cements.
Figure 8. Compressive strength of GIC modified by wollastonite and MTA, after storage in distilled water for 1 d, 7 d and 14 d. Test groups with the same superscript letter are not significantly different at P < 0 .05 level (one-way ANOVA, LSD's test).
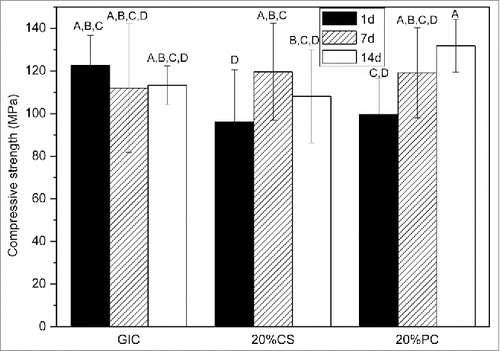
Figure 10. SEM images of the cements after soaking in SBF solution. (A) GIC after 1 h, (B) GIC after 14 d, (C) 20% wollastonite after 1 h (D) 20% wollastonite after 14 d, (E) 20% MTA after 1 h, (F) 20% MTA after 14 d.