Figures & data
Figure 1. Main pathways of NAD+ synthesis and consumption in mammals. NAD+ is either synthesized from tryptophan (de novo biosynthesis) or from NMN by NMNAT. NMN can be provided by NR and NAM. The synthesized NAD+ is broken down by NAD+-dependent enzymes such as SIRT1, PARP1, and CD38, and therefore the recycled NAM can be re-synthesized to NAD+ via the NAD+ salvage pathway. NAD±consuming enzymes have several functions. For example, SIRT1 controls circadian rhythm, whereas PARP1 and CD38 regulate DNA repair and mitochondrial function, respectively. Trp, tryptophan; NAD+, a reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NMNAT, nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase; NMN, nicotinamide mononucleotide; NR, nicotinamide riboside; NRK, nicotinamide riboside kinase; NAMPT, nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase; NAM, nicotinamide; SIRT1, sirtuin 1; PARP1, poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1; CD38, cluster of differentiation 38.
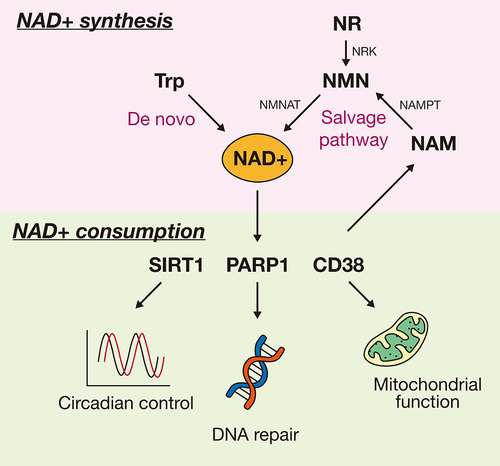
Figure 2. Effects of boosting NAD+ through the NAD+ salvage pathway by SIRT1 in the liver, skeletal muscle, and white adipose tissue. NMN is synthesized from NAM and NR by NAMPT and NRK, respectively. The synthesized NAD+ from NMN is used as a SIRT1 substrate, which leads to the recycling of NAD+ via the salvage pathway. In this process, NAD+ can exert different effects depending on the tissue. NAMPT, nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase; NAM, nicotinamide; NMN, nicotinamide mononucleotide; NR, nicotinamide riboside; NRK, nicotinamide riboside kinase; NMNAT, nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase; NAD+, reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; SIRT1, sirtuin 1.
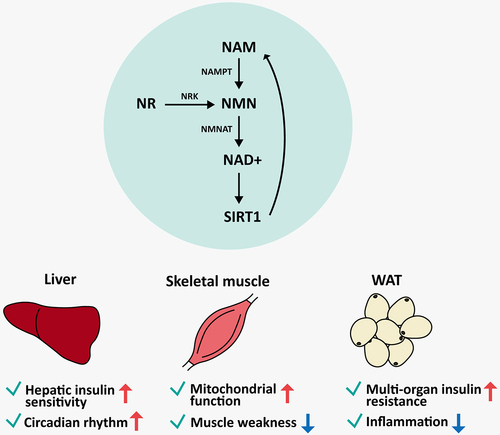
Table 1. Effects of NAD+ precursors in white adipose tissue1.
Table 2. Evidence of NAMPT function based on NAMPT genetically modified mouse models.
Data availability statement
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article [and/or] its supplementary materials.
