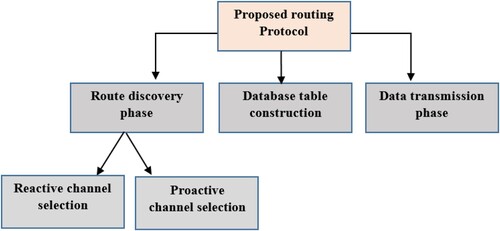
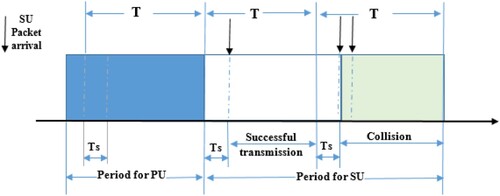
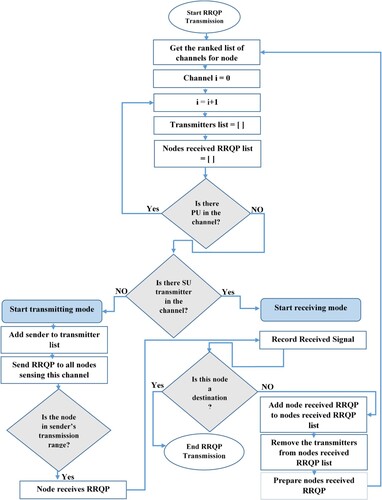
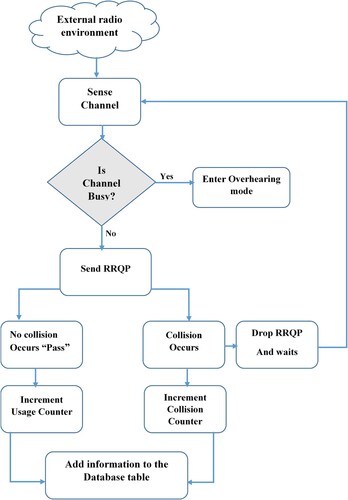
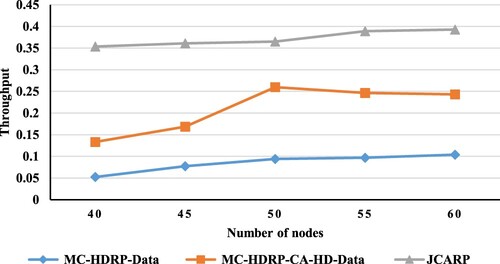
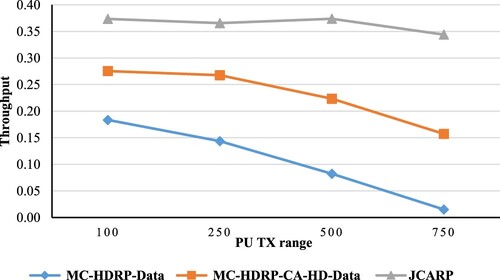
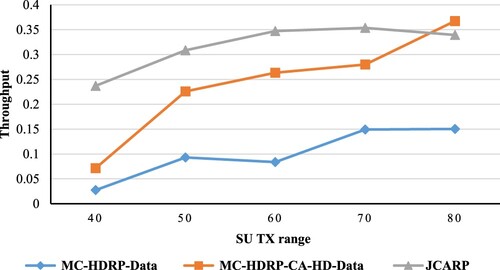
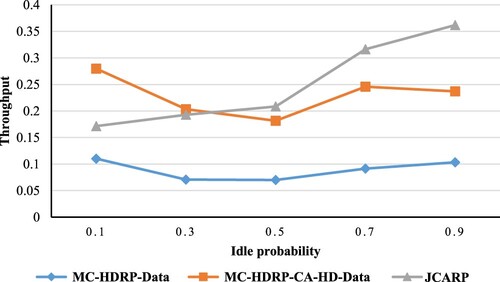
Figures & data
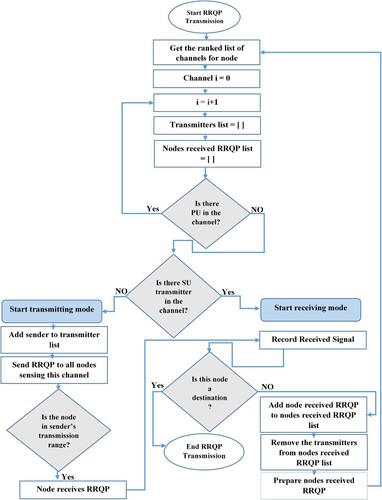
Table 1. The Format of RRQP.
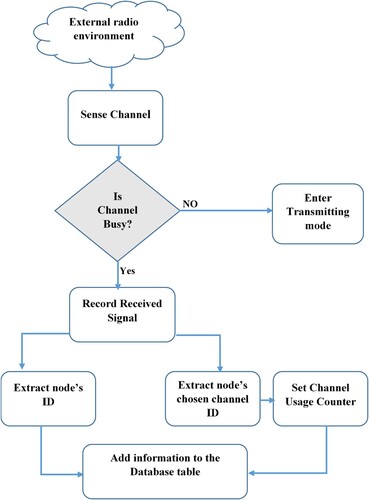
Table 2. Database table attributes.
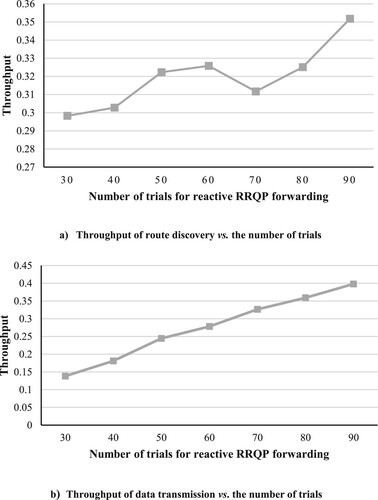
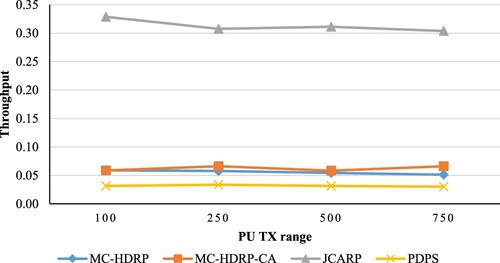
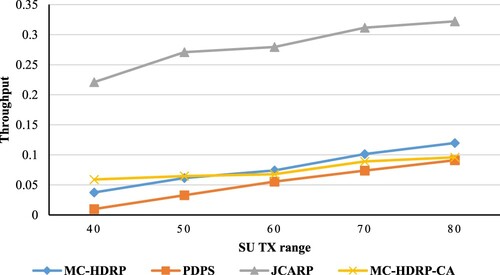
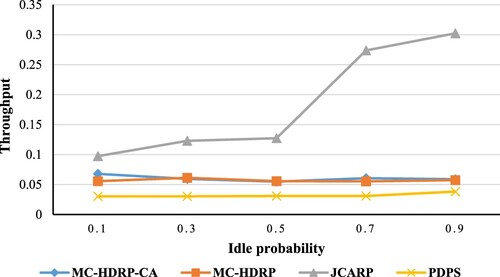
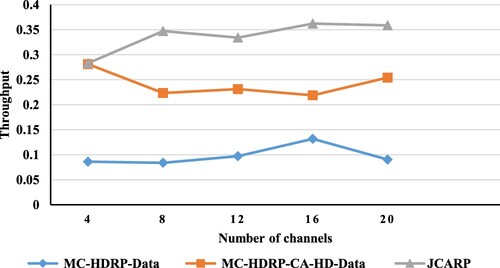
Table 3. The simulation experiments’ parameters.
Table A1. Database table of node A.
Table A2. A’s database table after calculating CUC.
Table A3. A’s database table after calculating channel usage probability.
Table A4. Final database table of node A.