Figures & data
Table 1 Lymphoid cell populations able to produce IL-22
Figure 1 IL-22 receptor structure.
Abbreviation: IL-22, interleukin-22; MAPK, mitogen-associated protein kinase.
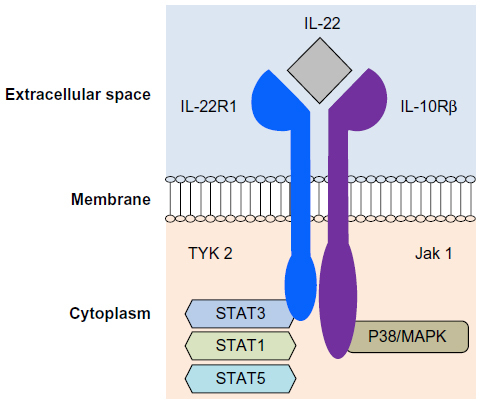
Table 2 IL-22 involvement in the response to pathogens
Figure 2 Effects of IL-22/IL-22R signaling in gut epithelial cells.
Abbreviation: IL-22, interleukin-22.
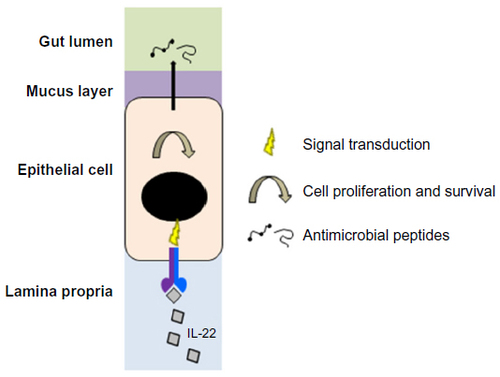
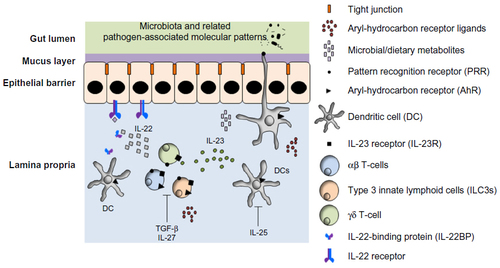
Figure 3 IL-22 production and regulation in the gut mucosa.
Abbreviations: AhR, aryl-hydrocarbon receptor; DC, dendritic cell; IL, interleukin; PAMP, pathogen-associated molecular pattern; PRR, pattern recognition receptor; TGF-β, Transforming growth factor beta; IL-22, interleukin-22.