Figures & data
Table 1 Breast MRI: cross-over studies between gadobenate dimeglumine and other GBCAs
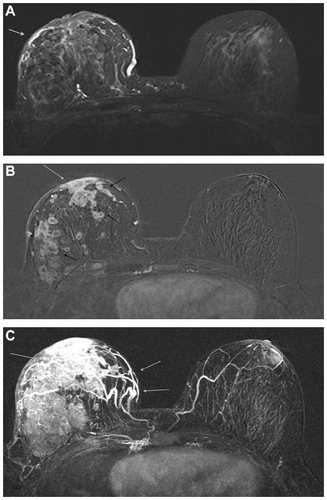
Figure 1 48-year-old woman with BI-RADS 6 lesions in the right breast detected on XR mammography and ultrasound (triple negative, IDC).
Abbreviations: MRI, magnetic resonance imagining; BI-RADS, Breast imaging-reporting and data system; IDC, invasive ductal carcinoma; XR, X-ray; DCIS, ductal carcinoma in situ.
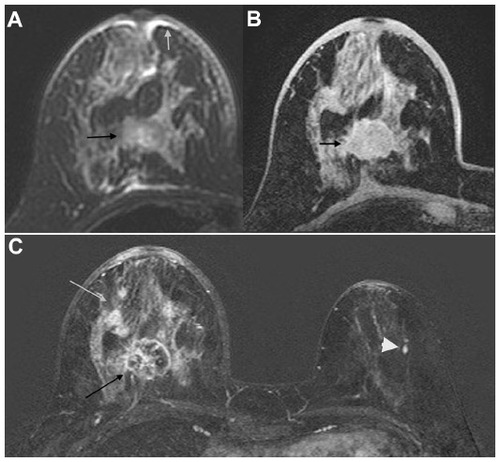
Figure 2 38-year-old woman with nipple retraction.
Abbreviations: MRI, magnetic resonance imagining; IDC, invasive ductal carcinoma.
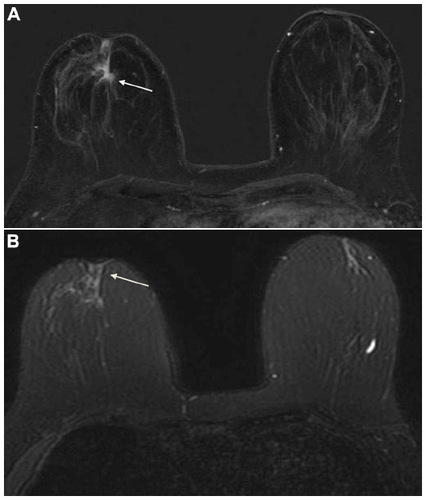
Figure 3 Breast MRI of a 59-year-old woman revealed a greater extension of the lesion on the right breast than XR mammography and ultrasound. At pathology both lesions were proved to be invasive ductal carcinoma.
Abbreviations: MRI, magnetic resonance imagining; XR, X-ray.
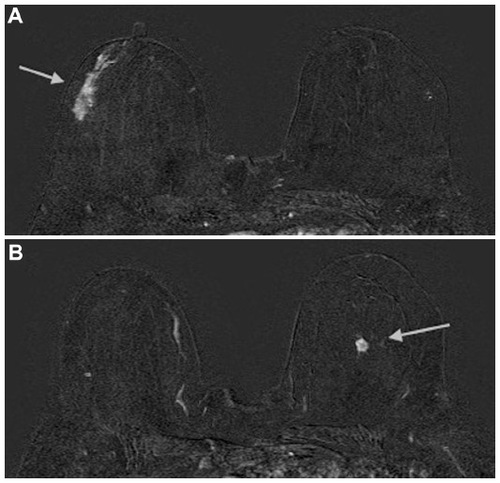
Figure 4 A 53-year-old woman with multiple lesions of the right breast, as seen on a breast ultrasound, proved to be invasive ductal carcinoma at pathology. She underwent a breast MRI to determine the extent of the disease and the multicentricity.
Abbreviations: MRI, magnetic resonance imagining.