Figures & data
A total of 79 blood samples from phase I oncology clinical trials were included for pharmacogenomic analysis using both ImmunoID NeXT™ WES and PharmacoScan™ assay. An orthogonal analysis was carried out to assess the concordance between WES and array-based assay in the commonly targeted regions within 28 core ADME genes. The exclusive variants that were unique to each technique were identified and followed by genotype-to-phenotype annotation.
ADME: Absorption, distribution, metabolism and elimination; SNP: Single-nucleotide polymorphism; SNV: Single-nucleotide variant; WES: Whole-exome sequencing.
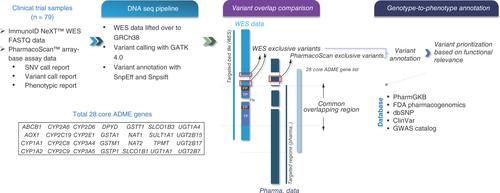
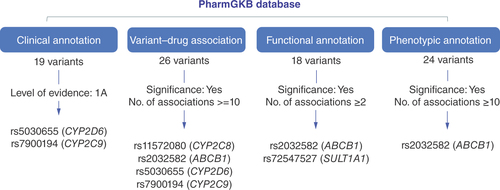
Table 1. Comprehensive summary of exclusive variants identified by PharmacoScan™.
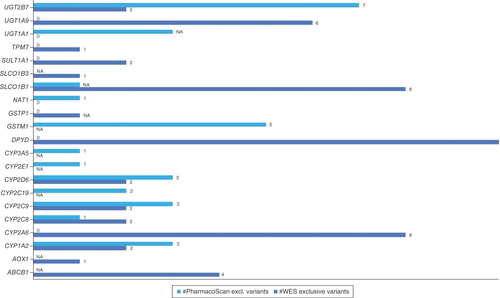
Overview of the exclusive performance of WES can also be observed from the image for CYP2A6, DPYD, TPMT.
NA: Genes for which no annotation data exist. ’0’: No variants detected by the technique; WES: Whole-exome sequencing.
Supplementary Table 4
Download PDF (595.1 KB)Supplementary Table 1
Download PDF (5.1 MB)Supplementary Table 2
Download PDF (26.4 MB)Data availability statement
Any requests for data by qualified scientific and medical researchers for legitimate research purposes will be subject to Merck’s (CrossRef Funder ID: 10.13039/100009945) Data Sharing Policy. All requests should be submitted in writing to Merck’s data sharing portal (https://www.merckgroup.com/en/research/our-approach-to-research-and-development/healthcare/clinical-trials/commitment-responsible-data-sharing.html). When Merck has a co-research, co-development, or co-marketing or co-promotion agreement, or when the product has been out-licensed, the responsibility for disclosure might be dependent on the agreement between parties. Under these circumstances, Merck will endeavor to gain agreement to share data in response to requests.
