Figures & data
Figure 1. Three methods of breast reconstruction. A. with a submuscular implant. B. with a latissimus dorsi flap (LD flap). C. with a pedicled transvers rectus musculocutaneous flap (TRAM flap). Courtesy Department of Clinical Photo, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark.
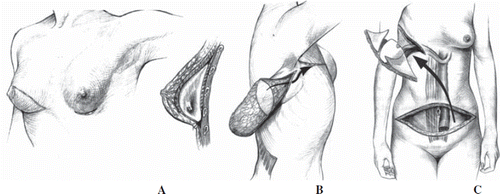
Figure 3. Postmastectomy breast reconstruction and common complications. A is reconstructions with implants. A2-3. Capsular contracture and loss of symmetry. B. Reconstructions with the LD flap. B2-3. Inferior color and size match. C. Reconstructions with the TRAM flap. C2-3. Insufficient skin color match and retraction after necrosis. Courtesy Department of Clinical Photo, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark.
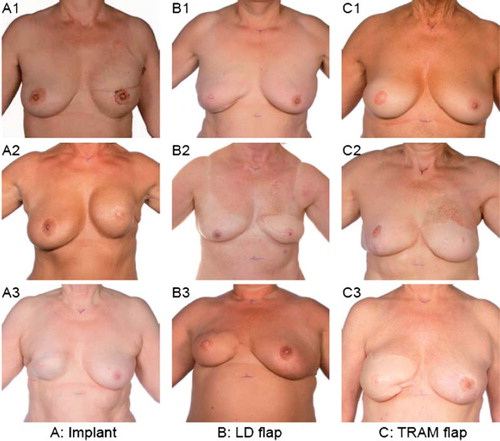
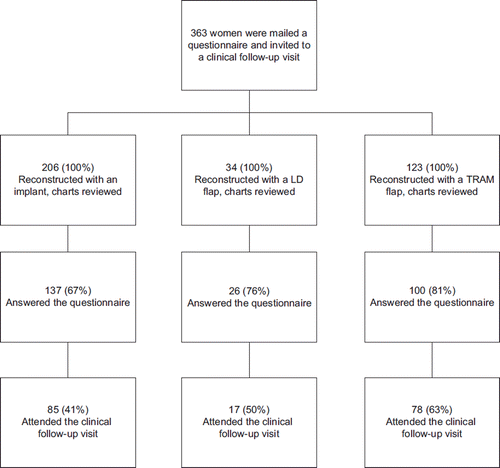
Table I. Patient demographics for women reconstructed with an implant, an LD flap or a TRAM flap at the time of reconstruction.
Table II. Data from questionnaire.
Table III. Data from follow-up visit.
Table IV. Complications after the first reconstructive procedure from the patient chart.