Figures & data
Table I. Clinicopathological parameters of OSCC patients.
Table II. Primers, PCR conditions and expected PCR product lengths.
Figure 1. Analysis of cDNA population in pN0, pN + and adjacent mucosa groups by DD RT-PCR. Total RNA isolated and pooled from two adjacent mucosa (A), three primary tumors without compromised lymph nodes (B) and three primary tumors with compromised lymph nodes (C) were reverse transcribed and PCR carried out as per the protocol described in the text. The heat denatured PCR products were electrophoresed on urea-polyacrylamide gel. The gels were dried and exposed to autoradiograph for 12–16 h at −70°C and developed until the DNA bands appeared on the film. The arrows indicate the transcripts which are differentially expressed in pN0 or pN + samples: 1: SCARB2; 2: G3BP2; 3: CSNK1A1; 4: SPRR2B.
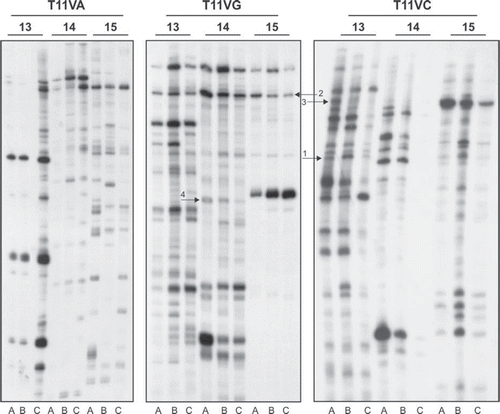
Table III. Methods used to validate 23 genes found to be differentially expressed between pN0/pN + tumor samples, on initial analysis.
Table IV. Identity of the differentially expressed transcripts, based on the homology search in NCBI–BLAST, between pN + /pN0 OSCC patients.
Figure 2. The samples were rank-ordered by their Nodal Index, determined by the discriminant analysis. The samples with negative score indicated that the tumors were predicted to be free of lymph node metastasis (pN0). The samples with positive scores indicated that the tumors were predicted to metastasize to the cervical lymph node (pN +). A,B. The prediction results in learning cases: Fourteen of the 16 samples in pN0 group were negative and 17 of 19 samples in the pN + group were positive. C,D. The prediction results in test case group: seven of 11 samples in pN0 group were negative and all of samples in the pN + group were positive.
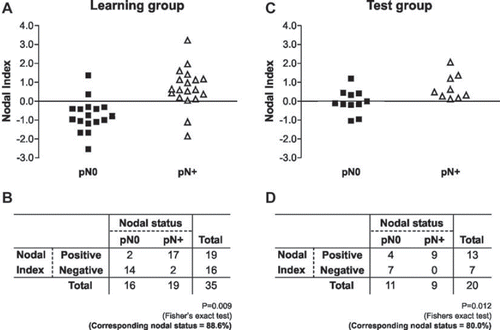
Table V. Logistic regression analysis for lymph node status in 35 OSCC patients.