Figures & data
Table 1. International ambient air standards for particulate matter.
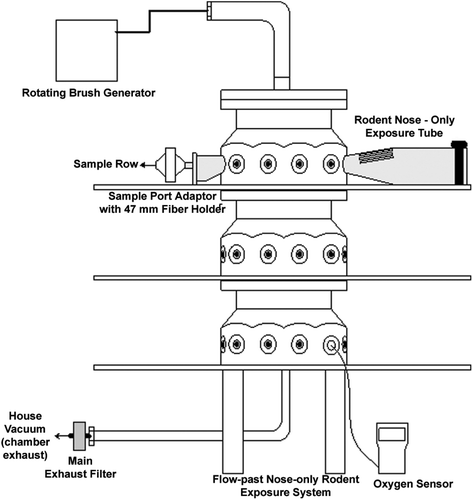
Table 2. Measured air concentration and average particle size for TRWP by exposure level.
Figure 2. Particle size distributions of tire and road wear particles (TRWP) used for animal exposure. (A) Representative histogram of mass median aerodynamic diameter (MMAD) particle size distribution of the 100 µg/m3 exposure group; (B) representative histogram of number-median aerodynamic diameter (NMAD) particle size distribution of the 100 µg/m3 exposure group.
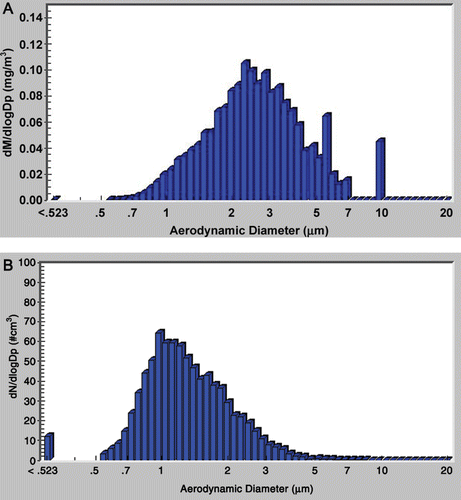
Figure 3. Body weight data for duration of study. Data are presented as mean ± SE (n = 5 per treatment group). *Represents day of sacrifice; body weight recording started in advance of study initiation.
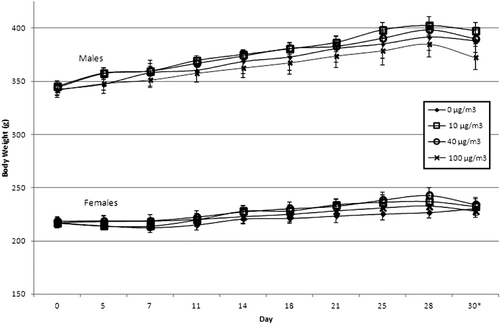
Figure 4. Cell differential profile in lavage fluid with tire and road wear particles (TRWP) exposure. Data are presented as mean ± SE. n = 10 per treatment group (males and females combined).
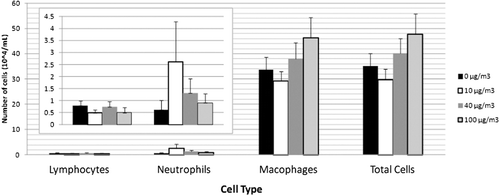
Figure 5. Inflammatory cytokine expression in lavage fluid with tire and road wear particles (TRWP) exposure. Data are presented as mean ± SE. n = 10 per treatment group (males and females combined). (A) interleukin-6 (IL-6); (B) growth-related oncogene-keratinocyte chemoattractant (GRO-KC); (C) tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α).
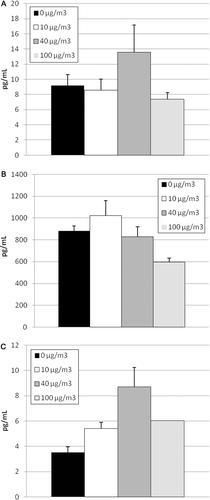
Figure 6. Markers of cytotoxicity in lavage fluid in response to tire and road wear particles (TRWP) exposure. Data are presented as mean ± SE. n = 10 per treatment group (males and females combined). (A) Total protein; (B) lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity; (C) alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity.
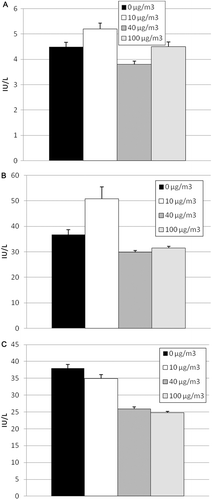
Figure 7. Histopathology of tire and road wear particles (TRWP) exposure. (A) Low power magnification of focal area of subacute inflammation in the lung. The perimeter is outlined by arrows to demonstrate the limited focal extent of minimal alteration. (B) Higher power magnification to illustrate infiltration of low numbers of mononuclear inflammatory cells interstitial in the thickened interalveolar wall and in alveolar spaces (asterisks) with few neutrophils (thin arrows). Hyperplasia of acinar lining epithelial cells indicated pneumocyte regeneration (thick arrows).
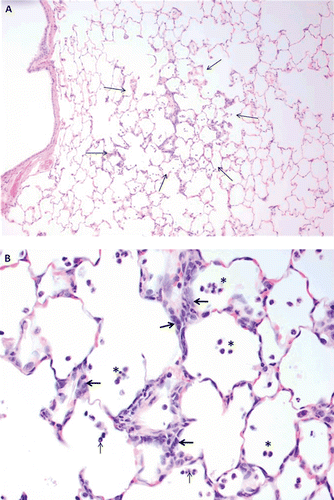
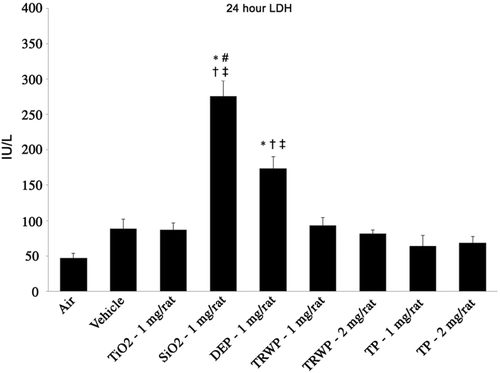
Figure 8. Sample results from comparative toxicity study: Intratracheal instillation. Data are presented as mean ± SE. n = 8 per treatment group (males and females combined). *Statistically different from air control; #Statistically different from vehicle control; †Statistically different from tire and road wear particles (TRWP) (1 mg). ‡Statistically different from tread particles (TPs) (1 mg).