Abstract
In this bibliometric analysis, the study explores the evolution of internal auditing and its transformation from a basic financial oversight function to a critical entity that manages various aspects of organizational culture, IT challenges, risk management and more. The study emphasizes the multifaceted role of modern auditors who must combine traditional practices with the demands of a rapidly changing business environment. Today’s auditors are instrumental in shaping resilient, ethical and socially aware companies. Looking back in time, the study illustrates how the discipline has grown in response to global financial crises, focusing on transparency, risk management and expanded auditing techniques. This evolution positions auditors as strategic partners within the organization rather than simply financial scrutineers. Furthermore, the study emphasizes the interplay between effective auditing and overall governance structures, highlighting that internal auditing is a nuanced craft continuously refined by context-specific variables. A thematic cluster analysis reveals the discipline’s complexity, emphasizing its fundamental principles and emerging focus areas. Finally, the study underscores the adaptability and future-focused nature of internal auditing, which remains committed to transparency, accountability and excellence in a dynamic global landscape.
IMPACT STATEMENT
The research provides a comprehensive bibliometric analysis of the evolution of internal auditing, highlighting its transition from a basic financial oversight function to a strategic, multifaceted role within organizations. The study emphasizes the auditor’s critical involvement in managing organizational culture, IT challenges, risk management, and governance, particularly in response to global financial crises. It underscores the importance of auditors in fostering ethical and socially responsible corporate environments and outlines the adaptability and future focus of the field. This research is instrumental for academic and practical applications, offering insights into the evolving complexities and emerging trends in internal auditing, thereby guiding the development of more effective, ethical, and resilient organizational practices.
1. Introduction
As academic progress continues, certain fields are gaining more importance due to their influence on shaping societal, economic and business paradigms. One such field is internal auditing (IA) and its effectiveness. With the constant evolution of the global business landscape in the 21st century, from game-changing technological advancements to sweeping regulatory reforms, the foundation of commerce and governance is continuously shifting. In this state of constant change, IA serves as a crucial guidepost, leading organizations towards operational consistency and accountability (DeZoort et al., Citation2002). Naturally, these dynamics spark academic and professional curiosity, leading to questions about how the effectiveness of internal auditing can be measured, optimized and contextualized in this rapidly changing environment.
Utilizing bibliometric analysis provides a well-structured and efficient method for exploring the complex landscape of the research (Yazdanjue et al., Citation2023), including internal auditing effectiveness. With the aid of bibliometric tools, we can meticulously examine the effectiveness of IA, explore its multifaceted aspects, detect emerging patterns, pinpoint areas of deficiency and synthesize insights to yield a comprehensive outlook (Van Eck & Waltman, Citation2010). This endeavour is important as it aims to consolidate collective knowledge and not just an academic exercise. This study aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the ongoing debate on the effectiveness of internal auditing. The outcome will benefit scholars, practitioners and decision-makers alike, enhancing their understanding and assisting them in their research and practical applications.
Integrating an effective IA function is a pivotal component that can greatly influence an organization’s overall health and resilience. Its value transcends academic debates and has practical implications for an organization’s capacity to adapt with agility and foresight in the face of challenges. By implementing a skilled IA function, organizations can enhance their ability to navigate adversity and emerge even stronger on the other side (Arena & Azzone, Citation2009). Moreover, IA is indispensable in preserving the sanctity of financial reporting, safeguarding against discrepancies and ensuring transparency in fiscal matters (Lin et al., Citation2011). This study aims to bridge the gap between academia and real-world consequences, emphasizing the broader impacts of our findings rather than merely operating in theoretical discussions.
This study thoroughly examines the available literature as part of a rigorous bibliometric analysis. A systematic approach allows us to identify the essential research areas and prominent works that shape the discourse. The study acknowledges scholars who have made significant contributions to the field. Moreover, the study adopts a geospatial perspective to gain insights into regional viewpoints and understand how diverse regions perceive the effectiveness of information architecture. This helps us comprehend the interplay of universal concepts and regional disparities.
2. Material and methods
2.1. Data sources and collection
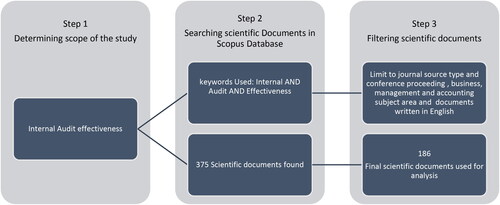
illustrates the graphical representation of the data sources and their collection information. The data collection process involves three steps: (1) determining the scope of the study, (2) searching scientific documents in the Scopus database, and (3) filtering scientific documents.
The first step of the data collection process in this bibliometric study is to determine its scope. The primary objective of this study is to define the research domain, ‘Internal Audit Effectiveness’. This step is crucial as it directs the entire research process and ensures the resulting data is accurate and relevant. The study comprehensively reviews the existing literature, theoretical frameworks and current industry practices related to internal audit effectiveness to establish the scope. This phase involves identifying the key dimensions and metrics of audit effectiveness that the study investigates.
The second step is searching scientific documents. Upon establishing the scope, a methodical literature search is conducted in the Scopus database. Scopus is reputed for its extensive coverage of a diverse range of subject areas (Mongeon & Paul-Hus, Citation2016), which is crucial for a study seeking to explore the multifaceted concept of internal audit effectiveness. It indexes various peer-reviewed journals, conference papers and book chapters, providing a broad spectrum of scholarly works necessary for a comprehensive bibliometric analysis. The search strategy is crafted using the conjunction of keywords ‘Internal AND Audit AND Effectiveness’ to maximize the retrieval of documents that are specifically relevant to both internal audit as a function and its effectiveness as a measure. The exhaustive search includes many scientific documents, such as articles, conference papers, reviews and books. The outcome of this step is the identification of 375 scientific documents, which serve as an initial corpus for potential inclusion in the study.
The third step is filtering scientific documents. This stage is characterized by a stringent selection process to refine the search results and ensure the quality and relevance of the data. Filters are applied to restrict the documents to those published in academic journals and conference proceedings. Journal articles and conference proceedings are typically subject to a peer-review process, which ensures that the research is scrutinized and validated by experts in the field before publication (Walker & Rocha da Silva, Citation2015). This process enhances the reliability and academic rigour of the content, which is paramount for a study aiming to assess the quality and impact of literature on internal audit effectiveness. The scope is further narrowed to business, management and accounting to align with the study’s thematic focus. The Focus of this study is internal auditing, which is closely associated with business, management and accounting disciplines. Additionally, the requirement for documents to be written in English facilitates a broader understanding and accessibility for the international scholarly community (Cinpolat, Citation2022). After applying specific criteria, the corpus is refined to 186 scientific documents. These 186 documents were then exported into the BibTeX file format. BibTeX is a format commonly used to manage bibliographies in academic and scientific writing. The BibTeX file used for analysis in this study contains citation information, bibliographical details, abstracts and keywords.
2.2. Data analysis
To analyse the scientific documents in the form of a BibTeX file, the study utilized RStudio, an open-source IDE for the R programming language, and the Bibliometrix add-on to conduct bibliometric analysis. RStudio is a popular tool for statistical computing, widely used in data science and academic research for creating graphics (Giorgi et al., Citation2022; Racine, Citation2012). Meanwhile, Bibliometrix is an add-on program for quantitative research in scientometrics and bibliometrics designed for RStudio software (Ingale & Paluri, Citation2022). The tool provides several features to perform a comprehensive bibliometric analysis. Bibliometrix allows users to analyse scientific literature using citation and co-citation analysis, collaboration networks and thematic analysis (Aria & Cuccurullo, Citation2017). The program enables users to import bibliographic data from multiple sources and conduct descriptive, network and factorial analyses (Aria & Cuccurullo, Citation2017). provides a detailed explanation of the bibliometric analysis and its various aspects used in this study.
Table 1. Description of bibliometric analysis.
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive analysis
3.1.1. Data description
This study used a bibliometric approach to analyse the evolution and trends in internal auditing effectiveness between 1981 and 2023. The study covers a significant time of over four decades and has sourced information from various reputable journals and conference proceedings. A detailed description of scientific documents used in this study is presented in .
Table 2. Data description.
This comprehensive study draws from a wide range of authoritative sources, including 113 journals and proceedings, highlighting the extensive research conducted in this field. To ensure accuracy, 186 documents were carefully reviewed. On average, these documents have been in circulation for approximately 9.63 years. The fact that each document has received an average of 19.22 citations underscores the relevance and critical nature of the literature that surrounds this subject (Internal auditing effectiveness).
A total of 718 keywords have been identified in the internal auditing effectiveness topic, with 170 from Keywords Plus and 548 from Author’s Keywords. This indicates the wide range of domain subtopics, methods and focuses. The 186 documents on the subject have been contributed by 441 authors, with 30 authors having penned single-authored documents. This suggests a mix of individual expert perspectives and collaborative efforts. Collaboration is evident in this domain, with an average co-authorship rate of 2.61 authors per document. Furthermore, 20.97% of these collaborations are international, indicating the global relevance and inter-country discourse.
From the available documents, the majority of them are in the form of articles, amounting to a total of 166. This implies that the principal focus is on original research or contributions to the field. The presence of 11 conference papers indicates active discourse and the exchange of new ideas in conferences, a crucial part of academic dialogue. Moreover, the seven reviews suggest periodic attempts to synthesize, evaluate and contemplate existing literature. The two notes may refer to concise communications or clarifications on pre-existing literature or concepts.
3.1.2. Sources Description
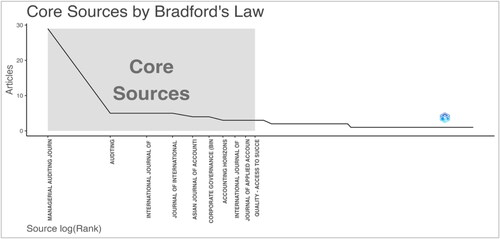
Bradford’s Law of scattering is a bibliometric principle that helps to identify core journals or sources in a particular field. The core idea is that a few journals (Zone 1) will provide a large portion of the articles on a particular topic, while subsequent zones will require an increasing number of journals to achieve the same coverage. In analysing the landscape of internal auditing effectiveness topic, the following observations can be made based on the provided data ().
Bradford’s Law is valuable for identifying the most important academic or research journals. lists the top 10 sources crucial for anyone studying internal auditing effectiveness, particularly those at the higher levels. These top sources will likely have a strong influence, rigorous peer review processes and in-depth discussions. Therefore, researchers, academics and practitioners should prioritize these journals for publication and literature review.
Table 3. Top 10 core courses by Bradford’s Law.
The Managerial Auditing Journal (MAJ) stands out significantly with 29 articles, making it the most prolific source in the dataset. Its contribution alone is more than five times that of its closest competitors. All the top 10 sources fall within Zone 1 of Bradford’s distribution, suggesting a strong consolidation of relevant literature within these journals. This concentration implies that researchers or practitioners looking for articles on internal auditing effectiveness studies would benefit greatly by primarily focusing on these journals.
The subsequent journals, namely Auditing, International Journal of Auditing and Journal of International Accounting, Auditing and Taxation, have contributed five articles. This shows a somewhat even distribution among these sources. The varied titles of the journals, ranging from generalized auditing journals like Auditing to more specific ones like Corporate Governance (Bingley) or Journal of Applied Accounting Research, suggest that the topic of internal auditing effectiveness is both broad and intersects with related disciplines. Including a journal like Quality - Access to Success hints at the research’s interdisciplinary nature, suggesting that quality management principles might be relevant and interwoven with auditing effectiveness.
A journal’s impact in academia can be gauged through various bibliometric indices, such as the h-index, g-index and m-index (). These metrics reflect how often articles from these journals are cited and thus provide a lens into their influence in the academic community MAJ, The MAJ emerges as the most impactful with the highest h-index of 16. Its g-index 29 indicates that its top 29 articles have been cited frequently (NP), reinforcing its influential position. With 889 total citations (TC) for 29 articles, it has been an authoritative source in the field since 1986.
Table 4. Top 10 sources impact.
Auditing and the International Journal of Auditing have an H-index and G-index of 5, but Auditing stands out with 309 TC from just five articles since 1999. The International Journal of Auditing has garnered 135 citations from its five articles since 2014, indicating its recent but rapidly growing influence. Emerging Influence of Corporate Governance (Bingley), with its first publication in 2018, has an impressive M-index of 0.667, suggesting a high yearly rate of impactful publications. The journals’ start years range from 1986 (MAJ) to 2020 (Asian Journal of Accounting Research), showing the domain’s long-standing pillars and emerging sources.
The Journal of Applied Accounting Research has an H-index and G-index of 3 from 3 articles but only 36 TC since 2006. Conversely, Accounting Horizons has garnered 234 citations from its three articles since 2001, indicating that citation volume sometimes equates to the h or g indices. The inclusion journals, namely, the Asian Journal of Accounting Research and the Asian Journal of Business and Accounting, indicate a growing academic interest in Asia. Their relatively recent start dates and m-indices signify their rising significance.
3.1.3. Author description
Authors’ relevance in academic research is determined by the quantity of their contributions and the quality and depth of their collaborations. By analysing the number of articles they have written and the fractionalized count of these articles, we can gauge both the author’s impact and their propensity for collaborative efforts. The total number of articles attributed to the author. Articles Fractionalized represents the fraction of authorship for each article, calculated by dividing the author’s articles by the number of co-authors. A lower fractionalized count relative to the number of articles indicates more frequent collaboration. presents the top 10 authors in internal auditing effectiveness studies.
Table 5. Top 10 most relevant authors.
Dominance of Eulerich M and Sun L, Both authors have penned four articles. Eulerich M, with a fractionalized count of 1.17, suggests a mixture of solo and collaborative endeavours. In contrast, Sun L’s count of 1.00 indicates equal involvement in all their articles, suggesting they may often be the primary authors. Krishnamoorthy G, despite having three articles, Krishnamoorthy G’s fractionalized count is a notable 2.33, suggesting he often collaborates, possibly taking on lead roles in multi-authored papers. This indicates a potential central figure in the domain, fostering collaborative research.
Alzeban A stands out with two articles but a fractionalized count of 2.00, suggesting they are primarily responsible for the work or possibly wrote solo articles. Drogalas G, Li C, Raman KK, Wood DA, Boonlua S and Brody RG show fractionalized counts lower than their total articles, indicating they frequently collaborate with others. Their collaborative nature can lead to diverse perspectives and approaches in their research. Some authors like Eulerich M and Sun L demonstrate a balance, contributing as individual researchers and collaborating. This flexibility suggests a diversified approach to research and an openness to different viewpoints.
The landscape of the most relevant authors in internal auditing effectiveness displays a rich tapestry of individual scholars and collaborative researchers. Figures like Krishnamoorthy G emerge as connectors, fostering joint efforts, while others like Alzeban A chart their course with individual contributions. These authors serve as crucial touchpoints for anyone delving into the domain, offering a blend of deep individual insights and the richness of collaborative discourse. Engaging with their works provides depth and breadth, essential for a comprehensive understanding of the field.
An author’s influence and relevance in a field are often gauged not just by the volume of their publications but by the impact these publications have over time. Using the metrics of frequency of publications (freq), TC, and the citations per year (TCpY), we can assess both the frequency and the influence of the top authors in the field of Internal Auditing Effectiveness over time ( and ).
Table 6. Author production over time.
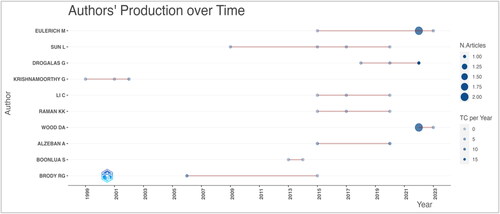
Alzeban A was published in 2015 and 2020, showing sustained interest in the field. While the 2015 article has garnered 28 citations over seven years (an average of 3.111 per year), the 2020 publication has already received 21 citations in just four years, indicating an increased citation rate of 5.25 per year. This suggests a growing influence of the author’s more recent works. With a single article in 2006, Brody RG secured 104 citations, averaging 5.778 per year over 18 years. This showcases this work’s long-standing influence and relevance in the field. Drogalas G shows an increasing citation trajectory, with his most recent 2022 publication already having 36 citations, amounting to 18 per year. This suggests the potential groundbreaking nature of the recent publication.
Eulerich M and Boonlua S have modest citations. It indicates that both authors have publications with lower TCpY values. For instance, Eulerich M’s 2015 publication has only 0.333 citations per year and Boonlua S’s 2013 and 2014 articles have 0.182 and 0 citations per year, respectively. This might indicate either niche topics or the need for these works to gain more visibility in the community. The type of publication, whether open-access or subscription-based, may also influence the number of citations.
The production metrics provide valuable insights into these authors’ temporal relevance and impact. While volume is important, the citation metrics underline their contributions’ significance and enduring value (Author Impact). presents the top 10 authors impacting the internal auditing effectiveness study. It is also evident that more recent works, such as those by Drogalas G in 2022, have rapidly garnered attention, implying the evolving nature of the research field and the importance of keeping abreast with the latest contributions.
Table 7. Top 10 author impact.
Several metrics are pivotal when gauging an author’s impact in any academic domain. Metrics such as the H-index, G-index, M-index, TC, the number of publications (NP) and the year they began publishing in the field (PY_start) are common metrics used to evaluate the author’s impact. provides more detailed information on what these metrics tell us about our top authors and their contributions to internal auditing effectiveness studies.
Drogalas G has made a noteworthy impact in a short span, with an H-index of 3, a G-index of 3, and the most recent PY_start (2018) on the list. The M-index of 0.5 further highlights this rapid ascent in the field. Eulerich M and Sun L have made balanced contributions to the field. Both authors have similar profiles with an H-index of 3, but Sun L has been active longer (since 2009) than Eulerich M (since 2015). Their G-index indicates that their top publications have received substantial citations.
Krishnamoorthy G has been active since 1999 and has received 76 citations, indicating the longevity and relevance of their work. However, due to a lower m-index, their impact velocity may be slower, which can be typical for long-time contributors. On the other hand, Brody RG has a high citation count, having amassed 107 citations from just two articles published since 2006, indicating the significant impact and relevance of those papers. Finally, Alzeban A. and D’Onza G. are recent contributors who have received noteworthy citations despite only beginning to publish in 2015. Their consistent h and g indices suggest they will continue publishing impactful work.
Burnaby PA has contributed to the field since 1992 and, with a lower m-index, provides important historical perspectives for a comprehensive understanding. D’Silva K and Coetzee P, who made their first contributions in 2007 and 2014, respectively, have consistently maintained influence, as shown by their h and g indices. A blend of veteran voices and emerging influencers marks internal auditing effectiveness studies. While authors like Krishnamoorthy G and Burnaby PA provide insights drawn from decades of experience, new entrants like Drogalas G bring fresh perspectives that are quickly gaining traction.
3.1.4. Affiliation and country origin description
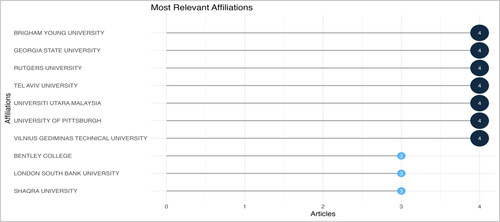
In any field of research, affiliations or institutions have a major impact as they offer the necessary infrastructure, resources and academic culture to promote excellence. Certain affiliations have demonstrated exceptional dedication and contribution in the internal auditing effectiveness domain (). Brigham Young University, Georgia State University, Rutgers University, Tel Aviv University, Universiti Utara Malaysia, University of Pittsburgh and Vilnius Gediminas Technical University have four articles each. This consistent output signifies that these institutions have established themselves as pivotal centres for research in internal auditing effectiveness. Their contributions likely range across various themes and sub-domains within the broader field.
The presence of affiliations from various regions, such as from the USA (Brigham Young, Georgia State, Rutgers and Pittsburgh) to Israel (Tel Aviv University), from Malaysia (Universiti Utara) to Lithuania (Vilnius Gediminas Technical University), underscores the global interest and international relevance of research in this domain. Within the Asian context, the contributions from Universiti Utara Malaysia highlight the importance of internal auditing effectiveness research in the region, perhaps reflecting regional business practices or regulatory environments.
Bentley College, London South Bank University and Shaqra University contributed three articles. While they might have fewer publications than the leading pack, their influence should not be understated. These institutions may have specific areas of expertise or niches within the broader domain, or they could be emerging as newer hubs of research excellence.
The list contains a mix of well-established universities known for their extensive research portfolios, such as Rutgers and Tel Aviv University, alongside institutions like Shaqra University, which may represent emerging centres of excellence. This diversity ensures a mix of seasoned perspectives and fresh takes on the subject.
The study of internal auditing effectiveness is a global endeavour, with key contributions from institutions across various continents. For anyone wishing to delve into this domain, these affiliations represent crucial hubs of academic activity. Engaging with research from these institutions offers a comprehensive understanding of the field. It would benefit scholars, students and practitioners to keep an eye on the outputs from these affiliations, as they will likely shape the discourse and direction of research in internal auditing effectiveness for years to come.
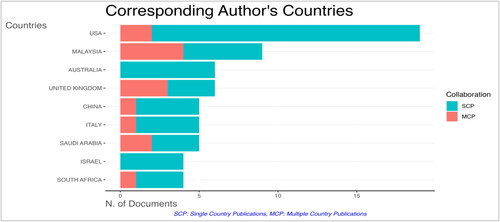
Academic research often reflects global trends, cultural differences and regional challenges. Regarding the study of internal auditing effectiveness, various countries have taken the lead in contributing to the field. displays the top 10 countries with the most relevant corresponding authors. Graphically, it is also presented in . By analysing the corresponding authors’ countries of origin, we get an insightful view of the global landscape of this domain.
Table 8. Top 10 most relevant countries by corresponding author.
With 19 articles, the USA sits at the zenith of this list. Its 17 Single Country Publications (SCP) and 2 Multi-Country Publications (MCP) highlight the country’s independent research capacity and some level of international collaboration. The nation’s well-established academic infrastructure and several key academic institutions are evident in its contributions. Malaysia comes in second with nine articles, interestingly, almost half of which (MCP Ratio of 0.444) are multi-country collaborations. This indicates that Malaysia holds strong local expertise and is actively engaged in international research dialogues.
United Kingdom showcases an even split between SCPs and MCPs, with a 0.5 MCP Ratio. This suggests that while the UK has indigenous research strengths, it’s also open to collaborative research endeavours with other nations. Countries like China, Malaysia and Saudi Arabia demonstrate the rising academic prowess of Asia in the field. Their independent and collaborative contributions suggest that internal auditing effectiveness is paramount in the region, likely influenced by their dynamic economies and evolving corporate landscapes.
Italy and the United Kingdom represent the European perspective, with 5 and 6 articles, respectively. Their research showcases local expertise and collaborative efforts, emphasizing the subject’s significance in European corporate and academic environments. Israel, South Africa and Tunisia, each with unique socio-economic contexts, contribute valuable perspectives to the global discourse. Their research might bring nuanced insights based on regional challenges and successes. Despite their contributions, countries like Australia and Israel have yet to venture into MCP. This indicates a strong local research ecosystem yet to engage extensively in international collaborations or a reflection of the specific studies captured in this dataset.
The study of internal auditing effectiveness is truly a global affair. The top contributing countries offer a mix of Western, Eastern and African perspectives, enriching the field with diverse experiences and approaches. For scholars and practitioners, understanding the nuances brought by each country can lead to a more comprehensive grasp of the subject. Whether it is the robust academic traditions of the USA, the emerging insights from Malaysia, or the unique perspectives from countries like Tunisia, each nation adds a distinct shade to the colourful canvas of internal auditing effectiveness research.
3.1.5. Most globally cited document description
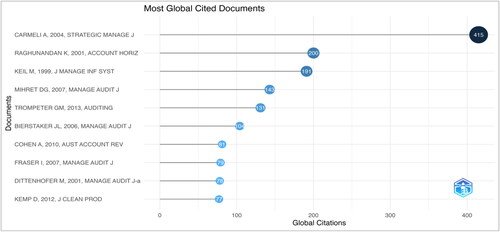
Citations, a testament to a document’s influence and relevance, play a pivotal role in gauging the impact of research on a discipline. The following analysis thoroughly examines the ten most cited documents in internal auditing effectiveness ().
A detailed description of the data shown in is presented in . Carmeli and Tishler (Citation2004) lead the pack with their work on the interplay between organizational intangibles and performance, as published in the Strategic Management Journal. Boasting 415 TC and an impressive normalized citation value of 1.97, this article underscores the intrinsic relationship between less tangible organizational factors and business outcomes. Raghunandan et al. (Citation2001) delve deep into audit committee compositions and their interactions with internal auditing, specifically focusing on Gray Directors. Their findings, published in Accounting Horizon Journal, have been cited 200 times, reinforcing the importance of committee dynamics in internal auditing processes.
Table 9. Top 10 most globally cited documents.
Keil and Robey (Citation1999) bring forth an interesting dimension by exploring troubled software projects and the de-escalation of commitment. Their paper in the Journal of Management Information Systems underscores the challenges and strategies related to software project management in the context of auditing. Getie Mihret and Zemenu Woldeyohannis (Citation2008) offer a unique regional perspective by highlighting the value-added role of internal audit within Ethiopia. Their case study, featured in the MAJ, accentuates regional factors’ significance in audit processes. Trompeter et al. (Citation2013) amalgamate various fraud-related research, giving readers a comprehensive understanding of fraudulent activities within organizations. Their synthesis in Auditing: A Journal of Practice & Theory’ holds immense value in guiding fraud detection and mitigation strategies. Bierstaker et al. (Citation2006) take a perception-centric approach, exploring accountants’ viewpoints on fraud detection and prevention. Their research highlights the crucial role that professionals’ perspectives play in shaping audit methodologies.
Cohen and Sayag (Citation2010) delve into the determinants of internal auditing effectiveness within Israeli organizations, showcasing the country-specific nuances and best practices. Fraser and Henry (Citation2007) pivot towards risk management, offering structures and methodologies for embedding risk processes within organizations. Their paper is a testament to the symbiotic relationship between risk management and auditing. Dittenhofer (Citation2001) pioneers an expansion of prevalent methods to gauge internal auditing effectiveness, pushing the boundaries of traditional frameworks. Kemp et al. (Citation2012) take a unique angle by intertwining corporate social responsibility (CSR), mining and the prevalent audit culture. Their work in the Journal of Cleaner Production highlights the audit discipline’s sustainability aspects.
Compiling the top 10 most cited papers showcases the vast breadth of topics explored in studies on the efficacy of internal auditing. These papers offer a thorough overview of the field, delving into intangible aspects of organizations, detecting fraud, analysing regional perspectives and managing risk. Researchers, students and practitioners stand to gain invaluable knowledge and methodology by closely examining these works, ultimately enhancing their understanding and practice.
3.1.6. The most relevant word description
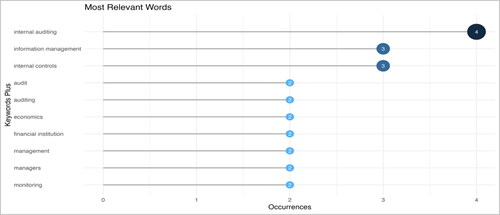
After analysing the most significant words (), it is evident that internal auditing is complex and involves multiple aspects. The frequently mentioned terms in studies on internal auditing effectiveness include internal auditing, information management, internal control, audit, auditing, economies, financial institutions, management, managers and monitoring. These words provide a glimpse into the multifaceted nature of internal auditing studies. They cover everything from foundational aspects like internal controls and the audit process to broader economic implications and the role of management. It indicates that the landscape of internal auditing is vast and multidimensional.
The study focuses on internal auditing, the independent appraisal function within an organization. Its main goal is to review and improve operations. Audits are conducted frequently to ensure that operations are functioning effectively. The audits mainly focus on the handling, processing and disseminating information. Information management is essential for audits to be thorough and effective. It involves systematically organising, retrieving, acquiring and maintaining information.
Internal controls are crucial to the audit process as they ensure the accuracy and integrity of financial and operational information, assess the effectiveness of operations and ensure compliance with laws and regulations. Audit involves examining records and activities to evaluate their quality, making both terms equally important. Economics studies the procedural aspects of auditing and its economic implications and theories that may inform or be informed by auditing practices. Financial institutions, such as banking, insurance and investment firms, are key players in the global economy, making it essential to focus on the specific challenges and nuances of auditing within these entities.
Management refers to the overall supervision and guidance of organizations or specific processes. In the context of auditing, it pertains to the management of audit processes or the interaction between auditors and higher management. It emphasizes the human element’s importance, recognising personnel’s role in operations. Their decisions, biases, competencies and actions can significantly impact the audit process and its outcomes. Continuous or periodic oversight is essential for auditing to ensure consistency and reliability. Monitoring highlights the dynamic nature of audits, where processes are evaluated at a specific time and possibly over extended periods.
3.1.7. Trend topics description
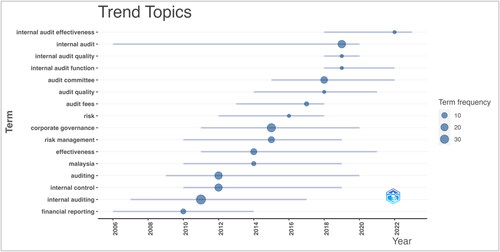
The list provided in covers a wide range of key topics in internal auditing and their emergence over time. It gives an overview of the themes that have remained important in the field. The trending topics provide a panoramic view of the evolving internal auditing landscape. From the core principles of auditing to the intricate complexities of risk management and corporate governance, the timeline shows the dynamic nature of the field and the continuous effort to improve efficiency and effectiveness.
Financial reporting is a fundamental aspect of any corporation, as it involves the disclosure of financial results and accompanying notes to external stakeholders. The importance of financial reporting was highlighted between 2006 and 2014, after the financial crises, when transparency and accuracy in financial reporting became paramount. The study found that refining and understanding the scope, processes and outcomes of internal auditing became a significant interest between 2007 and 2017, indicating evolving practices and methodologies. The term ‘auditing’ generally captures wider practices, including external audits. Its sustained interest from 2009 to 2020 suggests the evolving nature of auditing standards, tools and methodologies.
Between 2010 and 2019, there was a lot of discussion about internal control mechanisms and their significance in ensuring the accuracy and honesty of financial and operational information. Scholars and practitioners have been focusing on the effectiveness of audit practices and their outcomes and impacts from 2011 to 2021. Malaysia has had a particular interest during this period, which might indicate country-specific challenges, governance reforms or noteworthy auditing practices. Corporate governance has been in the spotlight between 2011 and 2020 due to increased scrutiny of boardroom practices and corporate scandals. It refers to corporations’ systems for directing and controlling their operations.
A testament to the increasing complexity of the modern business environment is the focus on ‘risk management’ between 2010 and 2019. This term indicates how businesses identify, assess and prioritize risks, often in tandem with audit functions. A closer look at the term ‘risk’ from 2012 to 2018 suggests that there has been a growing interest in understanding various types of risks, such as financial, operational and strategic risks and their implications for audits. This topic peaked between 2013 and 2018 and delves into audit costs, offering insights into the economics of the auditing profession, including factors that influence fees and the relationship between fee structures and audit quality.
3.2. Network analysis
3.2.1. Co-occurrence network analysis
Co-occurrence network analysis is a general approach for studying the structure of science and scholarly communication (Feicheng & Yating, Citation2014; Qiu et al., Citation2014). It is in the form of graphical representations of the relationships between elements in a dataset, where the elements can be keywords, authors, institutions or other entities (Mishra et al., Citation2021). The co-occurrence network examines links between keywords to understand knowledge components and structure in scientific fields (Radhakrishnan et al., Citation2017). Co-occurrence networks can be used to analyse the relationships between large datasets (van Eck & Waltman, Citation2014). A co-occurrence network is constructed in bibliometric analysis by identifying frequently occurring pairs of elements in the same document (Liu et al., Citation2015; Newman, Citation2004).
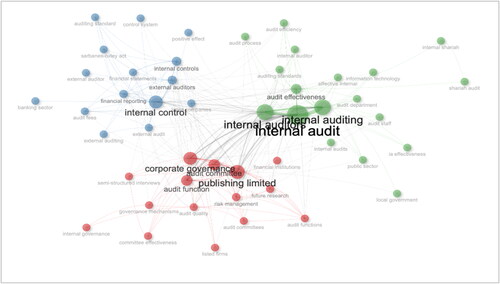
The co-occurrence network map provides graphical information on the internal audit effectiveness research (). To understand the detail behind the co-occurrence network map, Co-Word Network analysis is presented in . The Co-Word network analysis groups words based on their frequency in the literature. The network centrality is measured using three different methods, namely betweenness (BC), closeness (CC) and PageRank, to identify the importance of the nodes. The Co-Word network analysis links three groups of terms together: red, blue and green coloured nodes.
Table 10. Co-Word network analysis.
The BC of a node indicates its level of connection to the shortest paths leading to other nodes in the network. Nodes with high BC tend to represent important research themes or authors who work in different fields or sub-disciplines, linking them together. Conversely, the CC of a node measures that node’s average distance to all other nodes in the network. Nodes with high CC represent research topics or authors closely related to a wide range of other research topics, indicating their importance and cross-disciplinary relevance. In measuring the importance of research topics, authors, or publications, PageRank is an algorithm used to rank web pages based on their significance within co-occurrence networks.
Cluster 1 is corporate governance and research dynamics (Node with red coloured). Key nodes include ‘corporate governance’, ‘audit committee’, ‘risk management’ and ‘governance mechanisms’. This cluster encompasses organizational oversight, decision-making and risk mitigation terms. ‘Publishing limited’ might represent a prominent publisher or denote publishing trends in the field. The focus on ‘future research’ suggests an ongoing discourse on the evolution and enhancement of governance practices.
Cluster 2 is financial reporting and external audit (Node with blue coloured). This cluster primarily revolves around concepts linked to financial disclosure, regulatory compliance and external audit practices. Notable nodes include ‘internal control’, ‘financial reporting’, ‘external auditors’ and ‘Sarbanes-Oxley Act’ (a regulatory response to corporate scandals). The presence of ‘audit fees’ and ‘external audit’ underscores an economic dimension, hinting at the interplay between audit costs, quality and regulatory demands.
Cluster 3 is internal auditing practice and mechanisms (node with green coloured). Representing the core of the study, this cluster captures the nuances of internal auditing as a discipline and practice. Central nodes like ‘internal audit’, ‘internal auditing’, ‘audit effectiveness’ and ‘audit efficiency’ encapsulate the key performance indicators of the audit function. Specific terms such as ‘shariah audit’ and ‘local government’ hint at niche or regional studies within the broader discourse.
The Co-Word network analysis comprehensively paints the internal auditing academic landscape. At its heart lies the interplay between governance mechanisms, financial reporting standards and the practices and effectiveness of both external and internal audits. The intricate links between these nodes, from the nuances of Shariah compliance to the impact of information technology, mark the evolution of internal auditing as a multifaceted and dynamic discipline.
3.2.2. Thematic map analysis
Thematic map analysis is useful in bibliometric studies to identify and visualize major themes within a large literature (Kuipers et al., Citation2022). Through thematic map analysis, valuable insights into a research field can be gained by analysing trends and future research directions (Nasir et al., Citation2020). In a bibliometric study, themes are often used to categorize and understand the topics covered in the literature. These themes include basic, motor, niche, or emerging Fields (Bhatt et al., Citation2022; Cetin et al., Citation2022). Understanding these different types of themes and their dynamics can provide valuable insights into the structure and development of a research field (Donthu et al., Citation2021). Basic themes highlight the foundational areas of the research (Castillo-Vergara et al., Citation2018). Motor themes identify the field’s most active and influential areas (Barbosa & Ferreira-Lopes, Citation2023). Niche themes uncover specialized or underexplored areas (Caputo et al., Citation2022). Emerging themes reveal potential future directions (Franco et al., Citation2023). The graphical output of the thematic map analysis in this bibliometric study is presented in .
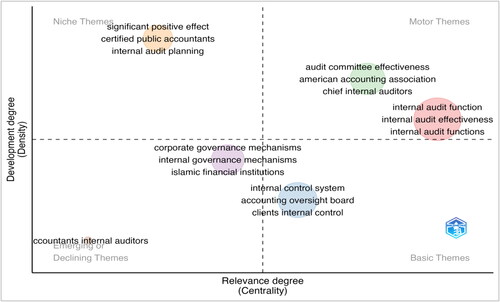
To obtain a comprehensive understanding of the visual graphic depicted in (Thematic map quadrant), shows a comprehensive bibliometric analysis of research related to internal audit effectiveness studies. It identifies six important clusters in this field: internal audit function (IAF), internal control system, audit committee effectiveness, corporate governance mechanisms, significant positive effect and accountant’s internal auditors. Each cluster has its terms, Callon’s centrality and density, centrality and density ranks and frequency of appearance in the literature.
Table 11. Thematic map cluster.
Callon’s Centrality measures a network’s interaction with other networks. It can detect, quantify and visualize the evolution of research on various topics (Cobo et al., Citation2011). Callon density measures the strength of internal ties among keywords in a research theme (Aria et al., Citation2020; Cobo et al., Citation2011). Rank centrality assigns rankings to nodes in a graph based on their importance within the network (Negahban et al., Citation2017). Rank density is used to measure the centrality of nodes in a network (Lee, Citation2006).
The process of thematic mapping clusters provides a structured and visual representation to understand the thematic concentration and development of a research field. The methodology uses Callon’s centrality and density indicators to comprehend the importance of each theme and its internal consistency, respectively.
Based on the thematic map, the IAF cluster is in the motor theme quadrant (). With a CallonCentrality of 4.106548421 and a CallonDensity of 79.62782799, this cluster emerges as one of the field’s most central and dense themes. Sixth in centrality and fourth in density, highlighting the theme’s foundational role in the research landscape. With 240 occurrences, it is clear that the ‘internal audit function’ is a primary focal point in internal auditing studies. It likely examines the role, responsibilities and broader impact of the internal audit within organizations.
The internal control system cluster belongs to the basic theme quadrant (). Boasting a CallonCentrality of 1.005555556 and a density of 64.81481481, this theme underscores the importance of systematic checks and balances in organizations. It ranks fourth in centrality and second in density, emphasizing the theme’s consistent internal development and its crucial interplay with other themes. Occurring 85 times, the consistent mention of an ‘internal control system’ underlines its importance in maintaining financial integrity and organizational accountability.
The audit committee effectiveness cluster is in the motor theme quadrant (). This theme, with a centrality of 1.82047619 and a remarkable density of 127.7827381, delves into the efficacy and roles of audit committees within enterprises. Positioned fifth in centrality and a notable fifth in density, this cluster showcases the continual effort to assess and enhance the efficiency of audit committees. A total of 52 mentions reflect the scrutiny and importance of the audit committee’s role in contemporary research.
According to the thematic map quadrant (), the corporate governance mechanisms cluster is the emerging theme. With values of 0.8 for centrality and 66.52777778 for density, this theme pivots around organizational structures and protocols that ensure proper oversight and management. Its third rank in centrality and density speaks to the theme’s significance in bridging multiple research domains and its internal consistency. Occurring 41 times, ‘corporate governance mechanisms’ remain a critical lens through which researchers explore business ethics, transparency and stakeholder management.
A significant positive effect cluster is on the niche theme. This theme, with a centrality of 0.422222222 and an extraordinary density of 281.6239316, possibly pertains to empirical findings indicating positive outcomes or benefits in the field. Its second rank in centrality and 6th in density suggests that while it might bridge various research areas, the theme might be more narrowly focused. With 28 mentions, this cluster hints at the empirical orientation of many studies in the domain, seeking to establish beneficial practices or correlations.
The accountant’s internal auditors cluster is in the emerging or declining quadrant. With a CallonCentrality of 0 and a CallonDensity of 50, this theme might explore the roles, comparisons, or interactions between accountants and internal auditors. Placed first in centrality and first in density, the theme’s ranking might seem counterintuitive given its low occurrence. It might indicate the foundational nature of the topic, even if it is not the primary research focus. Based on that interpretation, the accountant’s internal auditors cluster can be identified as a declining theme. Mentioned only twice, it underscores the basic understanding or differentiation between these roles in the broader context.
The thematic map reveals the intricate landscape of internal auditing research. From the fundamental roles of IAF and control systems to the evaluative studies of audit committee efficacy and governance mechanisms. The field showcases a blend of structural assessments and empirical evaluations. With an eye on effectiveness and positive outcomes, the domain continues to emphasize the roles of key organizational players like accountants and auditors.
3.2.3. Thematic evolution analysis
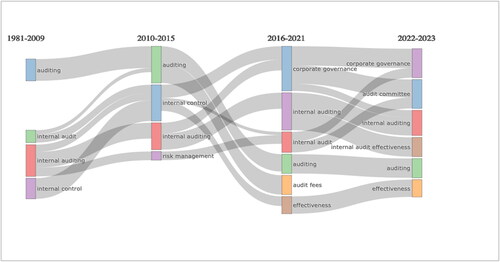
The data presented in offers a thorough understanding of the changes, continuities and new topics that have emerged in internal auditing over four decades. This knowledge is essential for scholars, practitioners and students who seek to understand the direction of the field.
During the period between 1981 and 2009, the topic of auditing was a major focus, and it remained relevant even in the bracket of 2010–2015. This indicates that the fundamental principles and practices of auditing underwent significant examination and refinement during those years. While the period from 1981 to 2009 primarily focused on ‘internal audit’ topics, the shift towards ‘fraud’ in 2010-2015 suggests a growing concern about detecting and preventing fraud in auditing practices. The subsequent transition to the theme of ‘corporate governance’ indicates an evolving understanding of the role of internal auditing in ensuring sound corporate governance practices. The theme of ‘internal control’ remained consistent throughout the decades, highlighting its foundational importance in the field. The emergence of the theme of ‘audit committee effectiveness’ suggests a nuanced exploration of the factors that make audit committees effective. Finally, the theme of ‘risk management’ made its entry towards the end of this era, indicating the increasing importance of risk considerations in internal auditing.
During the middle period (2010–2015 to 2016–2021), the field of auditing continued to evolve and new themes emerged. In 2016–2021, the focus shifted towards topics such as ‘audit fees’, indicating a need for a more detailed investigation of the economics of auditing. This led to a deeper understanding of the concept of ‘audit quality’ in relation to ‘corporate governance’, which became a major theme during this period. Interestingly, the focus on ‘Malaysia’ as a specific case study indicates the emergence of regional case studies or significant issues during this time. Furthermore, the themes of ‘effectiveness’ and ‘internal audit’ suggest a growing emphasis on evaluating the efficacy of control measures. The persistence of these themes into 2016–2021 and their association with ‘internal audit’ indicates the growing importance of risk assessments in internal audit procedures.
Auditing has remained a core theme in recent years (2016–2021 to 2022–2023), highlighting the ongoing importance of fundamental practices and challenges in the auditing domain. Corporate governance themes related to the ‘audit committee’ and ‘internal audit function’ have emerged, providing a more detailed exploration of roles and structures within corporate governance. The focus on effectiveness remains a primary concern, indicating that various audit processes and structures continue to be evaluated for their effectiveness. There has been a shift towards evaluating the effectiveness of internal audits, suggesting a convergence of general audit themes with notions of efficacy and performance evaluation. The continued emphasis on internal auditing underscores its enduring relevance, with explorations delving into the broader implications and innovations within this field.
Over the decades, internal auditing research has undergone a thematic evolution, resulting in a rich tapestry of exploration, deepening understanding and response to emerging challenges. In the early years, the focus was on the foundational aspects of auditing and internal control. At the same time, recent times have focused on the intricate interplay of risk, effectiveness and corporate governance. The field has demonstrated adaptability and depth, and for those working in this domain, understanding these shifts provides invaluable context and direction for future endeavours.
4. Discussion
4.1. Discussion based on most cited documents
The synthesis of key findings lies in the intricate connection between intangible organizational elements and performance highlighted in the seminal work by Carmeli and Tishler (Citation2004) presenting a compelling argument for expanding the evaluative criteria of internal auditing. This finding suggests that effectiveness in internal auditing is not merely a matter of compliance and financial accuracy but also involves assessing and nurturing the intangible drivers of organizational success, such as corporate culture and knowledge management. The intricate interplay between these elements and performance metrics requires internal auditors to understand organizational behaviour and strategic management comprehensively.
From the theoretical implications perspective, the collective insights from these studies necessitate reevaluating existing theoretical frameworks that govern internal auditing. The work on audit committee dynamics (Raghunandan et al., Citation2001) and the management of software projects (Keil & Robey, Citation1999) contribute to a growing body of literature that positions internal auditing within the broader context of organizational governance and strategic oversight. Therefore, the emerging theoretical perspective must integrate these intangible aspects, facilitating a more nuanced understanding of how internal auditing can contribute to sustainable organizational growth and performance.
From a methodological contributions standpoint, the bibliometric approach employed in the study offers a meta-analysis of the field’s progression, revealing the research trajectories and influence patterns within the domain of internal auditing as studied Dittenhofer (Citation2001). This methodological innovation charts the intellectual landscape and underscores the diversity and depth of research methodologies applied to understand internal auditing’s multifaceted role. It highlights the shift from conventional compliance-focused auditing towards more strategic, value-creating activities.
The practical implications of these findings are profound. For instance, the Ethiopian case study by Getie Mihret and Zemenu Woldeyohannis (Citation2008) elucidates the transformative potential of internal auditing in bolstering organizational efficiency and effectiveness in a developing economy context. Furthermore, the synthesis of fraud-related research and the accountants’ perceptions of fraud detection and prevention (Bierstaker et al., Citation2006) provide practical insights into the evolving role of internal auditors as key players in ensuring financial integrity and ethical conduct within organizations.
Fraser and Henry (Citation2007) that emphasis on risk management structures underscores the expanding role of internal auditing in preemptively identifying and mitigating risks. The shift towards a risk-based approach in auditing aligns with the proactive stance organizations must take in a rapidly changing business environment. Furthermore, exploration of the audit culture within the mining industry (Kemp et al., Citation2012) draws attention to the ethical dimensions of corporate operations. It reflects the internal audit’s increasing involvement in ensuring that organizations not only comply with regulations but also uphold ethical standards and demonstrate CSR, thus contributing to the broader societal demand for ethical business practices.
4.2. Discussion based on trend topic overtime
The period from 2015 onwards has marked a significant shift in internal auditing with the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain and data analytics. This integration has drastically altered the audit landscape, introducing new methodologies for risk assessment, fraud detection and data analysis. AI, for instance, has enabled auditors to analyse vast datasets more accurately and efficiently, identifying anomalies and patterns that might indicate potential risks or fraudulent activities. Similarly, blockchain technology has introduced new possibilities regarding data integrity and transparency. Adopting these technologies has enhanced the efficiency of audit processes and transformed the skill sets required for auditors, necessitating a blend of technical and traditional auditing knowledge.
The increasing emphasis on ESG factors since 2018 reflects a paradigm shift in internal auditing. Auditing has expanded beyond financial metrics to encompass environmental impact, social responsibility and governance practices. This trend underscores the growing awareness and concern over sustainable business practices and their long-term impacts on society and the environment. Auditors are increasingly involved in assessing how organizations manage their ESG risks, adhere to sustainability guidelines, and report on their ESG performance. This broadened scope signifies a holistic approach to auditing, wherein non-financial aspects are gaining prominence in determining an organization’s overall health and viability.
The surge in digitalization and the consequent rise in cyber threats have made cybersecurity a critical aspect of internal auditing from 2016 onwards. Internal auditors have taken on the crucial role of evaluating the effectiveness of cybersecurity measures, ensuring that organizations are adequately protected against digital threats and are compliant with data protection laws. This trend involves thoroughly assessing IT systems, data management practices and incident response plans. Auditors identify potential vulnerabilities and recommend measures to strengthen information security. This focus on cybersecurity auditing reflects the evolving nature of business risks in the digital age and the essential role of internal auditing in safeguarding digital assets.
The period since 2014 has been characterized by a dynamic regulatory environment, with new regulations continually being introduced and existing ones being updated. This evolving regulatory landscape has necessitated a proactive and adaptive approach to internal auditing. Auditors are increasingly involved in ensuring organizations comply with current regulations and prepare for future regulatory changes. This role extends beyond compliance checks to providing strategic insights and advisory services to help organizations navigate complex regulatory frameworks. The trend highlights the increasing importance of auditors as strategic partners in ensuring organizational adherence to legal and regulatory standards.
Globalization has expanded the operational boundaries of businesses, introducing new challenges in internal auditing. Since 2015, there has been a notable increase in cross-border auditing activities, necessitating auditors to understand various international auditing standards and practices comprehensively. This trend requires auditors to possess technical expertise and a deep understanding of cultural and legal contexts. The global nature of business operations today demands that internal auditors are adept at navigating diverse regulatory environments, understanding multinational business practices and effectively communicating across cultural boundaries.
The evolving landscape of internal auditing since 2017 has highlighted the need for continuous professional development and skill evolution among auditors. The increasing complexity of audit tasks, driven by technological advancements and changing business environments, requires auditors to update their skill sets constantly. There is a growing emphasis on developing diverse competencies beyond traditional auditing skills. This includes technical proficiency in emerging technologies, business acumen to understand complex business models, and soft skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving and effective communication. This trend underscores the profession’s commitment to staying relevant and effective in an ever-changing business world.
4.3. Discussion based on Co-Word network analysis
The analysis underscores the intricate relationship between corporate governance and internal auditing. Corporate governance frameworks provide the structure within which internal audits operate. Terms like ‘audit committees’ and ‘risk management’ are not just conceptual elements; they represent the foundational mechanisms through which internal audits gain relevance and effectiveness. For instance, the role of audit committees is pivotal in establishing the scope, authority and independence of IAF. Similarly, effective risk management practices are crucial for identifying potential areas of vulnerability within an organization, thus guiding the focus and methodology of internal audits. This interplay highlights the necessity for a robust governance structure to support effective internal auditing practices.
The cluster analysis also highlights the critical role of internal auditing in ensuring financial transparency and adherence to regulations like the Sarbanes–Oxley Act. This act, prompted by instances of corporate malfeasance, has significantly influenced the scope and rigour of internal audits, particularly in financial reporting. Internal audits serve as a vital check and balance, ensuring the integrity and reliability of financial statements. Including audit fees and external audits in this cluster further emphasizes the economic aspects of auditing. These considerations are essential for maintaining a balance between cost-effectiveness and the quality and thoroughness of audits, which are fundamental to investor confidence and regulatory compliance.
The mention of terms such as ‘shariah audit’ and ‘local government’ in the analysis points to the specialization and localization in the practice of internal auditing. These terms indicate that while internal auditing principles may be universally applicable, their implementation often requires adaptation to specific contexts. For instance, a Shariah audit implies adherence to Islamic financial principles, which may require auditors to have specialized knowledge. Similarly, auditing local government entities involves understanding the unique legal and operational frameworks that govern these bodies. This specificity underscores the need for internal auditors to possess diverse skills and knowledge tailored to various contexts.
The Co-Word network analysis positions internal auditing as a dynamic hub that connects diverse domains like corporate governance, financial reporting and regulatory landscapes. This interconnectedness implies that changes or advancements in one area inevitably impact internal auditing practices. For example, evolving governance models or new financial reporting standards can reshape the scope and focus of internal audits. Similarly, the emphasis on future research within this network suggests a commitment to continuous improvement and adaptation in the field, highlighting the importance of staying abreast of emerging trends, technologies and methodologies.
4.4. Discussion based on thematic map analysis
The IAF is foundational in internal auditing. It encompasses many activities, including audit planning, execution, reporting and follow-up. This theme’s significance lies in its adaptability to evolving business environments, technological changes and regulatory shifts. For instance, IAF have increasingly focused on cybersecurity risks in response to new data privacy regulations. A specific example is the role of internal audits in ensuring compliance with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union. Such adaptations illustrate how effective audit functions enhance organisational risk management and governance. The continuous evolution of this function demonstrates its dynamic nature and critical role in maintaining organizational integrity and efficiency.
The internal control system cluster is the organizational bedrock, ensuring integrity and efficiency. Detailed components of this system include the control environment, risk assessment, control activities, information and communication and monitoring activities. Each component plays a specific role; for example, the control environment sets the tone for an organization’s culture of integrity and ethics. By highlighting these components, we gain a tangible understanding of internal control systems. Furthermore, the relationship between robust internal control systems and enhanced organizational performance is evident, as strong control environments often correlate with reduced instances of fraud and error, bolstering organizational trust and stability.
The theme of audit committee effectiveness underscores the pivotal role of audit committees in governance and oversight. An effective audit committee is characterized by its independence, expertise and proactive engagement with internal and external audit functions. For instance, audit committees that regularly interact with auditors and have members with relevant financial expertise tend to be more effective in identifying and mitigating risks. Challenges these committees, such as maintaining independence in closely-held corporations and best practices like continuous professional development for committee members, are key to enhancing their effectiveness. The nuanced role of these committees in steering organizations towards ethical operations and safeguarding against risks highlights their indispensable role in the audit process.
Corporate governance mechanisms are integral to organisations’ strategic functioning and ethical grounding. This theme explores how these mechanisms are implemented and their subsequent impact on audit practices. Various governance models, such as shareholder and stakeholder models, have distinct implications for internal auditing. For instance, internal audits might focus more on sustainability and social responsibility in a stakeholder model. The interplay between governance structures and internal audit priorities reveals the multifaceted nature of corporate governance and its influence on the direction and scope of internal auditing.
The cluster titled ‘significant positive effect’ delves into specific internal auditing practices and methodologies that have empirically demonstrated benefits for organizations. This theme is enriched by examples such as the implementation of continuous auditing techniques, which have been shown to improve real-time risk assessment and operational efficiency. The quantifiable impacts of these practices on enhancing governance and risk management are significant. For instance, organizations employing continuous auditing often report improved detection of anomalies and quicker response times, thereby reducing risk exposure and enhancing decision-making processes.
The ‘Accountants Internal Auditors’ theme offers insights into accountants’ and internal auditors’ distinct yet complementary roles. While accountants primarily focus on financial reporting and compliance, internal auditors have a broader scope, encompassing risk assessment and organizational governance. The overlap and divergence in their functions are evident in financial audits, where both collaborate, yet with different focal points. Accountants might concentrate on the accuracy of financial statements, whereas internal auditors assess the effectiveness of the controls surrounding financial reporting. Understanding the dynamics of their collaboration, particularly in areas such as joint risk assessments or integrated auditing approaches, reveals the nuanced interplay between these two critical functions in the financial ecosystem.
4.5. Discussion based on thematic evolution
The period from 1981 to 2009 in internal auditing was marked by the establishing and evolution of its foundational principles and practices. This era laid the groundwork for robust financial systems and corporate governance frameworks. It witnessed the development of standardized auditing procedures and the establishment of ethical guidelines, which became the cornerstone of modern corporate governance. Auditing’s role during this time was to ensure financial integrity and accountability, reflecting a burgeoning recognition of the importance of transparent and reliable financial reporting. This period set the stage for the evolution of auditing, emphasizing the need for strong oversight and ethical conduct in financial practices.
Between 2010 and 2015, the auditing sector experienced a significant shift towards fraud detection and prevention. This change can largely be attributed to the repercussions of the 2008 financial crisis and the exposure of major financial scandals. There was an intensified global focus on uncovering financial improprieties and irregularities, leading to a greater emphasis on forensic auditing techniques and fraud risk management. This era marked a crucial evolution in auditing, expanding its scope from traditional financial auditing to a strong emphasis on identifying and preventing fraudulent activities. It highlighted the sector’s adaptability and responsiveness to global economic challenges.
In recent years, the significance of corporate governance concerning auditing has increasingly been acknowledged. Auditing began to be seen as a financial function and vital in establishing and maintaining ethical corporate governance. This period saw a shift towards how auditing could support and enhance governance structures, focusing on financial compliance and promoting ethical business conduct. The continued emphasis on ‘internal control’ and the burgeoning focus on ‘risk management’ indicated a move towards more comprehensive oversight of corporate activities, integrating ethical considerations into the auditing process.
From 2016 to 2021, internal auditing witnessed diversification and a growing focus on its economic aspects, notably the introduction of ‘audit fees’ as a significant topic. This development indicated a more holistic approach to auditing, considering the technical aspects and the economic implications. Discussions around audit fees brought to the forefront the issues related to the commercialization of auditing services and the potential influence of financial incentives on audit quality. This period underscored the need to balance the economic aspects of auditing with the imperative to uphold high-quality standards, reflecting a maturation in the approach to auditing practices.
More recently, the dialogue in the auditing community has extended beyond compliance, focusing increasingly on quality assurance within governance structures. The inclusion of ‘audit quality’ and ‘corporate governance’ in the thematic evolution reflects this shift towards a more holistic view of auditing’s role. The mention of ‘Malaysia’ suggests the importance of regional case studies or events with global ramifications, highlighting the interconnectedness of local and global auditing trends. This shift illustrates the industry’s responsiveness to evolving corporate governance needs, emphasizing the importance of quality and integrity in auditing practices.
4.6. Discussion based on association with previous studies
Alatawi et al. (Citation2023) conduct a comprehensive systematic literature review on the interplay between CSR and corporate performance in the tourism sector. This study’s insights are particularly relevant for understanding the intersection of internal auditing with CSR initiatives. It provides a framework for analysing how effective internal auditing can bolster CSR outcomes, influencing organisations’ financial and non-financial performance. This perspective can enrich the discussion on the role of internal auditing in enhancing broader corporate responsibility and performance metrics.
Lu et al. (Citation2022) study an in-depth review of international accounting and finance research focused on corporate board attributes and their impact on corporate outcomes. This research can significantly contribute to understanding the influence of audit committee composition on the effectiveness of internal auditing. This study highlights how variations in board structure, diversity and expertise can affect the efficiency and success of internal audits, thereby impacting overall corporate outcomes. These findings underscore the critical role of board attributes in shaping the effectiveness of internal auditing practices.
Alhossini et al. (Citation2021) provide a detailed analysis of corporate board committees, examining their impact on corporate outcomes from theoretical and empirical perspectives. This study’s approach is instrumental in understanding the nuances of how committee attributes at both individual and collective levels influence the effectiveness of internal auditing. Integrating various economic, accounting, sociological and socio-psychological perspectives offers a multifaceted view of these committees’ role in shaping effective internal auditing processes and the broader corporate outcomes.
In their systematic literature review, Ibrahim et al. (Citation2022) explore the evolving landscape of corporate risk disclosure practices. The study reviews numerous research articles published over two decades, comprehensively understanding how internal auditing standards and effectiveness influence risk disclosure. This research is crucial for gauging the role of internal audits in promoting transparency and accuracy in corporate risk disclosures. The insights from this study can be pivotal in contextualizing the thematic analysis of internal auditing effectiveness within the broader framework of risk management and disclosure.
Nguyen et al. (Citation2020) present a systematic literature review examining the impact of women on corporate boards concerning corporate financial and non-financial performance. The findings of this study are particularly significant for understanding the influence of gender diversity within audit committees on internal auditing practices. The research highlights how diversity in corporate governance, including audit committees, can affect the scope and outcomes of internal audits. Incorporating these insights into the analysis of internal auditing effectiveness can provide a unique perspective on the role of diversity in enhancing audit practices and outcomes.
A study focusing on Indonesia, conducted by Dzikrullah et al. (Citation2020), analyses the relationship between the quality of internal audit teams and various audit outcomes, including audit fees, audit quality, audit choice and audit opinion. This research, which utilized 722 observations from companies listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange during 2016–2017, provides valuable insights into how the IAF directly influences crucial aspects of auditing in a corporate setting. The findings from this study can be instrumental in understanding the role of internal audit quality in determining the effectiveness and efficiency of audit processes, particularly in emerging markets.
Tumwebaze et al.’s (Citation2018) study the contribution of corporate governance and the IAF to accountability in statutory corporations. This cross-sectional and correlational research, which involved a questionnaire survey of 66 corporations, offers an in-depth understanding of the interplay between corporate governance structures and the efficacy of IAF. The insights gained from this study are critical in emphasizing the role of robust governance frameworks in enhancing the effectiveness and accountability of internal auditing practices, particularly within the context of statutory corporations.
In their recent work, Amoako et al. (Citation2023) examine the relationship between IAF and sustainability audits in manufacturing firms. This study is particularly relevant today, where sustainability has become a key business focus area. It sheds light on how IAF align with and support sustainability initiatives within the manufacturing sector. The insights from this research can be applied to understand the evolving role of internal audits in ensuring financial and operational compliance and driving sustainable business practices.
Shuwaili et al.’s (Citation2023) study the public sector’s use of internal audit services to promote well-controlled organizational processes. It uses a mixed-methods approach to design a comprehensive internal audit effectiveness model for the public sector. The study identified 38 effectiveness factors across seven main categories, including communication between internal and external auditors, independence and authority of internal auditors, specialized human resources, technological resources, management support, organizational culture and audit plans. This research is particularly valuable for its contribution to a resource-based theory and for addressing the research gap in the field of internal audit efficacy in the public sector of developing countries.
Al Matari and Mgammal’s (Citation2019) study the role of internal audit in corporate governance and its influence on corporate performance in Saudi Arabia. These findings provide practical insights that complement the broader trends and themes identified in the study. This connection highlights the importance of examining the evolution of internal auditing and its specific impact on corporate governance and performance in various regional and sectoral contexts. Another Saudi study by Al-Matari et al. (Citation2022) provides specific, empirical insights into the characteristics of internal auditing and their impact on financial performance, enriching the broader understanding of internal auditing effectiveness that this study offers. This connection underscores the importance of examining internal auditing in terms of its general evolution and the context of specific organizational characteristics and sectoral dynamics.
Hazaea et al. (Citation2021) provide valuable insights into internal auditing research in China. These insights complement and enrich the broader, global perspective this bibliometric analysis offers. Understanding internal auditing on a global scale and within specific regional and cultural contexts is important. This will offer a more comprehensive view of the field. The regional perspective provides a valuable comparison to the global trends identified in this study, offering insights into geographical specificities and theoretical approaches in internal auditing.
The Yemeni study’s findings by Al-Yazidi et al. (Citation2023) on the role of IAF quality determinants and the moderating effect of senior management support in corporate governance effectiveness provide a detailed, empirical complement to the broader trends and themes identified in this bibliometric analysis. These findings provide a nuanced understanding of the dynamics between internal audit quality, senior management support and corporate governance effectiveness in the banking sector. It adds depth and specificity to the understanding of internal auditing effectiveness, particularly in the context of corporate governance and organizational support in the banking sector of a developing country.
This bibliometric analysis uncovers a shifting paradigm in internal auditing towards strategic, risk-focused and sustainability-oriented practices. Contemporary literature underscores the criticality of independence and objective assurance in IAF, highlighting their role in improving organizational operations, risk management, control and governance (Lenz & Hoos, Citation2023). Further, there is an emerging emphasis on the evolving roles of internal auditors, underlining their increasing relevance in organizational and societal contexts (Lenz & Jeppesen, Citation2022).
Research also calls for a focus on practical contributions and organizational improvements in internal auditing, pointing to the need for enhanced audit planning and skills development (Lenning & Gremyr, Citation2022). Additionally, the link between internal audit quality and investment efficiency is established, demonstrating the pivotal role of internal auditing in firm survival and profitability (Abbott et al., Citation2022). Internal auditing to broader global challenges, such as the sustainable development goals, indicates its expanding impact beyond traditional audit functions (Lenz & Chesshire, Citation2023). These contemporary insights resonate with the findings of this bibliometric analysis, indicating a paradigm shift in internal auditing towards a more integrated, strategic and sustainability-oriented approach.
5. Conclusions, implications, limitations and suggestions
5.1. Conclusion
The role of internal auditing has evolved significantly beyond its traditional function of financial oversight. It has become a vital entity responsible for managing organizational culture, IT challenges, human behaviour, risk management and social responsibility. However, as the corporate landscape rapidly evolves, internal auditors face the challenge of balancing traditional practices with adaptability, foresight and understanding various factors. Internal auditors must address intangible aspects, software project intricacies, fraud detection, regional influences and sustainability to become comprehensive organisational partners. Their contributions are invaluable in shaping resilient, ethical and socially responsible businesses in the 21st century.
This study highlights the evolution of internal auditing in response to financial crises, focusing on transparency and risk management. Auditing techniques have expanded to keep up with the ever-changing business landscape. Nowadays, successful audits depend on corporate governance and ethics, with auditors acting as strategic partners. Striking a balance between cost-effectiveness and quality is crucial for effective audit processes. The trends identified in this study demonstrate how adaptable and relevant the auditing profession is in maintaining organizational integrity in an ever-changing environment. Internal auditing is a multifaceted and interconnected discipline grounded in fundamental principles but influenced by broader governance frameworks, regulatory changes and evolving financial narratives. Effective internal auditing requires scientific and artistic approaches sharpened by context-specific insights.
The internal auditing landscape can be difficult to explore due to its complexity. However, cluster analysis can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of internal auditing. Thematic clusters, such as ‘Internal Audit Function’ and ‘Internal Control System’, serve as foundational pillars of understanding. More nuanced clusters, like ‘Significant Positive Effect’, suggest the field continually evolves, especially associated empirical study. The ‘Corporate Governance Mechanisms’ cluster is also significant, highlighting the interconnectedness of effective auditing and broader governance frameworks. Lastly, the ‘Accountant’s Internal Auditors’ cluster showcases the specific roles played by professionals within the financial and auditing ecosystem.
This study provides a detailed account of the evolution of internal auditing and how it has responded to new challenges. Although the focus has shifted over time from ‘auditing’ to ‘fraud’ and ‘audit quality’, it has always been intertwined with ‘corporate governance’. Even though internal auditing has dealt with regional differences and changing methodologies, the fundamental principles of ‘internal control’ and ‘effectiveness’ have remained unchanged. The field has proven its resilience through detailed examinations of the ‘audit committee’, ‘audit fees’ and the ‘internal audit function’. Internal auditing is a dynamic and self-aware discipline that upholds its core values while remaining adaptable and ambitious. The field’s ability to adjust to changing circumstances is a powerful testament to its commitment to ensuring transparency, accountability and excellence.
5.2. Implications
This study contributes significantly to the theoretical framework of internal auditing by tracing its evolution from its basic financial oversight role to becoming a comprehensive governance instrument. It proposes a paradigm shift in understanding IAF beyond traditional financial scrutiny to encompass broader organizational oversight, including risk management, IT governance and cultural audits. This broader perspective challenges existing theories that primarily view internal auditing through the lens of financial regulation and compliance.
The study highlights modern auditors’ multifaceted role, emphasising the need for an interdisciplinary approach in auditing research. The scope of existing theoretical models can be broadened by integrating concepts from information technology, organizational culture and ethics into the auditing discourse. This approach encourages a more holistic understanding of the auditing function, which is increasingly relevant in today’s complex business environments.
The study helps to improve risk management and governance theories. A bibliometric analysis enhances our understanding of internal auditing’s role in risk management and governance theories. The study shows that auditors are important in building strong, ethical organizational structures. It proposes that internal auditing should be more integrated into the larger corporate governance and risk management theoretical frameworks.
Practically, this study highlights the necessity for auditors to adapt and expand their skill sets to meet the demands of a rapidly changing business environment. Auditors must embrace a more strategic role within their organizations, moving beyond financial oversight to become instrumental in shaping corporate culture, ethical practices and resilience against various risks. This necessitates continuous professional development and a broader understanding of organizational dynamics.
Organizations need to revisit and revise their auditing practices in response to the expanded role of internal auditing. This includes adopting more comprehensive auditing techniques encompassing not just financial aspects but also IT, culture and ethical practices. The study underscores the importance of developing and implementing audit procedures responsive to the evolving business landscape and the complexities of modern organizations. The findings of this study suggest that organizations should strategically integrate internal auditing into their governance structures. Auditors should be viewed and positioned as key partners in governance, contributing to the strategic decision-making processes and ensuring transparency and accountability. This repositioning will require a cultural shift within organizations, recognizing the broader value of internal auditing beyond financial compliance.
5.3. Limitations of the study
This study presents a thorough bibliometric analysis of the development and significance of internal auditing. However, it has some limitations that need to be considered. The first limitation is that the scope of data collection is inherently restricted. While the study scrupulously examines existing literature, theoretical frameworks and present industry practices related to the efficacy of internal auditing, it might have unintentionally overlooked emerging theories or unconventional perspectives that still require wider recognition or establishment in the field. This oversight can potentially restrict the study’s ability to encompass the complete range of internal auditing’s evolving role.
One limitation of the study is its reliance on the Scopus database and the restriction to English-language documents. While Scopus has extensive coverage, excluding research published in other languages or housed in different academic databases may result in an incomplete understanding of internal auditing effectiveness on a global scale. This limitation is especially significant given the diverse and multinational nature of the field.
It is important to note that the study’s filtering process prioritises documents from academic journals and conference proceedings related to business management and accounting. However, this approach might unconsciously limit the perspectives examined. Focusing predominantly on these traditional academic sources, the study could benefit from critical insights or innovative approaches in less conventional or interdisciplinary publications. Consequently, this could hinder the breadth and depth of analysis.
5.4. Suggestions for future research
Some suggestions for future studies are proposed to overcome the limitations in the current research on internal auditing effectiveness. First, future studies should include more data sources, such as publications in different languages and databases. This will enhance the research’s comprehensiveness and provide a more accurate representation of the global discourse on internal auditing.
Integrating interdisciplinary perspectives is crucial to enhancing research on internal audit effectiveness. Drawing insights from organizational behaviour, psychology, cultural studies and information technology could provide invaluable perspectives on the multifaceted nature of internal auditing. An interdisciplinary approach would facilitate a more comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the challenges and opportunities within the field.
Exploring the impact of technological advancements on internal auditing can offer valuable insights into adapting auditing practices in the digital age. With business processes becoming increasingly digitized and data-driven, it is crucial to understand how these technological changes affect the role and effectiveness of internal auditors. By investigating these dynamics, we can better comprehend the changes that need to be made to improve the efficiency of auditing practices in the digital era.
To better understand how effective internal audits are, it would be helpful to use both quantitative and qualitative research methods. This means using bibliometric analysis and conducting interviews, focus groups and case studies. These additional methods would provide a more practical perspective, allowing us to examine practitioners’ real-world challenges and gain valuable insights from their experiences. Overall, this would enhance our understanding of internal audit effectiveness and provide a more comprehensive picture of the topic.
Disclosure statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author.
Data availability statement
Data are available upon request.
Additional information
Funding
Notes on contributors
Sofik Handoyo
Sofik Handoyo is an associate professor in management accounting at the Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Padjadjaran (Indonesia). He holds a master’s degree in small business studies from the University of Leipzig (Germany) and a PhD from Universitas Padjadjaran (Indonesia). His research interest covers strategic management accounting, business, and management.
References
- Abbott, L. J., Barr-Pulliam, D., Buslepp, W. L., & Parker, S. (2022). The real effects of internal audit function quality: Evidence from investment strategies. Journal of Accounting, Auditing & Finance, 1–30. https://doi.org/10.1177/0148558X211069218
- Al Matari, E. M., & Mgammal, M. H. (2019). The moderating effect of internal audit on the relationship between corporate governance mechanisms and corporate performance among Saudi Arabia listed companies. Contaduría y Administración, 64(4), 1. https://doi.org/10.22201/fca.24488410e.2020.2316
- Al-Matari, E. M., Hazaea, S. A., Senan, N. A. M., Mgammal, M., & Mohamed, A. M. E. (2022). Do characteristics of internal audit directly affect the performance of Saudi financial sector? Quality Access to Succes, 23(190), 97–30. https://doi.org/10.47750/QAS/23.190.11
- Al-Yazidi, A. M., Alhebri, A., Al-Matari, E. M., Abdullah, M. F., & Alkebsee, R. H. (2023). Role of quality determinants of the internal audit function in corporate governance effectiveness. Senior management support as moderator: Evidence from Yemeni commercial banks. Banks and Bank Systems, 18(2), 48–62. https://doi.org/10.21511/bbs.18(2).2023.05
- Alatawi, I. A., Ntim, C. G., Zras, A., & Elmagrhi, M. H. (2023). CSR, financial and non-financial performance in the tourism sector: A systematic literature review and future research agenda. International Review of Financial Analysis, 89, 102734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.irfa.2023.102734
- Alhossini, M. A., Ntim, C. G., & Zalata, A. M. (2021). Corporate board committees and corporate outcomes: An international systematic literature review and agenda for future research. The International Journal of Accounting, 56(01), 2150001. https://doi.org/10.1142/S1094406021500013
- Amoako, G. K., Bawuah, J., Asafo-Adjei, E., & Ayimbire, C. (2023). Internal audit functions and sustainability audits: Insights from manufacturing firms. Cogent Business & Management, 10(1), 2192313. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311975.2023.2192313
- Arena, M., & Azzone, G. (2009). Identifying organizational drivers of internal audit effectiveness. International Journal of Auditing, 13(1), 43–60. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1099-1123.2008.00392.x
- Aria, M., & Cuccurullo, C. (2017). bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. Journal of Informetrics, 11(4), 959–975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2017.08.007
- Aria, M., Misuraca, M., & Spano, M. (2020). Mapping the Evolution of Social Research and Data Science on 30 Years of Social Indicators Research. Social Indicators Research, 149(3), 803–831. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-020-02281-3
- Barbosa, M. W., & Ferreira-Lopes, L. (2023). Emerging trends in telecollaboration and virtual exchange: A bibliometric study. Educational Review, 75(3), 558–586. https://doi.org/10.1080/00131911.2021.1907314
- Bhatt, A., Joshipura, M., & Joshipura, N. (2022). Decoding the trinity of Fintech, digitalization and financial services: An integrated bibliometric analysis and thematic literature review approach. Cogent Economics & Finance, 10(1), 1–50. https://doi.org/10.1080/23322039.2022.2114160
- Bierstaker, J. L., Brody, R. G., & Pacini, C. (2006). Accountants’ perceptions regarding fraud detection and prevention methods. Managerial Auditing Journal, 21(5), 520–535. https://doi.org/10.1108/02686900610667283
- Caputo, A., Manesh, M. F., Farrukh, M., Farzipoor Saen, R., & Randolph-Seng, B. (2022). Editorial: Over a half-century of management decision: A bibliometric overview. Management Decision, 60(8), 2129–2147. https://doi.org/10.1108/MD-05-2022-0698
- Carmeli, A., & Tishler, A. (2004). The relationships between intangible organizational elements and organizational performance. Strategic Management Journal, 25(13), 1257–1278. https://doi.org/10.1002/smj.428
- Castillo-Vergara, M., Alvarez-Marin, A., & Placencio-Hidalgo, D. (2018). A bibliometric analysis of creativity in the field of business economics. Journal of Business Research, 85, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2017.12.011
- Cetin, M., Long, B., & Gottlieb, M. (2022). A 10-year bibliometric analysis of publications in emergency medicine. The American Journal of Emergency Medicine, 58, 215–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2022.06.016
- Cinpolat, H. Y. (2022). A bibliometric analysis of global research trends on biomarker studies in Alzheimer’s disease. Demiroğlu Bilim Üniversitesi Florence Nightingale Tıp Dergisi, 8(1), 005–010.
- Cobo, M. J., López-Herrera, A. G., Herrera-Viedma, E., & Herrera, F. (2011). An approach for detecting, quantifying, and visualizing the evolution of a research field: A practical application to the Fuzzy Sets Theory field. Journal of Informetrics, 5(1), 146–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2010.10.002
- Cohen, A., & Sayag, G. (2010). The effectiveness of internal auditing: An empirical examination of its determinants in Israeli organisations. Australian Accounting Review, 20(3), 296–307. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1835-2561.2010.00092.x
- DeZoort, F. T., Hermanson, D. R., Archambeault, D. S., & Reed, S. A. (2002). Audit committee effectiveness: A synthesis of the empirical audit committee literature. Audit Committee Effectiveness: A Synthesis of the Empirical Audit Committee Literature, 21, 38.
- Dittenhofer, M. (2001). Internal auditing effectiveness: An expansion of present methods. Managerial Auditing Journal, 16(8), 443–450. https://doi.org/10.1108/EUM0000000006064
- Donthu, N., Kumar, S., Mukherjee, D., Pandey, N., & Lim, W. M. (2021). How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. Journal of Business Research, 133, 285–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.04.070
- Dzikrullah, A. D., Harymawan, I., & Ratri, M. C. (2020). Internal audit functions and audit outcomes: Evidence from Indonesia. Cogent Business & Management, 7(1), 1750331. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311975.2020.1750331
- Feicheng, M., & Yating, L. (2014). Utilising social network analysis to study the characteristics and functions of the co-occurrence network of online tags. Online Information Review, 38(2), 232–247. https://doi.org/10.1108/OIR-11-2012-0124
- Franco, P., De Felice, F., Kaidar-Person, O., Gabrys, D., Marta, G. N., Banini, M., Livi, L., Jagsi, R., Coles, C. E., Poortmans, P., & Meattini, I. (2023). Equity, diversity, and inclusion in radiation oncology: A bibliometric analysis and critical review. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics, 116(2), 232–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2023.02.026
- Fraser, I., & Henry, W. (2007). Embedding risk management: Structures and approaches. Managerial Auditing Journal, 22(4), 392–409. https://doi.org/10.1108/02686900710741955
- Getie Mihret, D., & Zemenu Woldeyohannis, G. (2008). Value-added role of internal audit: An Ethiopian case study. Managerial Auditing Journal, 23(6), 567–595. https://doi.org/10.1108/02686900810882110
- Giorgi, F. M., Ceraolo, C., & Mercatelli, D. (2022). The R language: An engine for bioinformatics and data science. Life (Basel, Switzerland), 12(5), 648. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12050648
- Hazaea, S. A., Zhu, J., Al-Matari, E. M., Senan, N. A. M., Khatib, S. F. A., & Ullah, S. (2021). Mapping of internal audit research in China: A systematic literature review and future research agenda. Cogent Business & Management, 8(1), 1938351. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311975.2021.1938351
- Ibrahim, A. E. A., Hussainey, K., Nawaz, T., Ntim, C., & Elamer, A. (2022). A systematic literature review on risk disclosure research: State-of-the-art and future research agenda. International Review of Financial Analysis, 82, 102217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.irfa.2022.102217
- Ingale, K. K., & Paluri, R. A. (2022). Financial literacy and financial behaviour: A bibliometric analysis. Review of Behavioral Finance, 14(1), 130–154. https://doi.org/10.1108/RBF-06-2020-0141
- Keil, M., & Robey, D. (1999). Turning around troubled software projects: An exploratory study of the deescalation of commitment to failing courses of action. Journal of Management Information Systems, 15(4), 63–87. https://doi.org/10.1080/07421222.1999.11518222
- Kemp, D., Owen, J. R., & van de Graaff, S. (2012). Corporate social responsibility, mining and “audit culture”. Journal of Cleaner Production, 24, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2011.11.002
- Kuipers, S., Van Der Wilt, A., & Wolbers, J. (2022). Pandemic publishing: A bibliometric review of COVID-19 research in the crisis and disaster literature. Risk, Hazards & Crisis in Public Policy, 13(4), 302–321. https://doi.org/10.1002/rhc3.12262
- Lee, J. Y. (2006). Centrality measures for bibliometric network analysis. Journal of the Korean Society for Library and Information Science, 40(3), 191–214. https://doi.org/10.4275/KSLIS.2006.40.3.191
- Lenning, J., & Gremyr, I. (2022). Unleashing the potential of internal audits: A review and research agenda. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 33(9–10), 994–1010. https://doi.org/10.1080/14783363.2021.1911635
- Lenz, R., & Chesshire, J. (2023). Rethinking internal audit: Governance needs gardening. EDPACS, 68(3), 7–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/07366981.2023.2255432
- Lenz, R., & Hoos, F. (2023). The future role of the internal audit function: Assure. Build. Consult. EDPACS, 67(3), 39–52. https://doi.org/10.1080/07366981.2023.2165361
- Lenz, R., & Jeppesen, K. K. (2022). The future of internal auditing: Gardener of governance. EDPACS, 66(5), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/07366981.2022.2036314
- Lin, S., Pizzini, M., Vargus, M., & Bardhan, I. R. (2011). The role of the internal audit function in the disclosure of material weaknesses. The Accounting Review, 86(1), 287–323. https://doi.org/10.2308/accr.00000016
- Liu, Z., Yin, Y., Liu, W., & Dunford, M. (2015). Visualizing the intellectual structure and evolution of innovation systems research: A bibliometric analysis. Scientometrics, 103(1), 135–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-014-1517-y
- Lu, Y., Ntim, C. G., Zhang, Q., & Li, P. (2022). Board of directors’ attributes and corporate outcomes: A systematic literature review and future research agenda. International Review of Financial Analysis, 84, 102424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.irfa.2022.102424
- Mishra, M., Sudarsan, D., Santos, C. A. G., Mishra, S. K., Kar, D., Baral, K., & Pattnaik, N. (2021). An overview of research on natural resources and indigenous communities: A bibliometric analysis based on Scopus database (1979–2020). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 193(2), 59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08793-2
- Mongeon, P., & Paul-Hus, A. (2016). The journal coverage of Web of Science and Scopus: A comparative analysis. Scientometrics, 106(1), 213–228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-015-1765-5
- Nasir, A., Shaukat, K., Hameed, I. A., Luo, S., Alam, T. M., & Iqbal, F. (2020). A bibliometric analysis of corona pandemic in social sciences: A review of influential aspects and conceptual structure. IEEE Access: Practical Innovations, Open Solutions, 8, 133377–133402. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2020.3008733
- Negahban, S., Oh, S., & Shah, D. (2017). Rank centrality: Ranking from pairwise comparisons. Operations Research, 65(1), 266–287. https://doi.org/10.1287/opre.2016.1534
- Newman, M. E. J. (2004). Coauthorship networks and patterns of scientific collaboration. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101(1), 5200–5205. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0307545100
- Nguyen, T. H. H., Ntim, C. G., & Malagila, J. K. (2020). Women on corporate boards and corporate financial and non-financial performance: A systematic literature review and future research agenda. International Review of Financial Analysis, 71, 101554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.irfa.2020.101554
- Qiu, J. P., Dong, K., & Yu, H. Q. (2014). Comparative study on structure and correlation among author co-occurrence networks in bibliometrics. Scientometrics, 101(2), 1345–1360. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-014-1315-6
- Racine, J. S. (2012). Rstudio: A platform-independent ide for R and sweave. Journal of Applied Econometrics, 27(1), 167–172. http://www.jstor.org/stable/41337225 https://doi.org/10.1002/jae.1278
- Radhakrishnan, S., Erbis, S., Isaacs, J. A., & Kamarthi, S. (2017). Novel keyword co-occurrence network-based methods to foster systematic reviews of scientific literature. PLoS One, 12(3), e0172778. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0172778
- Raghunandan, K., Rama, D. V., & Read, W. J. (2001). Audit committee composition, “gray directors,” and interaction with internal auditing. Accounting Horizons, 15(2), 105–118. https://doi.org/10.2308/acch.2001.15.2.105
- Shuwaili, A. M. J., Hesarzadeh, R., & Bagherpour Velashani, M. A. (2023). Designing an internal audit effectiveness model for public sector: Qualitative and quantitative evidence from a developing country. Journal of Facilities Management, https://doi.org/10.1108/JFM-07-2022-0077
- Trompeter, G. M., Carpenter, T. D., Desai, N., Jones, K. L., & Riley, R. A.Jr. (2013). A synthesis of fraud-related research. Auditing: A Journal of Practice & Theory, 32(1), 287–321. https://doi.org/10.2308/ajpt-50360
- Tumwebaze, Z., Mukyala, V., Ssekiziyivu, B., Tirisa, C. B., & Tumwebonire, A. (2018). Corporate governance, internal audit function and accountability in statutory corporations. Cogent Business & Management, 5(1), 1527054. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311975.2018.1527054
- Van Eck, N., & Waltman, L. (2010). Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics, 84(2), 523–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3
- van Eck, N. J., & Waltman, L. (2014). CitNetExplorer: A new software tool for analyzing and visualizing citation networks. Journal of Informetrics, 8(4), 802–823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2014.07.006
- Walker, R., & Rocha da Silva, P. (2015). Emerging trends in peer review—a survey [Review. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 9, 169. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2015.00169
- Yazdanjue, N., Yazdanjouei, H., Gharoun, H., Khorshidi, M. S., Rakhshaninejad, M., & Gandomi, A. H. (2023). A comprehensive bibliometric analysis on social network anonymization: Current approaches and future directions. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.13179. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2307.13179