Abstract
The purpose of this study was to provide a comprehensive review of previous studies on management control systems (MCS). The study tries to evaluate the key aspects that research on MCS mentioned from 1970 to 2023. Using qualitative methods and VOSviewer software, the study collected and analysed data from the Gale Academic OneFile and OpenAlex databases. The paper examined 2279 articles, including 248 from Gale Academic OneFile and 2031 from OpenAlex. The publications were collected based on articles with the keywords ‘management accounting system’ and ‘sustainable development’. After collection, the articles are classified and arranged according to 6 perspectives. The results show that during the research period (1970–2023), articles on the topic ‘Control Management’ appeared the most with 1850 times. Next are articles with ‘Business’ appearing 1658 times and ‘Computer science’ appearing 1570 times. The topic ‘Management control system’ ranked fourth with 1273 appearances. Results also show that general studies on MCS are conducted with the most significant number of articles (37), with the greatest concentration from 2020 to 2023. The decreasing level includes research on administrative control, detailed control, strategic control, control methods and cultural control. Control tools such as planning and performance measurement also received much attention. The study also found the most influential authors in MCS research (by number of citations and articles) and the countries, universities and journals with the most publications on MCS. The current study provides scholars and researchers with insights from previous investigations into essential areas of MCS. Thereby, it provides a new contribution and comprehensive assessment by highlighting what has been done and what remains to be done in research on MCS. Furthermore, our study reveals future research opportunities and agendas in MCS.
1. Introduction
Along with the increasingly diverse development of business activities, MCS is essential in helping bring value to businesses (Ittner et al., Citation2003) and has become necessary for the management of subsidiaries by the parent company (Rodrigues et al., Citation2023). MCS facilitates strategy implementation and enhances organizational performance (Franco-Santos et al., Citation2012). In recent years, sustainable development strategies for businesses have become an important issue globally. Governance controls with a core value focused on sustainability play an active role in organizations, informing decisions to achieve strategic goals. The advent of management control has gradually overcome the limitations of financial accounting when only considering past information. The core value of management control mobilises individuals and attracts collective support towards sustainable development for the organization. This is increasingly valuable compared to traditional profit-seeking goals (Jollands et al., Citation2015).
‘Management’ refers to the most effective way of using an organization’s resources to achieve predetermined goals (Benabdelkrim El Filali & Hassainate, Citation2018). Laying the first foundation for the theory of MCS, cited by many scholars in research, is Anthony (Citation1965). Subsequently, MCS has received attention in the past two decades, from theoretical framework studies to applied studies in many fields (Bin-Nashwan et al., Citation2017). Research on MCS has become more popular from the 1970s to the present. For management control, some studies have focused on evaluating achieved results by comparing them with initially planned goals. However, as environmental and economic threats have increased, companies have gradually embraced the principles of sustainable development. Accordingly, research on MCS associated with the sustainable growth of organizations is also receiving more attention. By translating the general principles of sustainability into business practices empowering and engaging employees, businesses apply sustainability better as it permeates all organizational activities (Bansal, Citation2002; Dana et al., Citation2021; Pham & Hoang, Citation2019). Rehman et al. (Citation2021) demonstrated that using environmental control systems significantly affects an organization’s ecological sustainability, sustainability performance, and environmental strategies. Despite being aware of the importance of sustainable development, many organizations still do not pay attention to environmental strategy and management controls associated with the environment. Kabuye et al. (Citation2019) explored the role of internal control systems in improving financial performance. They found the internal control system’s positive, significant impact on financial performance. Every organization has the ability to improve its financial performance if it designs, implements and maintains an effective internal control system and has an effective financial reporting structure.
Studies on the link between MCS, mindfulness and sustainability have explored the role of MCS in promoting sustainability and corporate social responsibility and the connection between mindfulness and sustainability (Shahbaz & Sajjad, Citation2021). Ditillo (Citation2012) emphasizes the relevance of management control for knowledge integration on a project-by-project basis. From there, he proposes a framework to explain how MCS promote knowledge transfer across organizational units in knowledge-intensive firms. Gunarathne and Lee (Citation2020) researched ecological control affecting sustainable development in agricultural enterprises in Sri Lanka. The results show that procedural ecological controls have changed due to internal and external challenges faced during different stages of sustainable management development. The findings highlight the need to understand better organizational actions in promoting sustainable agricultural management. Henri and Journeault (Citation2010) have shown that the application of financial and strategic control methods for environmental management has an indirect effect on economic performance in the context of (i) the level of higher environmental exposure, (ii) higher public visibility, (iii) higher environmental concern, and (iv) more significant scale. In Pondeville et al. (Citation2013) study, market stakeholders, communities, and shareholders drive environmental actions and develop MCS. In another study by Gunarathne et al. (Citation2021), scholars found statistically significant evidence to assert that environmental management strategies are positively related to organisations’ economic and environmental performance. Strauss et al. (Citation2022) highlight the role of management control in regulating and stimulating creative processes. They assert that management control opens up different ‘spaces’ that serve particular functions while simultaneously being interrelated in innovative co-creation. Sahlin and Angelis (Citation2019), through exploring the literature on performance management in the context of dynamic, changing and competitive environments, found a weak relationship between performance management systems, motivation and dynamic capability.
Evaluation and overview of previously published studies on various issues always attract the attention of researchers and scholars. There have been many valuable reviews and research overviews, such as assessments of social responsibility, financial and non-financial efficiency (Alatawi et al., Citation2023), on the characteristics of corporate boards and board committees and corporate outcomes (Alhossini et al., Citation2021; Lu et al., Citation2022); on risk disclosure (Ibrahim et al., Citation2022); on women on corporate boards and corporate financial and non-financial performance (Nguyen et al., Citation2020). Regarding MCS, researchers and scholars are interested from many different angles. Therefore, it is necessary to have assessments and overviews on aspects such as theoretical development, research trends, studies on MCS associated with sustainable development and organizational performance, or MCS studies by each field.
Previous review and evaluation studies have certain outstanding features. First, previous studies focused on developing the theoretical framework of MCS, the purpose of MCS, the components of MCS, the meaning and measurement of contextual variables, and issues related to MCS theory development (Anthony & Govindarajan, Citation2007; Chenhall, Citation2003; Epstein & Manzoni, Citation1998; Hansen et al., Citation2007; Malmi & Brown, Citation2008; Merchant & Van der Stede, Citation2017; Silva-Domingo, Citation2015; Simons, Citation2000; Strauß & Zecher, Citation2013; Vale et al., Citation2022). These studies have compiled the literature related to MCS according to different databases such as ACM, Elsevier, Web of Science, Scopus and Google Scholar and according to different periods such as 1981 to 2020 (Vale et al., Citation2022), twentieth and twenty-first centuries (Ghandour, Citation2021).
Second, previous studies aimed to examine MCS research trends (Cahyono, Citation2023), statistics in terms of published research trends, industries, background information, and countries (Bin-Nashwan et al., Citation2017), the tendency to focus on MCS and performance appraisal systems (Vale et al., Citation2022). Each field and country considers trends in MCS and has not been evaluated in connection with sustainable development.
Third, previous studies focused on the relationship between MCS and organizational performance. Statistics have clarified the interest in MCS as a performance driver, supporting strategy implementation, and an essential tool for achieving organizational goals (Alastal et al., Citation2023; Shahbaz & Sajjad, Citation2021).
Fourth, previous studies are concerned with the techniques of MCS (Chenhall & Euske, Citation2007), the control process (Cambalikova & Misun, Citation2017), how to cope with disadvantages, and barriers to implementing MCS (Lill et al., Citation2021; Weber & Roetzel, Citation2021), MCS associated with entrepreneurial entrepreneurship (Frare et al., Citation2022).
In summary, previous overview studies on MCS have had specific values and contributions, from the theoretical framework to assessing research trends related to performance associated with the particular context in the country and type of activity. Unlike previous studies, we focus on the statistics of MCS studies over a more extended period, and they are more updated. At the same time, we select the scope of research on MCS associated with sustainable development – currently a primary concern of countries and organizations in the context of constant fluctuations in challenges from the rapid development of the economy. This is the gap that we chose to conduct this study.
Thus, from the role of providing information to serve long-term decision-making associated with sustainable development goals for businesses and society, within the research scope of the article, we want to systematize the study on MCS conducted from 1970 to August 2023. Our study contributes to the management accounting literature by systematically studying MCS in the context of sustainable development on thematic aspects, content about MCS, most influential authors in MCS research, countries, universities and journals with the most publications on MCS. From there, it points out the research trend of MCS in the coming time. This study aims to answer the following questions:
Q1. What are the main topics in MCS research?
Q2. What contents of MCS are associated with sustainable development?
Q3. Which authors have been most influential in MCS research?
Q4. Which countries publish the most MCS research?
Q5. Which universities publish the most on MCS research?
Q6. Which journals publish the most research on MCS?
The motivation of this research is based on the analysis of the role of the MCS and the importance of management control information to the organisation’s sustainable development. The research motivation also comes from limitations in previous general research on this issue. We conducted this study to review research on MCS over a long period (from 1970 to August 2023). Based on addressing the stated research questions, we hope to contribute to the literature review a comprehensive picture of research on MCS and sustainable development with statistics for scholars, researchers, students and all those interested, as well as universities and countries around the world.
Our article includes five parts. After the introduction, in session 2, we provide the theoretical background and identify the basic concepts of the literature review. Section 3 describes the research method and data processing methods. Section 4 covers the research results and discusses them. In Section 5, we conclude the findings and future research directions.
2. Theoretical basis
2.1. Management control system
By reviewing several empirical studies from different perspectives from journals that have been conducted on MCS and its role in the strategy and performance of companies, Bin-Nashwan et al. (Citation2017) found that MCS has received attention over the past two decades, contributing to enriching an organization’s performance evaluation activities. Anthony (Citation1965) was the first to lay the foundation for the theory of MCS and is cited by many scholars in their studies. After that, this theory of MCS was further developed and applied by scholars in many fields, such as Otley (Citation1994), Simons (Citation1995), and Simons and Merchant (Citation1986). Simons and Merchant (Citation1986) used agency theory and psychology in management control. Simons (Citation1995) focuses on strategic control. Emmanuel et al. (Citation1990) study of management control in conjunction with an accounting-based framework shows that accounting remains an essential element of management control, as it can integrate all aspects of an organization.
The concept of the MCS was first developed by Anthony (Citation1965). According to this, a MCS is the process by which managers ensure resources are used effectively to achieve organizational goals. According to Simons (Citation1995), MCS is formal, information-based routines and procedures that managers use to maintain or change patterns in corporate activities. Since the above initial views, many scholars have also introduced different concepts of MCS when considering MCS, including systematically using management accounting to achieve company goals and other controls, such as individual and organizational controls (Chenhall, Citation2003).
These definitions have limited the MCS approach. Accordingly, MCS consists primarily of planned controls based on accounting data, monitoring of activities, mechanisms for integrating and measuring performance, and separation of administrative rules from strategic and operational controls. Although MCS focuses on implementing strategy, the above views do not consider the organization’s environmental development.
2.2. Sustainable development
Sustainable development has been a term of great interest in the past two decades (Moon, Citation2007; Redclift, Citation2005). Although there are many different views, the concept with the most support is that of the World Commission on Environment and Development (United Nations, Citation1987). Accordingly, sustainable development is the development that meets the needs of the present without affecting the ability of future generations to meet their needs. Thus, sustainable development aims to balance the three aspects of environment, society and economy. These three aspects are essential, dependent and mutually reinforcing (Bansal, Citation2005). To achieve their goals and build successful strategies, businesses need to engage in sustainable development, considering it an intangible asset that improves performance and creates opportunities from innovations and internal change (Nixon et al., Citation2011).
Studies on the impact of sustainable development on financial performance and operational efficiency have also been conducted by many scholars. Peloza (Citation2009) found that 59% of 128 academic articles showed a relationship between social and environmental performance and financial performance measures. Aguinis and Glavas (Citation2012) point out that sustainable development creates positive non-financial business outcomes. Terms are synonymous with sustainable development, such as sustainable business or corporate social responsibility (Ebner & Baumgartner, Citation2006; Naudé, Citation2012). Thus, sustainable development is not only technical but has diverse applications that create different meanings in many contexts (Hopwood et al., Citation2005; Velázquez Gomar & Stringer, Citation2011). Due to the mixing of terms, to have a comprehensive view of sustainable development, we refer to the concept as related to the three aspects of environment, social responsibility and economic development.
2.3. Management control system associated with sustainable development
Administrative controls continue to be a significant concern for organizations of all types. With changes in individual expectations, economic and social environments and technological capabilities, control practices have changed over the past 50 years since Anthony (Citation1965) developed the theoretical framework of MCS. However, most fundamental analyses performed in recent years still have reference value. The basic principles do not change, but the practical application needs to be linked to changes in circumstances and the environment.
Otley (Citation1999) suggests that in organizations, MCS includes goals, strategies, measures, motivations, information flows, and contextual issues, such as the external environment, organizational culture, and social and historical control. Anthony and Govindarajan (Citation2007) posit that MCS assists management in steering the organization toward strategic goals and competitive advantage. Accordingly, consideration of MCS should not only focus on economic aspects but also pay more attention to behavioural aspects of organizational activities such as culture, administration and MCS processes.
There are two perspectives on MCS in organizations: (i) The traditional perspective emphasizes control techniques, focusing on internal processes within the enterprise such as planning, estimating, measuring performance and issues related to motivation; (ii) The modern perspective focuses on solving problems of scope within and outside the organization (Hared et al., Citation2013). Control mechanisms can be found everywhere in organizations; for example, budgetary control used interactively (Malmi & Brown, Citation2008), balanced scorecard control (Kaplan & Norton, Citation1992), control by formal procedures (Simons, Citation1995) and shared values in the context of social control (Ouchi, Citation1980). A control mechanism can be defined as a management activity or routine that influences all or some members of an organization to act or make decisions for the best benefit to regulate consistently with at least one of the issues of personal orientation, motivation, and constraints (Silva-Domingo, Citation2015).
From an internal and external perspective, for successful management control, in addition to technical factors, it is necessary to consider environmental characteristics; the system must adapt to the environment (Collins, Citation1982; Emmanuel et al., Citation1990). In other words, a company must address strategic issues (how the organization relates to the environment) and operational issues (effectively applying plans to achieve overall goals). Thus, the management control process must be considered from social and organisational dimensions. Control elements in the MCS include cultural control, administrative control and control process. The purpose is to assess an organisation’s internal and external social, economic and cultural aspects, dealing with the socio-political, economic and cultural circumstances of the environment in which it operates (Malmi & Brown, Citation2008).
With social transformation, market changes, internationalization, and increased competition in many sectors, MCS has also changed to match. Change must originate from mechanical and formal control systems, from employees (passive objects of control) to system change, which involves organizational and motivational factors. Open control systems are designed based on psychosocial mechanisms, control with environmental changes, and control that considers the organisation’s cultural and anthropological aspects.
3. Research methods
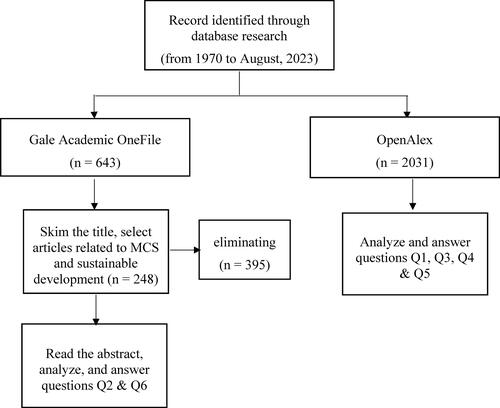
The research process can be summarized through the following steps:
Select data source:
Selected research data includes samples related to MCS associated with sustainable development. Building a research bibliography on MCS requires diverse documents from reputable academic journals, books, and websites, especially the ability to discover and connect global information from data sources. With that criterion, we use VOSviewer’s Gale Academic OneFile and OpenAlex databases to collect research data.
Determine search keywords:
We built a group of keywords to search and identify research-related information by searching titles, abstracts and full-text articles. Keywords that reflect the main content of our research focus on MCS associated with sustainable development are selected, including ‘management accounting systems’ and ‘sustainable development’.
Collect and analyze data from Gale Academic OneFile database:
From the Gale Academic OneFile database, we searched for the keyword ‘management accounting system’. The results collected 643 related articles from 1970 to August 2023 (accessed August 30, 2023). According to this approach, studies published in non-ranked journals were excluded.
Next, we skimmed the titles, eliminated articles not on the right research topic, such as management accounting information systems (MAIS) and management accounting (MA), and added criteria to filter keywords related to ‘sustainable development’. We eliminated 395 inappropriate articles for this step, leaving 248 remaining for MCS analysis associated with sustainable development. Read the abstract, filter the data and use Microsoft Excel to compile results to answer the research question about MCS content related to sustainable development (Q2) and which journals publish the most articles about MCS (Q6).
Collect and analyze data from the OpenAlex database:
Using VOSviewer software, we filter data with the keyword ‘management accounting systems’ in the OpenAlex database. The results were 2031 related articles. The data collected in this period is used for analysis and answers to the questions: Which main topics in MCS research are of most interest (Q1), which authors have the most influence in MCS publications (Q3), which countries have the most MCS publications (Q4) and which universities have the most MCS publications (Q5).
The research implementation process is shown in .
4. Research results
4.1. Statistics on the number of articles about MCS
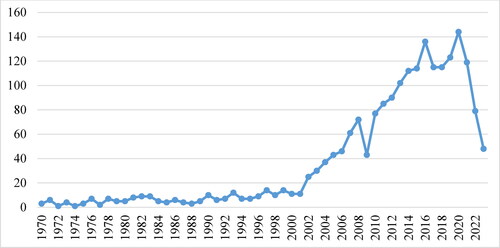
The MCS studies from 1970 to August 2023 are divided into three periods. In the early stages (from 1970 to 2001), research on MCS was not popular; the total number of articles was less than 20. In some years, there were only 1 to 3 articles, such as 1970, 1972, 1974, and 1977. In the following period (from 2002 to 2016), the number of publications on MCS gradually increased, ranging from 25 to 136 articles; 2009 alone decreased more than the previous year. In the recent period (from 2017 to August 2023), the number of publications fluctuated unevenly, gradually decreasing from 2017 to 2019, reaching the highest peak in 2020 with 144 articles. However, the number of subsequent publications from 2021 to now has sharply reduced (from the beginning of the year to August 2023, there were only 48 articles).
shows the number of publications related to MCS over time.
4.2. Main topics of interest about MCS
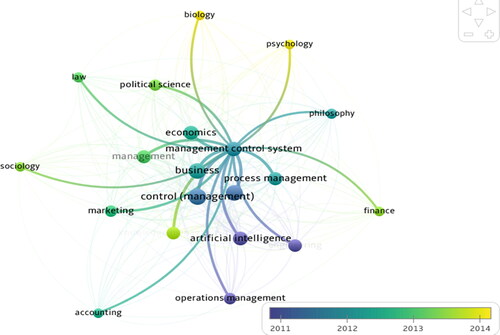
To answer the question of which major topics have been most researched about MCS from 1970 to the present (Q1), we searched the most frequently occurring keywords among 2031 articles about MCS from the OpenAlex database. The results show that 20 keywords appear the most. The keyword ‘Control Management’ appears the most with 1850 times, and ‘Management Control System’ seemed 4th with 1273 views. Other business, management, finance, and accounting keywords are also related and appear in many articles about MCS. Information technology fields, such as computer science and artificial intelligence (AI), are also widely practised with MCS. MCS research also covers many areas, such as economics, engineering, political science, philosophy, psychology, law, biology and sociology ().
Table 1. Top 20 most appearing keywords.
shows the statistics of keywords appearing frequently over time. Accordingly, the ‘management control system’ seemed a lot in 2012. Research on management, such as operations, AI, and control with MCS, was conducted extensively before 2011. Study from 2014 onwards has become more diverse in many fields of political science, psychology, biology, sociology, and finance.
4.3. MCS research content is associated with sustainable development
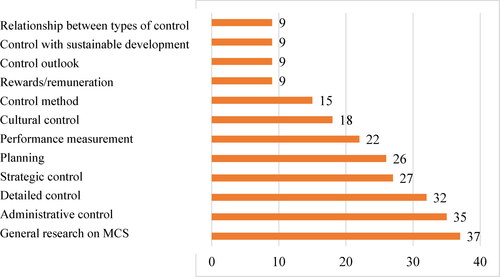
Combined with data analysis from the abstract reading of 248 articles in the Gale Academic OneFile database, the main topics researched on MCS include 12 contents, shown in . Overview studies on MCS are implemented with the most significant number of articles (37), with the greatest concentration from 2020 to 2023. Content groups on control, such as administrative control, detailed control, strategic control, cultural control and control methods, also attracted many publications (35, 32, 27, 18 and 15 articles). Control tools such as planning and performance measurement also receive much attention (26 and 22 articles). The remaining group controls sustainable development, types of control, prospect control and rewards and remuneration (9 articles).
4.4. The most influential authors in MCS research
We filtered from 2031 MCS articles in the OpenAlex database to evaluate the most influential authors in MCS research. The statistical results are reflected in and (articles with the most citations), and (authors with the most citations), and (authors with the most publications on MCS).
Figure 5. Citations of documents by publication year.
Source: The authors summarize the research results.
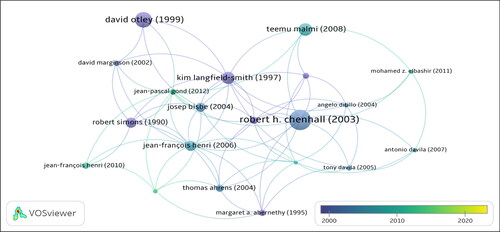
Figure 6. Citations of authors by average publication years.
Source: The authors summarize the research results.
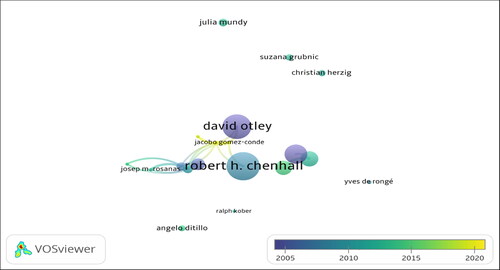
Table 2. Top 20 articles with the most citations (n = 2031).
Table 3. Top 20 authors with the most citations (n = 2031).
Table 4. Top 20 authors with the most articles about MCS (n = 2031).
Accordingly, the article with the most citations during the research period is ‘Management control systems design within its organizational context: findings from contingency-based research and directions for the future’ (Chenhall, Citation2003) with 2318 citations. Next is the article ‘Performance management: a framework for MCS research’ (Otley, Citation1999) with 1548 citations. The article ‘Management control systems as a package – Opportunities, challenges and research directions’ ranks third with 1122 cited and ranked fourth is the article ‘Management control systems and strategy: A critical review’ (Langfield-Smith, Citation1997) with 1084 citations.
adds information about citations over time. Accordingly, the article by Chenhall (Citation2003) has been widely cited over a long period, from 2000 to the present. Langfield-Smith (Citation1997) and Otley (Citation1999) works were cited many times before 2000. The article by Malmi and Brown (Citation2008) has been widely cited from 2010 until now.
Regarding the author with the most citations, the number of citations focuses on Chenhall, R. (2884 times), Ottley, D. (2407 times), Langfield-Smith, K. (1670 times), Brown, D. (1234 views) and Malmi, T. (1140 views). These authors all lead in citations from one article to articles related to MCS. The remaining authors have a relatively large gap with this leading group, with citations ranging from 59 to 822 ().
adds information about citations over time. Chenhall, R. H.’s articles were highly cited from 2005 to 2015, and Ottley, D. and Langfield-Smith, K. were highly cited before 2005. As for other authors, most are cited from 2000 to the present. This result is similar to the article citations over time in .
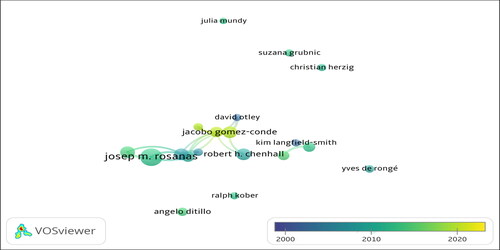
shows the top 20 authors with the most articles on MCS. Accordingly, the leader is Josep M. Rosanas (24 articles), nearly double that of the second 4 authors, Jacobo Gomez-Conde, Chenhall, R. H., George Foster and Natalia Cuguero-Escofet (13 articles). The next group has a negligible difference: Antonio Davila, Ernesto Lopez-valeiras, Brown, D., Malmi, T. (9–11 items). The remaining authors have published from 5 to 8 articles.
adds publication times. Accordingly, Josep M. Rosanas’s articles focus on the period 2010 to 2020, while Jacobo Gomez-Conde published a lot in the 2020s. Chenhall, R. H., George Foster and Natalia Cuguero-Escofet published a lot in the years before 2010. The remaining authors primarily published in the period from 2010 to 2020.
4.5. Countries with the most MCS publications
shows the top 10 countries publishing the most MCS research. Leading the countries with the most MCS publications is the United States (117 articles), which is far ahead of the remaining countries. The next group is Australia, France, and Spain (61 to 70 articles). Asian countries participating are China and Indonesia (57, 58 articles). The remaining countries have articles from 43 to 50, including Italy, the UK, Germany, and Brazil.
Table 5. Top 10 countries with the most articles about MCS (n = 2031).
4.6. Universities publish the most research on MCS
shows the universities with the most MCS publications. This number is divided into two groups. The first group with the highest number of articles, from 17 to 21 papers, are Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina (Brazil), University of Navarra (Spain) and Monash University (Australia). Among them, Monash University has the highest number of citations (4475 times). The second group is universities with lessons from 11 to 13. This group includes schools such as the University of Auckland (New Zealand), Autonomous University of Madrid (Spain), Macquarie University (Australia), Pablo de Olavide University (Spain), Montpellier Business School (France) and Bocconi University (Italy).
Table 6. Top 10 schools with the most articles about MCS (n = 2031).
4.7. Journals that publish the most articles about MCS
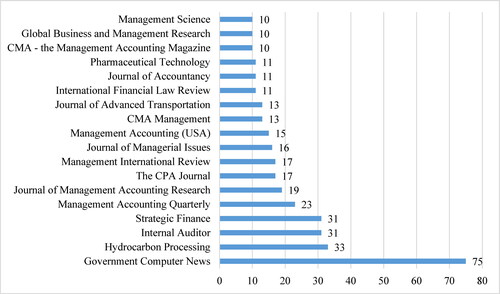
Statistical results of the journal publishing the most articles about MCS on the Gale Academic OneFile database (n = 248) are shown in . Government Computer News (US) journal leads with 75 articles, followed by the second group, with 31–33 articles, including Strategic Finance, Internal Auditor, and Hydrocarbon Processing. The third group (15–23 articles) is Journals specializing in Management and management accounting. The 4th group (10–13 articles), in addition to the magazines of Management Accounting and Business Administration, also includes the fields of Law, Transport, and Pharmaceuticals.
5. Conclusion
From the above analysis, we have answered six research questions through data collection from the Gale Academic OneFile (n = 248) and OpenAlex (n = 2031) databases. We have presented evidence of scholarly interest in MCS research based on statistical data from 1970 to August 2023. MCS research increased sharply from 2001 to 2020; most is in 2020, with 144 articles.
Regarding topic and content, the keywords ‘Control Management’ and ‘Management Control System’ appear the most in research on MCS. The overall research content on MCS was conducted with the most significant number of articles (37/248 articles), with the greatest concentration from 2020 to 2023. Next is the content group on control, such as administrative control, detailed control, strategic control, cultural control, and control methods. Control tools such as planning, performance measurement, and control with sustainable development, as well as types of control, prospect control, rewards, and remuneration, are prominent in MCS research with sustainable development.
Regarding the author with the most influence in MCS research, we evaluate according to three criteria: the article with the most citations, the author with the most citations, and the author with the most publications on MCS. Thereby, prominent authors such as Chenhall, R. H., Ottley, D., Langfield-Smith, K. had publications before 2010. Authors Brown, D., Malmi, T., Jacobo Gomez-Conde, George Foster, and Natalia Cuguero-Escofet have published many publications from 2010 to the present.
Regarding the countries with the most MCS publications, the United States is the leader, followed by Australia, France, Spain and Asian countries (China and Indonesia). Some other countries also have many articles, including Italy, UK, Germany, and Brazil.
The study also showed the top 10 universities with the most publications on MCS and the top 18 leading journals with articles on MCS.
Our findings inform literature reviews for MCS studies. It contributes to enriching the body of knowledge in management accounting literature by systematically studying MCS in the context of sustainable development. Our research results will help scholars and researchers master the research contents related to MCS that are attracting widespread attention, the most influential authors in MCS research, countries, universities and journals with the most publications on MCS. From there, it helps them determine MCS’s research trends in the future. Furthermore, this study provides readers with helpful reference information when looking up documents about MCS. The study also proposes data collection methods through the database and VOSviewer software for researchers to use in general data collection. Collecting data on other databases or Google Scholar is also a suggestion for future available research on MCS. Furthermore, future investigations are needed to substantiate the findings of MCS across different formats and in other institutions.
Author contribution statement
Oanh Thi Tu Le: Conceptualized, designed, and wrote the first draft of the article. Anh Le Thi Hong: Participate in collecting, analyzing and interpreting data. Thuy Thi Thanh Vu: Participate in collecting, analyzing and interpreting data. Thanh Thi Cam Tran: Participate in collecting, analyzing and interpreting data. Cong Van Nguyen: Participated in the conception and design, drafted the article, edited it critically for intellectual content, and gave final approval of the version to be published. All authors agree to be responsible for all aspects of the work.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the respected Editor-in-Chief, Editors and Reviewers for their valuable comments. We genuinely believe this has enhanced the quality of the manuscript.
Disclosure statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Data availability statement
Data included in article/supplementary material/referenced in article.
Additional information
Notes on contributors
Oanh Thi Tu Le
Oanh Thi Tu Le is an Associate Professor, Senior Lecturer and Head of the Department of Management Accounting at the University of Labor and Social Affairs (ULSA), Vietnam. With nearly 20 years of teaching and research experience in accounting, auditing and finance, she has published many research articles in various peerreviewed and refereed journals.
Anh Thi Hong Le
Anh Thi Hong Le is a Master of Economic Law and a main lecturer at the National Economics University, Vietnam. She has nearly 30 years of experience teaching and researching in the fields of economic law and civil law. She is the author and co-author of many research articles in various peer-reviewed and refereed journals.
Thuy Thi Thanh Vu
Thuy Thi Thanh Vu is a PhD in economics, main lecturer and Deputy Head of the Office of Accounting - Finance of the University of Labor and Social Affairs (ULSA), Vietnam. Her main research fields are banking and finance. Her publications focus on capital structure, cash flow management and risk management.
Thanh Thi Cam Tran
Thanh Thi Cam Tran is an Associate Professor, Senior Lecturer and Head of the Faculty of Economics & Accounting at Quy Nhon University, Vietnam. She has over 25 years of teaching and research experience in accounting, auditing and economic analysis. She is also the author and co-author of many research articles in various peer-reviewed and refereed journals.
Cong Van Nguyen
Cong Van Nguyen is a PhD and Economics Professor. He is currently a senior expert and lecturer at the Industrial University of Ho Chi Minh City and a visiting professor at many other universities in the field of Economics in Vietnam. His research field is quite diverse, including issues of macroeconomics and microeconomics. He is the author and co-author of many research articles in various peer-reviewed and refereed journals. He is also the author, editor and co-author of many books used for undergraduate and graduate training in the field of economics in Vietnam.
References
- Abernethy, M. A., & Brownell, P. (1997). Management control systems in research and development organizations: The role of accounting, behavior and personnel controls. Accounting, Organizations and Society, 22(3-4), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0361-3682(96)00038-4
- Abernethy, M. A., & Lillis, A. M. (1995). The impact of manufacturing flexibility on management control system design. Accounting, Organizations and Society, 20(4), 241–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/0361-3682(94)E0014-L
- Aguinis, H., & Glavas, A. (2012). What we know and don’t know about corporate social responsibility. Journal of Management, 38(4), 932–968. https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206311436079
- Ahrens, T., & Chapman, C. S. (2004). Accounting for flexibility and efficiency: A field study of management control systems in a restaurant chain. Contemporary Accounting Research, 21(2), 271–301. https://doi.org/10.1506/VJR6-RP75-7GUX-XH0X
- Alastal, A. Y. M., Jamil, C. Z. M., & Abd-Mutalib, H. (2023). Management control system: A literature review. In J. Kacprzyk (Ed.), In Studies in systems, decision and control (pp. 475–483). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-28314-7_41
- Alatawi, I. A., Ntim, C. G., Zras, A., & Elmagrhi, M. H. (2023). CSR, financial and non-financial performance in the tourism sector: A systematic literature review and future research agenda. International Review of Financial Analysis, 89, 102734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.irfa.2023.102734
- Alhossini, M. A., Ntim, C. G., & Zalata, A. M. (2021). Corporate board committees and corporate outcomes: An international systematic literature review and agenda for future research. The International Journal of Accounting, 56(01), 2150001. https://doi.org/10.1142/S1094406021500013
- Anthony, R. N. (1965). Planning and control systems: A framework for analysis (1st ed.). Division of Research, Graduate School of Business Administration, Harvard University.
- Anthony, R. N., & Govindarajan, V. (2007). Management control systems (12th ed.). Mc-Graw-Hill IRWIN.
- Arjaliès, D.-L., & Mundy, J. (2013). The use of management control systems to manage CSR strategy: A levers of control perspective. Management Accounting Research, 24(4), 284–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mar.2013.06.003
- Bansal, P. (2002). The corporate challenges of sustainable development. Academy of Management Perspectives, 16(2), 122–131. https://doi.org/10.5465/ame.2002.7173572
- Bansal, P. (2005). Evolving sustainably: A longitudinal study of corporate sustainable development. Strategic Management Journal, 26(3), 197–218. https://doi.org/10.1002/smj.441
- Benabdelkrim El Filali, Y., & Hassainate, M. S. (2018). The contribution of management control to the improvement of university performance. Journal of North African Research in Business, 2018(2018), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.5171/2018.842469
- Bin-Nashwan, S. A., Abdullah, N. S., & Obaid, M. M. (2017). A review of literature in management control system (MCS), business strategy, and firm’s performance. International Journal of Management Research & Review, 7(2), 99–112. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/329512076_A_Review_of_Literature_in_Management_Control_System_MCS_Business_Strategy_and_Firm's_Performance
- Bisbe, J., & Otley, D. (2004). The effects of the interactive use of management control systems on product innovation. Accounting, Organizations and Society, 29(8), 709–737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aos.2003.10.010
- Cahyono, S. (2023). A bibliographic study for management control systems on Journal of Management Accounting Research. Jurnal Bisnis dan Akuntansi, 25(1), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.34208/jba.v25i1.1798
- Cambalikova, A., & Misun, J. (2017). The importance of control in managerial work. Conference: International Conference Socio-Economic Perspectives in the Age of XXI Century Globalization (pp. 218–229).
- Chenhall, R. H. (2003). Management control systems design within its organizational context: Findings from contingency-based research and directions for the future. Accounting, Organizations and Society, 28(2-3), 127–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0361-3682(01)00027-7
- Chenhall, R. H., & Euske, K. J. (2007). The role of management control systems in planned organizational change: An analysis of two organizations. Accounting, Organizations and Society, 32(7-8), 601–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aos.2006.09.007
- Collins, F. (1982). Managerial accounting systems and organizational control: A role perspective. Accounting, Organizations and Society, 7(2), 107–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/0361-3682(82)90015-0
- Dana, L.-P., Mahdi Rounaghi, M., & Enayati, G. (2021). Increasing productivity and sustainability of corporate performance by using management control systems and intellectual capital accounting approach. Green Finance, 3(1), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.3934/GF.2021001
- Davila, A., & Foster, G. (2007). Management control systems in early-stage startup companies. The Accounting Review, 82(4), 907–937. https://doi.org/10.2308/accr.2007.82.4.907
- Davila, A., Foster, G., & Oyon, D. (2009). Accounting and control, entrepreneurship and innovation: Venturing into new research opportunities. European Accounting Review, 18(2), 281–311. https://doi.org/10.1080/09638180902731455
- Davila, T. (2000). An empirical study on the drivers of management control systems’ design in new product development. Accounting, Organizations and Society, 25(4-5), 383–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0361-3682(99)00034-3
- Davila, T. (2005). An exploratory study on the emergence of management control systems: Formalizing human resources in small growing firms. Accounting, Organizations and Society, 30(3), 223–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aos.2004.05.006
- Ditillo, A. (2004). Dealing with uncertainty in knowledge-intensive firms: The role of management control systems as knowledge integration mechanisms. Accounting, Organizations and Society, 29(3-4), 401–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aos.2003.12.001
- Ditillo, A. (2012). Designing management control systems to foster knowledge transfer in knowledge-intensive firms: A network-based approach. European Accounting Review, 21(3), 1–26. https://doi.org/10.1080/09638180.2012.661939
- Ebner, D., & Baumgartner, R. J. (2006, September 4). The relationship between sustainable development and corporate social responsibility. Corporate Responsibility Research Conference. https://www.crrconference.org/Previous_conferences/downloads/2006ebnerbaumgartner.pdf
- Elbashir, M. Z., Collier, P. A., & Sutton, S. G. (2011). The role of organizational absorptive capacity in strategic use of business intelligence to support integrated management control systems. The Accounting Review, 86(1), 155–184. https://doi.org/10.2308/accr.00000010
- Emmanuel, C., Otley, D., & Merchant, K. (1990). Accounting for management control. Springer US. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4899-6952-1
- Epstein, M., & Manzoni, J.-F. (1998). Implementing corporate strategy: From Tableaux de Bord to balanced scorecards. European Management Journal, 16(2), 190–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0263-2373(97)00087-X
- Franco-Santos, M., Lucianetti, L., & Bourne, M. (2012). Contemporary performance measurement systems: A review of their consequences and a framework for research. Management Accounting Research, 23(2), 79–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mar.2012.04.001
- Frare, A. B., Cruz, A. P. C. d., Lavarda, C. E. F., & Akroyd, C. (2022). Packages of management control systems, entrepreneurial orientation and performance in Brazilian startups. Journal of Accounting & Organizational Change, 18(5), 643–665. https://doi.org/10.1108/JAOC-04-2021-0052
- Ghandour, D. A. M. (2021). Analytical review of the current and future directions of management accounting and control systems. European Journal of Accounting, Auditing and Finance Research, 9(3), 42–73. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3819654
- Gond, J.-P., Grubnic, S., Herzig, C., & Moon, J. (2012). Configuring management control systems: Theorizing the integration of strategy and sustainability. Management Accounting Research, 23(3), 205–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mar.2012.06.003
- Gunarathne, A. D. N., & Lee, K. (2020). Eco‐control for corporate sustainable management: A sustainability development stage perspective. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 27(6), 2515–2529. https://doi.org/10.1002/csr.1973
- Gunarathne, A. D. N., Lee, K., & Hitigala Kaluarachchilage, P. K. (2021). Institutional pressures, environmental management strategy, and organizational performance: The role of environmental management accounting. Business Strategy and the Environment, 30(2), 825–839. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2656
- Hansen, D. R., Mowen, M. M., & Guan, L. (2007). Cost management: Accounting and control (6th ed.). South-Western College Publishers.
- Hared, B. A., Abdullah, Z., & Huque, S. M. R. (2013). Management control systems: A review of literature and a theoretical framework for future researches. European Journal of Business and Management, 5(25), 1–14. https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/78487574.pdf
- Henri, J. F. (2006). Management control systems and strategy: A resource-based perspective. Accounting, Organizations and Society, 31(6), 529–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aos.2005.07.001
- Henri, J. F., & Journeault, M. (2010). Eco-control: The influence of management control systems on environmental and economic performance. Accounting, Organizations and Society, 35(1), 63–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aos.2009.02.001
- Hopwood, B., Mellor, M., & O’Brien, G. (2005). Sustainable development: Mapping different approaches. Sustainable Development, 13(1), 38–52. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.244
- Ibrahim, A. E. A., Hussainey, K., Nawaz, T., Ntim, C., & Elamer, A. (2022). A systematic literature review on risk disclosure research: State-of-the-art and future research agenda. International Review of Financial Analysis, 82, 102217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.irfa.2022.102217
- Ittner, C. D., Larcker, D. F., & Randall, T. (2003). Performance implications of strategic performance measurement in financial services firms. Accounting, Organizations and Society, 28(7-8), 715–741. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0361-3682(03)00033-3
- Jollands, S., Akroyd, C., & Sawabe, N. (2015). Core values as a management control in the construction of “sustainable development”. Qualitative Research in Accounting & Management, 12(2), 127–152. https://doi.org/10.1108/QRAM-04-2015-0040
- Kabuye, F., Kato, J., Akugizibwe, I., & Bugambiro, N., Ntim, C. G. (Reviewing editor) (2019). Internal control systems, working capital management and financial performance of supermarkets. Cogent Business & Management, 6(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/23311975.2019.1573524
- Kaplan, R. S., & Norton, D. (1992). The balanced scorecard: Measures that drive performance. Harvard Business Review, 70(1), 71–79. https://hbr.org/1992/01/the-balanced-scorecard-measures-that-drive-performance-2
- Langfield-Smith, K. (1997). Management control systems and strategy: A critical review. Accounting, Organizations and Society, 22(2), 207–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0361-3682(95)00040-2
- Lill, P., Wald, A., & Munck, J. C. (2021). In the field of tension between creativity and efficiency: A systematic literature review of management control systems for innovation activities. European Journal of Innovation Management, 24(3), 919–950. https://doi.org/10.1108/EJIM-11-2019-0329
- Lu, Y., Ntim, C. G., Zhang, Q., & Li, P. (2022). Board of directors’ attributes and corporate outcomes: A systematic literature review and future research agenda. International Review of Financial Analysis, 84, 102424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.irfa.2022.102424
- Malmi, T., & Brown, D. A. (2008). Management control systems as a package – Opportunities, challenges and research directions. Management Accounting Research, 19(4), 287–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mar.2008.09.003
- Marginson, D. E. W. (2002). Management control systems and their effects on strategy formation at middle-management levels: Evidence from a U.K. organization. Strategic Management Journal, 23(11), 1019–1031. https://doi.org/10.1002/smj.271
- Merchant, K., & Van der Stede, W. (2017). Management control systems: Performance measurement, evaluation and incentives (4th ed.). Pearson.
- Moon, J. (2007). The contribution of corporate social responsibility to sustainable development. Sustainable Development, 15(5), 296–306. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.346
- Naudé, M. (2012). Sustainable organizational development and reflection: A good combination? Corporate Ownership and Control, 9(2), 364–375. https://doi.org/10.22495/cocv9i2c3art6
- Nguyen, T. H. H., Ntim, C. G., & Malagila, J. K. (2020). Women on corporate boards and corporate financial and non-financial performance: A systematic literature review and future research agenda. International Review of Financial Analysis, 71, 101554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.irfa.2020.101554
- Nixon, W., Burns, J., & Jazayeri, M. (2011). The role of management accounting in new product design and development decisions. CIMA Research Executive Summary Series, 9(1), 1–7.
- Otley, D. (1994). Management control in contemporary organizations: Towards a wider framework. Management Accounting Research, 5(3-4), 289–299. https://doi.org/10.1006/mare.1994.1018
- Otley, D. (1999). Performance management: A framework for management control systems research. Management Accounting Research, 10(4), 363–382. https://doi.org/10.1006/mare.1999.0115
- Ouchi, W. G. (1980). Markets, bureaucracies, and clans. Administrative Science Quarterly, 25(1), 129–141. https://doi.org/10.2307/2392231
- Peloza, J. (2009). The challenge of measuring financial impacts from investments in corporate social performance. Journal of Management, 35(6), 1518–1541. https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206309335188
- Pham, L. T., & Hoang, H. V. (2019). The relationship between organizational learning capability and business performance. Journal of Economics and Development, 21(2), 259–269. https://doi.org/10.1108/JED-10-2019-0041
- Pondeville, S., Swaen, V., & De Rongé, Y. (2013). Environmental management control systems: The role of contextual and strategic factors. Management Accounting Research, 24(4), 317–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mar.2013.06.007
- Redclift, M. (2005). Sustainable development (1987–2005): An oxymoron comes of age. Sustainable Development, 13(4), 212–227. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.281
- Rehman, S. U., Bhatti, A., Kraus, S., & Ferreira, J. J. M. (2021). The role of environmental management control systems for ecological sustainability and sustainable performance. Management Decision, 59(9), 2217–2237. https://doi.org/10.1108/MD-06-2020-0800
- Rodrigues, M., Alves, M. D. C., Oliveira, C., Ferreira da Silva, A., & Silva, R. (2023). Is it possible for leading companies to affect the control system of their subsidiaries?. Cogent Business & Management, 10(3), 2283062. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311975.2023.2283062
- Sahlin, J., & Angelis, J. (2019). Performance management systems: Reviewing the rise of dynamics and digitalization. Cogent Business & Management, 6(1), 1642293. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311975.2019.1642293
- Shahbaz, W., & Sajjad, A. (2021). Integrating management control systems, mindfulness and sustainability: An occupational health and safety perspective. Corporate Governance: The International Journal of Business in Society, 21(3), 433–449. https://doi.org/10.1108/CG-06-2020-0242
- Silva-Domingo, L. (2015). Management control: Unsolved problems and research opportunities. Innovar, 25(56), 11–20. https://doi.org/10.15446/innovar.v25n56.48986
- Simons, R. (1990). The role of management control systems in creating competitive advantage: New perspectives. Accounting, Organizations and Society, 15(1-2), 127–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/0361-3682(90)90018-P
- Simons, R. (1995). Levers of control: How managers use innovative control systems to drive strategic renewal. Harvard Business School Press.
- Simons, R. (2000). Performance measurement and control systems for implementing strategy: Text and cases. Prentice Hall.
- Simons, R. A., & Merchant, K. A. (1986). Research and control in complex organizations: An overview. Journal of Accounting Literature, 5(1986), 183–203.
- Strauß, E., & Zecher, C. (2013). Management control systems: A review. Journal of Management Control, 23(4), 233–268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00187-012-0158-7
- Strauss, E., Malz, S., & Weber, J. (2022). The role of management controls in new product development: Codifying a collective source of creativity. European Accounting Review. https://doi.org/10.1080/09638180.2022.2082994
- United Nations. (1987). Report of the World Commission on environment and development: Our common future. https://gat04-live-1517c8a4486c41609369c68f30c8-aa81074.divio-media.org/filer_public/6f/85/6f854236-56ab-4b42-810f-606d215c0499/cd_9127_extract_from_our_common_future_brundtland_report_1987_foreword_chpt_2.pdf
- Vale, J., Amaral, J., Abrantes, L., Leal, C., & Silva, R. (2022). Management accounting and control in higher education institutions: A systematic literature review. Administrative Sciences, 12(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci12010014
- Velázquez Gomar, J. O., & Stringer, L. C. (2011). Moving towards sustainability? An analysis of CITES’ conservation policies. Environmental Policy and Governance, 21(4), 240–258. https://doi.org/10.1002/eet.577
- Weber, M., & Roetzel, P. G. (2021, January 30). Bridging organizational resilience and management control systems – A systematic review. SSRN Electronic Journal. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3785416