Abstract
This scholarly investigation explores the complex correlation between corporate governance and artificial intelligence (AI), recognizing the dynamic nature of the digital revolution. The research consists of two primary interactions: the initial interaction explicates the importance of corporate governance, and the subsequent one examines the incorporation of artificial intelligence applications into governance frameworks. By utilizing a descriptive and analytical approach, this study examines the extent to which current legal frameworks are congruent with the opportunities and challenges presented by digital transformation. The function of AI in reducing the risks associated with unethical financial and managerial practices is a primary concern, as it contributes to the ethical fortification of nations and businesses. The results emphasize the criticality for organizations to strictly comply with governance regulations, highlighting compliance as a fundamental element in demonstrating financial well-being, promoting expansion, and fortifying competitiveness in the corporate sphere. The findings have significant ramifications for both policymakers and organizations. Policymakers and organizations should adopt a proactive strategy to utilize AI’s capabilities, improving corporate governance practices and effectively navigating the intricacies of the digital age.
1. Introduction
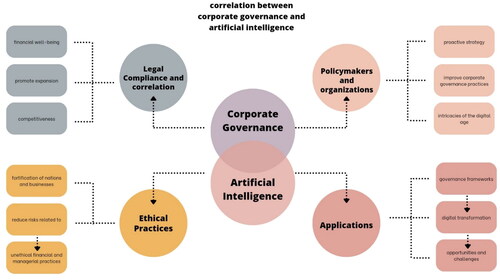
The notion of governance assumes a crucial role in facilitating and influencing the operations of enterprises and companies on a global scale (Alshurideh et al., Citation2022; Debbarma & Choi, Citation2022; Feliciano-Cestero et al., Citation2023; Schaltegger et al., Citation2022). Credibility and management transparency are fundamental characteristics that serve as the foundation for a company’s reputation and operational efficacy within the corporate sphere (Bag et al., Citation2023; Nawrocki & Szwajca, Citation2022). In order to maintain the integrity of these values, the comptroller utilizes a series of regulatory articles that verify business activities are in accordance with the relevant legal framework, such as the Jordanian Law of Companies (Al-Shawabkeh et al., Citation2022; Alkhasawneh & Khasawneh, Citation2023; Mahafzah et al., Citation2023; Malkawi, Citation2022). The emergence of multinational firms and businesses at a global level has generated a significant demand for robust legal frameworks that can effectively manage their operations and strategically guide their future market endeavors (Furr et al., Citation2022; Kosuru & Venkitaraman, Citation2023). The implementation of these legal frameworks plays a crucial role in cultivating the competitive advantage of firms (Alkaraan et al., Citation2023; Hao et al., Citation2023; Wen et al., Citation2022). The emergence of the concept of corporate governance occurred in this particular setting is rather more vital to be included in such technological demand environment (Munir & Djaelani, Citation2022). Corporate governance encompasses a comprehensive array of managerial, coordinating, and organizational strategies that are implemented to protect a company’s reputation and effectively accomplish its broad goals (Barine & Minja, Citation2023; Kavadis & Thomsen, Citation2023). Furthermore, it involves the careful arrangement of connections between the board of directors and the stockholders of a corporation (García-Ramos et al., Citation2023). Consequently, this leads to a corpus of legal regulations that govern the behavior of corporations (Nay, Citation2023; Scharlach et al., Citation2023). The significance attributed to corporate governance is apparent in multiple legislative bodies throughout the Arab region (Areneke et al., Citation2022; Alfalah et al., Citation2022; Ismail et al., Citation2023). Significantly, in 2016, the Egyptian legislative body introduced the Egyptian Guide for Corporate Governance with the endorsement of the corporate comptroller (Abdou, Citation2023). In the subsequent year of 2017, Jordan also took similar action by actively pursuing the adoption of improved corporate governance norms (Ananzeh et al., Citation2022; Alghemary et al., Citation2023). Given the rapid global adoption of digital transformation, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into corporate governance procedures has become imperative in order to maintain the legitimacy and stability of firms (Musleh Al-Sartawi et al., Citation2022). The notion of artificial intelligence involves the application of technical software by specialized devices to execute tasks and independently learn and enhance performance via the analysis of available data (Ahmed et al., Citation2022; Bouschery et al., Citation2023). This enables the effective resolution of various issues while mitigating the occurrence of errors (Himeur et al., Citation2023). Pengyu et al. examines the relationship between artificial intelligence (AI) and corporate sustainable development in Chinese listed companies. Findings show AI promotes sustainable development, focusing on environmental governance and social responsibility. However, internal and external pressures, such as Confucian culture and public pressure, can hinder its positive effects. AI can alleviate financing constraints, reduce costs, improve supply chain performance, and reduce risks (Chen et al., Citation2023). The focus of this investigation is on the examination of the significance of devising a legal framework model for the adoption of artificial intelligence in Jordanian businesses. The work holds importance due to its potential to leverage the utilization of artificial intelligence in the field of corporate governance (Al-Habashneh, Citation2023; Qasaimeh & Jaradeh, Citation2022). The objective of this attempt is to promote the implementation of organizational structure and adherence to regulations by providing a clear structure to adopt legal framework based on a collection of legal articles that organizations in Jordan might follow. The study demonstrates a broad scope of relevance that transcends national boundaries, encompassing a global context. Additionally, it aims to provide insights into the issues and opportunities that arise from the implementation of artificial intelligence (AI) in corporate governance, specifically within the Jordanian setting. Therefore, the methodology of the study is organized into three essential components. Firstly, it sheds light on the obstacles that organizations encounter when undertaking their digital transformation endeavors, thereby making a valuable contribution towards narrowing the existing knowledge gap in this domain. The results of this primary objective of the theoretical aspect is to enhance the ability of organizations to effectively comply with the principles of governance. The methodology will also initiate the main steps that will create such effective and practical significance for companies that operate in the fields of (AI) and legally involve it within its corporate governance. Then, it proposes a structured methodological framework to examine the pertinent legal articles, instructions, and regulations. This approach integrates legal perspectives and jurisprudential examination in order to provide full responses to the research inquiries. The proposed framework includes several stages, research techniques, and analytical tools to help with the transition to AI-powered processes. Furthermore, this article contributes to organizations’ compliance with legal governance rules by providing evidence-based insights and recommendations, thereby promoting improved efficiency and effectiveness. This is achieved by aiding firms to proceed in digital transformation while simultaneously ensuring adherence to governance-related legal provisions. In addition, it adds valuable insights for organizations seeking to use AI technologies that enhance corporate governance and overall operational effectiveness. For feasible legal compliance and AI driven corporate governance, the paper highlights the identification of legal articles in the law that enable firms in achieving governance. Likewise, the objective is to ascertain if these legal requirements have effectively developed a robust legal structure that enables organizations to participate in digital transactions amidst the current worldwide digital revolution. The article’s results and discussion sections present primary findings and guidelines that are then used as the basis for formulating recommendations and drawing conclusions in the study. depicts the graphical abstract of the study.
2. Methodology
This paper proposes a complete procedure for developing a legal governance model in the context of Jordanian enterprises within the rapidly rising realm of AI. The goal is to develop a systematic strategy that ensures adherence to ethical and regulatory standards while encouraging innovation and progress in artificial intelligence. The incorporation of AI into Jordanian businesses is critical to technological innovation and economic prosperity. AI technologies have the ability to transform many industries, improve operational efficiency, and spur creativity (Ahmed et al., Citation2022; Al-Habashneh, Citation2023; Bouschery et al., Citation2023; Chen et al., Citation2023; Himeur et al., Citation2023; Qasaimeh & Jaradeh, Citation2022). However, successful AI adoption necessitates an organized and systematic strategy that takes into account ethical concerns, legal compliance, and the unique obstacles of the Jordanian corporate sector. The three pillars of the methodology are: Corporate governance, AI in business and the proposed legal governance model for Artificial Intelligence Implementation in Jordanian Industry.
2.1. Corporate governance
The legislation under consideration ought to emphasize the fundamental principles and jargon associated with corporate governance in Jordan. Using this article’s comprehensive exposition on corporate governance, lawmakers should acquire a succinct and unambiguous understanding of the regulatory structure that regulates the activities and leadership of businesses. The agreement delineates the rights and obligations of various entities, such as the proprietors, shareholders, and board of directors. It is advisable to incorporate an article that delves into the historical development of management and sound governance. The article’s components furnish an elaborate historical narrative of the progression of corporate governance in Jordan, elucidating its inception while remaining adaptable to integrate illustrations and interpretations of good governance.
It is essential to examine models of global governance to compose articles that correspond with a proposed governance structure. This stage is of great assistance when examining the worldwide perspective on corporate governance, as it underscores the pivotal significance of governance frameworks following worldwide financial crises and corporate controversies. It is imperative to underscore the significance of governance in fostering financial openness, transparency, and competitiveness. Corporate governance investigates the protocols implemented to reconcile the conflicting interests of various stakeholders, including investors, management, and other critical entities. It is crucial to emphasize the significance of corporate governance in enhancing the global competitiveness and risk management of businesses. Corporate governance also involves the supervision and administration of an extensive array of operational responsibilities.
2.2. Corporate governance mechanisms in AI
The primary purpose of this article is to examine in depth the concept of AI in corporate governance and how to make it ethically and legally compliant. Intelligence and artificiality are two main components of AI. It is important to include an article that defines and explains the capabilities of AI to comprehend and navigate unknown situations and perform cognitive tasks. The application of artificial intelligence (AI) in governance has attracted considerable interest and has been the subject of extensive research. AI applications in governance span various topics, including policy formulation, decision-making, public service delivery, and regulatory supervision. It is necessary to investigate the legal functions that AI applications perform in corporate governance at this stage, including their capacity to generate algorithms, analyze data, and facilitate decision-making processes. Legislators should properly identify AI so that the proposed articles of the law can support decision-making by AI based on specific outlined constraints. The legal significance of AI in corporate governance should focus on the board of directors and senior management officers. This statement examines the compatibility between the incorporation of AI and the existing legal frameworks regulating corporate governance and control. Utilizing AI ensures transparent processes and functions. The authors recommend implementing the law to enhance transparency and disclosure in corporate governance. The focus is on AI’s role in enhancing financial transparency and information accessibility. The ability of the Jordanian system to support and promote the use of cutting-edge IT resources and AI applications in the commercial sector, as well as the benefits of digital transformation, is crucial to excelling in the ranking of doing business reports. Therefore, the legal framework should facilitate the inclusion of technology in governance and provide financial incentives to keep it up-to-date.
2.3. The proposed legal governance framework for artificial intelligence in corporate governance
2.3.1. Review of literature
The first step to enable such framework is to thoroughly examining and integrating established academic material on the governance and management of AI across several sectors. This step aims at extensively investigating the relationship between corporate governance and artificial intelligence to establish a solid grasp of the subject and navigate it effectively.
2.3.2. Creating a conceptual structure
This step aims to offer clear and straightforward definitions and conceptual boundaries for corporate governance and artificial intelligence (AI). This step aims to lay a solid foundation for understanding the responsibilities and significance of this concept in the business context.
2.3.3 Historical legal context
The historical legal context refers to the background and circumstances surrounding a particular legal issue or event in the past. It encompasses the prevailing laws, regulations, and judicial practices that shaped AI in business. This step examines the historical context of corporate governance and the use of AI in business processes. Official regulations about corporate governance in Jordan still need to be established. The articles of the Jordanian Companies Law acknowledge certain principles of corporate governance. The Securities Act of 2002 and the Companies Law of 1997 govern Jordanian corporations. Both statutes mandate interference, transparency, and the expeditious disclosure of financial and non-financial information. Looking at the current state of the law and how AI is being used in corporate governance helps reach the goal of making a legal tool that makes these changes possible and gives lawmakers a solid academic understanding of the reasons behind these changes.
2.3.4. Legal framework
This research looks into the legal framework that governs the incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) into corporate governance in the commercial realm. This analysis focuses on essential Jordanian laws, rules, and recommendations and how it can be fitted to work in harmony with international regulations. At present, Jordan lacks any formally recognized regulations about corporate governance. Jordanian company law incorporates certain corporate governance principles, providing a solid foundation for corporate governance regulation. To illustrate, consult Articles (140) and (141) of the 1997 Companies Law.
In collaboration with the International Finance Corporation (IFC) and the Companies Control Department of the World Bank Group, Jordan issued codes and principles of corporate governance and a non-mandatory code of conduct for private entities in 2012. Non-Listed Public Shareholding Companies, Limited Liability Companies, and Shareholding Companies: The OECD Corporate Governance Principles constituted this regulation (Ministry of Industry, Trade and Supplies, Department of Company Control, Citation2012).
The purpose of this framework is to assess and recommend which corporate governance practices are applicable in Jordan. To capture the strengths and avoid the weaknesses of AI in corporate governance, it is necessary to establish a well-defined structural legal framework based on Jordanian company law. Further the compatibility of existing Jordanian legislative mandates and the incorporation of artificial intelligence into the corporate governance framework should be examined.
2.3.5. Evaluation of legal interpretation
The development of the proposed legal framework should be further refined to adopt the new structure of the laws and bylaws, depending on the interpretation of legal information. During this phase, the proposed framework will undergo fine-tuning and corrective measures, thoroughly investigating the legal interpretations, attitudes, and viewpoints surrounding the incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) in corporate governance. It investigates the legal complexities and potential roadblocks in this arena.
The methodology proposes a framework for assisting Jordanian firms in implementing AI technologies. The goal is to take a complete and adaptive approach to AI integration that is technically sound, ethically responsible, and legally acceptable (Al-Habashneh, Citation2023; Al-Gasawneh et al., Citation2022; Awamleh & Bustami, Citation2022; Qasaimeh & Jaradeh, Citation2022). By bringing together its three primary pillars and the factors that affect each of them—efficiency, competitiveness, the need for specialized training, and cybersecurity considerations—as advised a legal governance model can be established that recognizes the value of AI in the workplace and protects the security of its data. The comprehensive methodology of the proposed model offers a well-structured and rigorous means of analyzing the legal governance framework for AI in Jordanian businesses. The complex relationship between corporate governance and artificial intelligence in today’s business environment can be further explored in more depth in the future by combining descriptive and analytical methods.
3. Results
3.1. Jordanian company law and corporate governance approaches
As stated earlier, official regulations pertaining to corporate governance in Jordan are nonexistent at this time. The articles of the Jordanian Companies Law incorporate certain corporate governance principles, which serve as the foundation of corporate governance regulations.
Clearly, Jordanian company law is based on a mandatory corporate law model. It ensures adherence to legal obligations by furnishing a comprehensive and precise delineation of the duties entailed in isolating managers and other high-ranking executives from the organization.
Numerous articles of the law prescribe the conduct of officers and managers, containing mandatory and regulatory provisions. Managers and officers can gain insight into oversight and responsibility, equitable treatment of employees and shareholders, safeguarding stockholders against conflicts of interest, transparency, and penalties by perusing relevant articles.
Article (144) outlines the agenda, specific dates, and procedures that the board of directors must adhere to during the General Assembly Meeting.
Article 165 establishes the General Assembly’s authority to remove the Chairman and members of the Board of Directors, along with the precise percentage required to carry out this authority.
In addition to Article 172, which specifies the proportion of members necessary to convene an extraordinary meeting of the General Assembly.
Article 98/d ensures equal treatment of all shareholders and stockholders, as permitted by the court.
For any purpose, shareholders may request access to the shareholder register pertaining to their shareholding.
Safeguard the interests of the shareholders. Articles 140 and 141 stipulate the dates and responsibilities of the Board of Directors in achieving transparency through the use of diverse financial documents (e.g. annual balance sheet, profit and loss statement, cash flows), as well as the ability to compare the statements and their elucidations with those of the preceding fiscal year. Perform the necessary procedures to certify all statements. Additionally, they possess the prerogative to examine the firm’s auditors’ report and the annual report of the Board of Directors, which details the organization’s operations and projections for the upcoming year. Furthermore, in order to foster transparency and mitigate potential conflicts of interest, Article (148) explicitly forbids board members from holding public office, unless such employment is as government representatives. Additionally, it forbids them from assuming membership on the Board of Directors of a competing company that operates in a sector analogous to their own. Furthermore, it serves to shield the contracts and projects from any personal interest of the chairman, general manager, or any employee.
Additionally, penalties for violations of transparency and deception are explicit and severe. For example, under Article 278, anyone who
‘Issues shares, share certificates, or delivers them to their owners, or offers them for negotiation, before the approval of the Company Memorandum of Association and the approval of the founding of the company, or permits the company to increase its authorized capital before announcing that in the Official Gazette’; ‘makes fictitious subscriptions for shares or accepts subscriptions therefore in an illusory or unreal manner for non-existent or unreal companies.’
‘Issues corporate bonds and offers them for negotiation before their maturity in a manner that violates the provisions of this law.’
‘Prepares the balance sheet of any company and its profit and loss account in a manner which does not reflect reality, or incorporates in the report of the company’s board of directors or in its auditors’ report incorrect statements and conveys to its general assembly incorrect information, or conceals information and clarifications, which should be declared by the force of law, to conceal the real status of the company from the shareholders or other concerned parties.’
‘Distributes the profits that are fictitious or incompatible with the real position of the company.’
Therefore, Jordanian company law closely aligns with the legal framework aptly suggested for developing nations lacking the necessary components of an institutional corporate governance system. This is particularly significant given the concurrent aspirations of developing countries to establish financial markets, which would facilitate access to financing and ultimately enable financial markets to function within those developing countries.
Jordan may need to adopt a legal strategy with a limited track record of market liberalization due to these factors. Jordan, which adopted liberalization upon joining the WTO in 2000, still requires additional experience to effectively manage capital markets. However, the limited number of departments at the Company Control Department for Governance results in an absence of effective institutions to support sound governance. Special attentions to these divisions, which require additional improvement and support from a solid legal framework is therefore needed. In addition, the need to address dearth of expertise, which can be remedied by implementing AI in reporting and decision-making procedures is recommended.
3.2. Findings
The findings derived from this research provide useful insights into the significance of governance and the incorporation of AI within the context of corporate governance. The findings of this study can be further examined in an inclusive manner.
The initial result emphasizes the significant role that governance plays in lowering the costs associated with financial and managerial corruption that nations and corporations encounter. This discovery underscores the crucial significance of governance in fostering ethical conduct and ensuring responsibility within organizational contexts. By embracing governance principles, organizations can mitigate the probability of corruption, financial impropriety, and subsequent financial burdens.
Ensuring the preservation of the integrity of commercial activities and fostering trust among stakeholders are of paramount importance. The second outcome provides a brief, though all-encompassing, exposition of governing. The concept is depicted as a methodology for guiding and managing the operational activities of an organization. Furthermore, governance is commonly described as a complex framework that encompasses a range of mechanisms aimed at organizing and overseeing interactions among important actors, such as the board of directors, executives, and shareholders. The provided statement highlights the intricate nature of governance and its influence on the conduct of corporations.
The third outcome provides insight into the many incentives that governance mechanisms can provide to the board of directors and managers as they strive to achieve the goals of the corporation. These incentives function as motivational stimuli that foster responsible decision-making and behaviors directed towards the attainment of organizational objectives. Governance systems play a crucial role in improving organizational efficiency and performance by effectively aligning the interests of individuals and the organization.
The fourth result emphasizes the wide range of technologies encompassed within the field of artificial intelligence. The statement recognizes that AI has seen significant development, transforming into a multifaceted notion that encompasses a wide range of applications and the ability to do numerous tasks. The comprehension of this concept is of utmost importance as it establishes the foundation for examining the multifaceted characteristics of artificial intelligence in the context of corporate governance.
In terms of financial transparency and disclosure, artificial intelligence is investigated as a potential tool in the field of corporate governance in the fifth outcome. AI is widely believed to be a game-changing tool for reducing accounting errors and increasing business openness. This result is in line with the evolving state of corporate reporting, wherein cutting-edge technology is increasingly used to ensure the reliability and accessibility of financial data.
4. Discussion
The results highlight the critical role of governance in combating corruption and encouraging ethical behavior in business settings. The authors offer a deep dive into governance, drawing attention to its nuanced nature and persuasive power in achieving business aims. The results also recognize AI technologies’ vast potential and applicability for boosting transparency and accuracy in corporate governance processes. These findings significantly enhance the perceived comprehension of the complex interplay between governance and artificial intelligence (AI) in the current business landscape (Al-Habashneh, Citation2023; Al-Gasawneh et al., Citation2022). The paper’s remarks and recommendations offer useful insights for commercial enterprises, governments, and organizations aiming to manage the dynamic realm of corporate governance and artificial intelligence (AI) (Awamleh & Bustami, Citation2022; Ministry of Industry, Trade and Supplies, Department of Company Control, Citation2012). In order to delve into these results and recommendations, a comprehensive analysis for the issue was conducted.
4.1. Recommendations
One recommendation emphasizes the significance of commercial enterprises conforming to governance standards. It promotes the adoption and maintenance of governance processes by companies that are in accordance with ethical standards and regulatory obligations. Through this strategic approach, organizations can effectively protect their financial stability and enhance their competitive advantage in the marketplace. This recommendation serves as a pragmatic framework for organizations to augment their corporate governance processes. Additionally, the legal amendments pertaining to artificial intelligence (AI) in governance are of paramount importance. The second recommendation is directed towards the Jordanian legislature, with the aim of encouraging the enactment of law amendments that especially pertain to the incorporation of artificial intelligence in the realm of corporate governance. The aforementioned revisions ought to delineate legal principles and structures that regulate the conscientious and open application of artificial intelligence (AI) within corporate entities. The advice that researchers provide to the legislature encourages the demonstration of a proactive approach in arguing for legal frameworks that are able to adapt to the rapid progress of technology. The final recommendation emphasizes the importance of firms actively adopting digital transformation and integrating artificial intelligence. The statement recognizes the capacity of AI applications and technologies to bring about significant changes in improving company operations, decision-making processes, and overall efficiency. It is highly recommended that companies allocate resources and provide training in order to properly harness the benefits of artificial intelligence (AI).
These recommendations together with the adherence to governance principles are of paramount importance (Mansour et al., Citation2022). This inference underscores the need to adhere to governance standards within the context of commercial enterprises. This highlights the significance of adhering to such practices, as they not only have implications for a company’s financial standing but also have an effect on its competitive standing within the market (Alrjoub et al., Citation2023). The antecedent conclusion is based on the notion that governance principles are crucial for increasing ethical behavior, transparency, and responsibility in the workplace (Al-Rahamneh et al., Citation2023). By adhering to these recommendations, businesses can gain the trust of their constituents, enhance their market standing, and ultimately gain a competitive advantage. The second finding which is supported by a recommendation emphasizes updating Jordan’s legal system (Albalawee & Al Fahoum, Citation2023; Al-Balawi, Citation2022). Thirdly, organizations must fully embrace digital transformation and integrate AI into their operations, highlighting the significance of this trend. This exemplifies the vast array of AI applications and resources (Ahmad et al., Citation2023). This finding is consistent with the ever-changing business environment in which digitalization and AI are crucial for enhancing competitiveness and operational efficiency. Companies must adjust to technological changes to remain competitive globally (Broo et al., Citation2022). Failure to do so may result in being left behind.
In summary, the aforementioned results and recommendations provide a comprehensive viewpoint on the convergence of governance and artificial intelligence within the business domain. The significance of ethical behavior, legal structures, and technological adjustment in influencing the trajectory of corporate governance is emphasized. By following these recommendations, Jordanian corporations and government can more effectively traverse the dynamic realm of governance and the integration of artificial intelligence. It is worth mentioning that The proposed legal governance of AI in corporate governance faces several challenges, including rapid technological changes, complex AI systems, an interdisciplinary nature, and global implementation. Ethical considerations, lack of precedents, and data privacy and security are also significant issues. Legal frameworks must be adaptable to changes in technology and business practices, as rigidity may hinder innovation. Enforcement challenges may arise due to a lack of resources and expertise. Unintended consequences of AI regulations can be challenging, and addressing these limitations requires ongoing collaboration between legal experts, technologists, policymakers, and stakeholders. It is crucial to revisit and update regulations to keep pace with technological advancements and changing societal needs.
5. Conclusion
The article contends vehemently for incorporating legal articles into Jordanian company law that specifically address the use of artificial intelligence applications and their governance implications. This recommendation recognizes the imperative need to establish legal frameworks that can adapt rapidly to rapid technological advancements, particularly the incorporation of artificial intelligence into business operations. By introducing legal amendments, Jordan can provide corporations seeking to integrate AI governance structures with clear and thorough guidance. The conclusion highlights the crucial role that ethical conduct, legal modifications, and technological adaptation play in determining the trajectory of corporate governance in the evolving landscape of artificial intelligence. Businesses and governments are implored to take the initiative in determining how to safely and ethically integrate artificial intelligence. Acceptance of the transformative potential of AI technologies and adherence to established ethical standards are required.
In today’s technologically advanced society, using AI in corporate governance is crucial. To maximize the benefits that AI applications can provide, businesses and government officials in Jordan are urged to revise their strategies to keep up with the rapid tempo of technological advancement. They can increase corporate productivity, transparency, and competition by doing so.
In light of these findings, it is evident that the existing legal frameworks must be revised to permit the use of artificial intelligence in business management. The importance of ethical behavior, legislative clarity, and technical readiness in influencing the future of corporate governance in Jordan is emphasized. If businesses and government agencies adhere to these guidelines, they can confidently manage the ever-changing convergence of governance and AI.
Authors’ contributions
Authors have made equally substantial contributions to all of the following: The conception and design of the study, or acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; Drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; Final approval of the version to be submitted.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants.
Disclosure statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest to report regarding the present study.
Data availability
The data used in this article is publicly published and referenced within the article.
Additional information
Notes on contributors

Nasir Albalawee
N. AlBalawee obtained his Bachelor’s degree in Law from Irbid National University. Then he obtained his Master’s degree in Specialized Law from Jadara University and PhD in Civil and Commercial Law from the World Islamic Science and Education University. He has also obtained a professorship in professional practice. Currently, he is the chairman of the law department in the Faculty of Law, Jadara University. His specializations include Commitment resources, Labor Law, Commercial Laws, Nominal Contracts, and e-Commerce. His current research interests are e-commerce, civil Law, and Commercial Law. He has many national and international consultations on civil and commercial laws. He has published more than 14 refereed articles.

Amjed Al Fahoum
Prof. Amjed Al-Fahoum has more than 33 years of industrial and academic experience. Currently he is serving as the founding Dean of School of Engineering Technology (SET) at Al-Hussein Technical University. Previously, he served as project manager and vice dean for accreditation and quality assurance at Luminus Technical University College (Al Quds College) and the president of the board of trustees for Zarqa National community college. Before that, he served at Yarmouk University and Princess Sumayah University for Technology as an academic professor. Prof. Al Fahoum was the founder and the chairperson for the biomedical systems and Informatics Engineering Department at Yarmouk University, a founding Director of the Biomedical Center of Excellence, and a director of the Academic Entrepreneurship Center of Excellence. He taught specific courses at Jordan University of Science and Technology and German Jordanian University. His research over the last eight years has focused on Systems Engineering, quality assurance, and Entrepreneurship. Prof. Al-Fahoum holds a PhD in Electrical Engineering from Wisconsin University and has strong record of achievements in international and national research companies. Prof. Al-Fahoum has been acting as principal investigator on more than 12 graduate students’ thesis and he is an author and co-author of more than 50 international research articles. Prof. Al-Fahoum led as a principal investigator 16 industrially funded projects and produced more than 21 technical reports. Prof. Al-Fahoum taught more than 27 courses and supervised more than 500 students in their graduate and technical field training. He contributed to the establishment of 3 centers of excellence, 15 enterprises, raised more than 15 Million JD Funds, and created more than 2000 job opportunities.
References
- Abdou, M. (2023). Egypt: Recent trends and developments in public law. Yearbook of Islamic and Middle Eastern Law Online, 22(1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1163/22112987-20230036
- Ahmad, H., Hanandeh, R., Alazzawi, F., Al-Daradkah, A., ElDmrat, A., Ghaith, Y., & Darawsheh, S. (2023). The effects of big data, artificial intelligence, and business intelligence on e-learning and business performance: Evidence from Jordanian telecommunication firms. International Journal of Data and Network Science, 7(1), 35–40. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.ijdns.2022.12.009
- Ahmed, I., Jeon, G., & Piccialli, F. (2022). From artificial intelligence to explainable artificial intelligence in industry 4.0: A survey on what, how, and where. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 18(8), 5031–5042. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2022.3146552
- Albalawee, N., & Al Fahoum, A. S. (2023). Islamic legal perspectives on digital currencies and how they apply to Jordanian legislation. F1000Research, 12, 97. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.128767.2)
- Al-Balawi, N. M. S. (2022). Provisions for unilaterally amending the contract in Jordanian law. Baltic Journal of Law & Politics, 15(2), 408–417.
- Alfalah, A. A., Muneer, S., & Hussain, M. (2022). An empirical investigation of firm performance through corporate governance and information technology investment with mediating role of corporate social responsibility: Evidence from Saudi Arabia telecommunication sector. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 959406. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.959406
- Al-Gasawneh, J., Al-Hawamleh, A., Alorfi, A., & Al-Rawashde, G. (2022). Moderating the role of the perceived security and endorsement on the relationship between per-ceived risk and intention to use the artificial intelligence in financial services. International Journal of Data and Network Science, 6(3), 743–752. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.ijdns.2022.3.007
- Alghemary, M., Al-Najjar, B., & Polovina, N. (2023). What do we know about real earnings management in the GCC? Journal of Accounting in Emerging Economies, 1-33. https://doi.org/10.1108/JAEE-06-2023-0180
- Al-Habashneh, F. M. (2023). The impact of artificial intelligence on the economy in Jordan. Resmilitaris, 13(3), 841–858.
- Alkaraan, F., Elmarzouky, M., Hussainey, K., & Venkatesh, V. G. (2023). Sustainable strategic investment decision-making practices in UK companies: The influence of governance mechanisms on synergy between industry 4.0 and circular economy. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 187, 122187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2022.122187
- Alkhasawneh, A., & Khasawneh, F. A. (2023). Legal issues of consumer privacy protection in the cloud computing environment: Analytic study in GDPR, and USA legislations. International Journal of Cloud Computing, 12(1), 40–62. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJCC.2023.129773
- Al-Rahamneh, N. M., Al Zobi, M. T. K., & Bidin, Z. (2023). The influence of tax transparency on sales tax evasion among Jordanian SMEs: The moderating role of moral obligation. Cogent Business & Management, 10(2), 2220478. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311975.2023.2220478
- Alrjoub, A. M. S., Bataineh, A., Al Qudah, L. A. M., Al Othman, L. N., Alkarabsheh, F., & Aburisheh, K. E. (2023). The impact of quality costs as a mediator in the relationship between management accounting systems and financial performance: The Case of Jordan. International Journal of Professional Business Review, 8(4), e01462. https://doi.org/10.26668/businessreview/2023.v8i4.1462
- Al-Shawabkeh, T. M., Al-Ajaleen, B. A., & Al-Daraweesh, N. M. (2022). The securities issued by joint-stock companies: Shares and loan securities. Polit Journal, 2(4), 166–185.
- Alshurideh, M., Kurdi, B., Alzoubi, H., Obeidat, B., Hamadneh, S., & Ahmad, A. (2022). The influence of supply chain partners’ integrations on organizational performance: The moderating role of trust. Uncertain Supply Chain Management, 10(4), 1191–1202. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.uscm.2022.8.009
- Ananzeh, H., Alshurafat, H., Bugshan, A., & Hussainey, K. (2022). The impact of corporate governance on forward-looking CSR disclosure. Journal of Financial Reporting and Accounting, 1-20. https://doi.org/10.1108/JFRA-10-2021-0379
- Areneke, G., Khlif, W., Kimani, D., & Soobaroyen, T. (2022). 13. Do corporate governance codes matter in Africa? Research handbook on corporate board decision-making, Chapter 13 (pp. 273). UK: Edward Elgar Publishing Limited.
- Awamleh, F. T., & Bustami, A. N. (2022). Examine the mediating role of the information technology capabilities on the relationship between artificial intelligence and competitive advantage during the COVID-19 pandemic. SAGE Open, 12(3), 215824402211194. https://doi.org/10.1177/21582440221119478
- Bag, S., Rahman, M. S., Srivastava, G., Shore, A., & Ram, P. (2023). Examining the role of virtue ethics and big data in enhancing viable, sustainable, and digital supply chain performance. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 186, 122154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2022.122154
- Barine, K., & Minja, D. (2023). Effective Corporate Governance: Theory and Best Practices. Vernon Press.
- Bouschery, S. G., Blazevic, V., & Piller, F. T. (2023). Augmenting human innovation teams with artificial intelligence: Exploring transformer‐based language models. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 40(2), 139–153. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpim.12656
- Broo, D. G., Kaynak, O., & Sait, S. M. (2022). Rethinking engineering education at the age of industry 5.0. Journal of Industrial Information Integration, 25, 100311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jii.2021.100311
- Chen, P., Chu, Z., & Zhao, M. (2023). The road to corporate sustainability: The importance of artificial intelligence. Technology in Society, 76, 102440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2023.102440
- Debbarma, J., & Choi, Y. (2022). A taxonomy of green governance: A qualitative and quantitative analysis towards sustainable development. Sustainable Cities and Society, 79, 103693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2022.103693
- Feliciano-Cestero, M. M., Ameen, N., Kotabe, M., Paul, J., & Signoret, M. (2023). Is digital transformation threatened? A systematic literature review of the factors influencing firms’ digital transformation and internationalization. Journal of Business Research, 157, 113546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2022.113546
- Furr, N., Ozcan, P., & Eisenhardt, K. M. (2022). What is digital transformation? Core tensions facing established companies on the global stage. Global Strategy Journal, 12(4), 595–618. https://doi.org/10.1002/gsj.1442
- García-Ramos, R., Díaz, B. D., & Olalla, M. G. (2023). The relationship between the structure of the board of directors and firm performance in family versus non-family firms. European Journal of International Management, 20(2), 299–322. https://doi.org/10.1504/EJIM.2023.131366
- Hao, X., Fu, W., & Albitar, K. (2023). Innovation with ecological sustainability: Does corporate environmental responsibility matter in green innovation? Journal of Economic Analysis, 2(3), 21–42. https://doi.org/10.58567/jea02030002
- Himeur, Y., Elnour, M., Fadli, F., Meskin, N., Petri, I., Rezgui, Y., Bensaali, F., & Amira, A. (2023). AI-big data analytics for building automation and management systems: a survey, actual challenges and future perspectives. Artificial Intelligence Review, 56(6), 4929–5021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-022-10286-2
- Ismail, M. D., Kathim, A. M., & Al-Kanani, M. M. (2023). Corporate governance and its impact on the efficiency of internal control on non-profit government institutions: An exploratory study. International Journal of Professional Business Review, 8(1), e01155-e01155. https://doi.org/10.26668/businessreview/2023.v8i1.1155
- Kavadis, N., & Thomsen, S. (2023). Sustainable corporate governance: A review of research on long‐term corporate ownership and sustainability. Corporate Governance: An International Review, 31(1), 198–226. https://doi.org/10.1111/corg.12486
- Kosuru, V. S. R., & Venkitaraman, A. K. (2023). Advancements and challenges in achieving fully autonomous self-driving vehicles. World Journal of Advanced Research and Reviews, 18(1), 161–167.
- Mahafzah, E., Alshible, M., & Garaibeh, Z. (2023). Legal protection of personal data in Jordan considering international standards. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 58, 1.
- Malkawi, B. (2022). Corporate governance and the audit function in Jordan and the UK: A comparative perspective. Global Business Law Review, 11, 112.
- Mansour, M., Aishah Hashim, H., Salleh, Z., Al-Ahdal, W. M., Almaqtari, F. A., & Abdulsalam Qamhan, M. (2022). Governance practices and corporate performance: Assessing the competence of principal-based guidelines. Cogent Business & Management, 9(1), 2105570. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311975.2022.2105570
- Ministry of Industry, Trade and Supplies, Department of Company Control. (2012).
- Munir, M., & Djaelani, M. (2022). Information technology and repositioning of human resource management functions. Journal of Social Science Studies (JOS3), 2(2), 50–55. https://doi.org/10.56348/jos3.v2i2.28
- Musleh Al-Sartawi, A. M. A., Hussainey, K., & Razzaque, A. (2022). The role of artificial intelligence in sustainable finance. Journal of Sustainable Finance & Investment. https://doi.org/10.1080/20430795.2022.2057405
- Nawrocki, T. L., & Szwajca, D. (2022). The importance of selected aspects of a company’s reputation for individual stock market investors—Evidence from Polish capital market. Sustainability, 14(15), 9187. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159187
- Nay, J. J. (2023). Large language models as fiduciaries: A case study toward robustly communicating with artificial intelligence through legal standards. arXiv Preprint, arXiv:2301.10095.
- Qasaimeh, G. M., & Jaradeh, H. E. (2022). The impact of artificial intelligence on the effective applying of cyber governance in Jordanian commercial banks. International Journal of Technology, Innovation and Management (IJTIM), 2(1), 68–86.
- Schaltegger, S., Christ, K. L., Wenzig, J., & Burritt, R. L. (2022). Corporate sustainability management accounting and multi‐level links for sustainability–A systematic review. International Journal of Management Reviews, 24(4), 480–500. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijmr.12288
- Scharlach, R., Hallinan, B., & Shifman, L. (2023). Governing principles: Articulating values in social media platform policies. New Media & Society, 146144482311565. https://doi.org/10.1177/14614448231156580
- Wen, H., Zhong, Q., & Lee, C. C. (2022). Digitalization, competition strategy and corporate innovation: Evidence from Chinese manufacturing listed companies. International Review of Financial Analysis, 82, 102166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.irfa.2022.102166