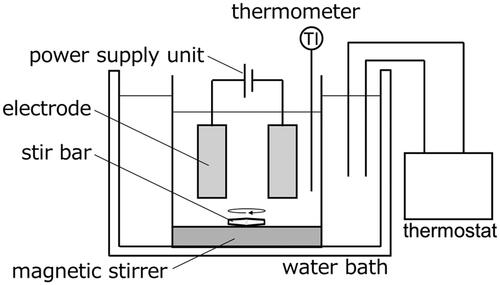
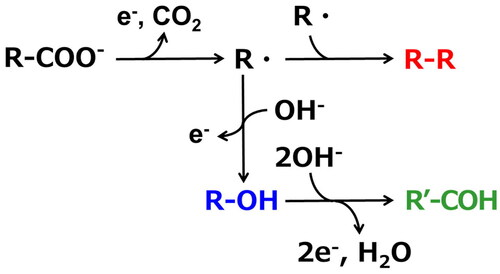
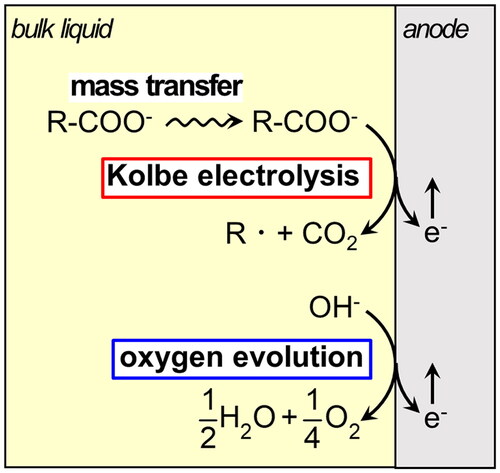
Figures & data
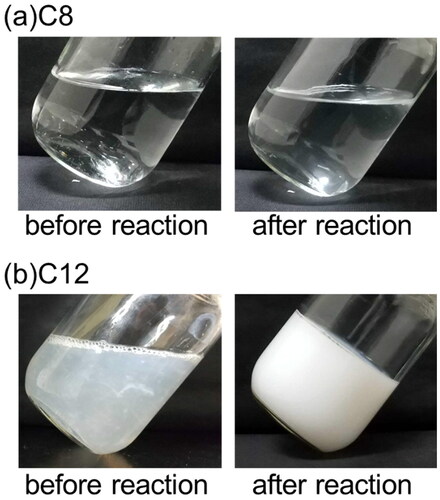
Figure 2. Chromatograph of hexane solution extracting liposoluble components in electrolysis with R-COONa (T = 20 °C, E = 20 V, Q = 1000 C).
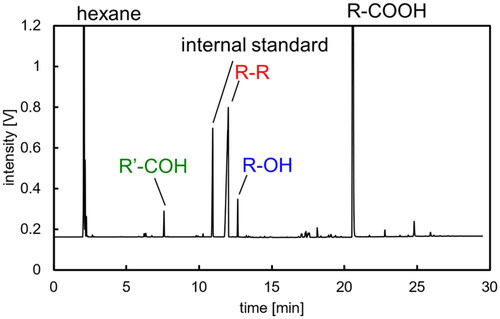
Figure 4. Conversion and yields of R-COOH and R-COONa in electrolysis (T = 20 °C, E = 20 V, Q = 1000 C).
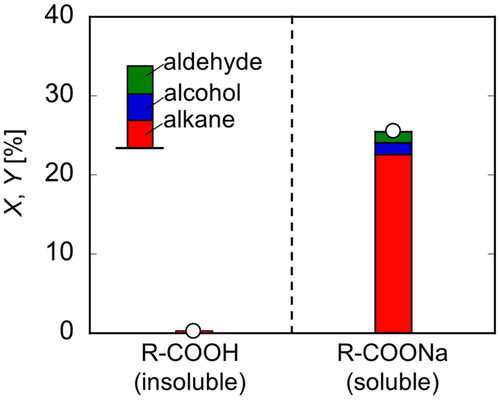
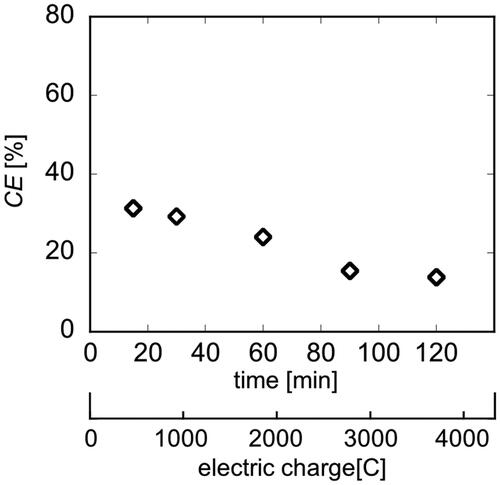
Figure 5. Concentration profiles of reactant and product and pH in electrolysis of R-COONa (T = 20 °C, E = 20 V).
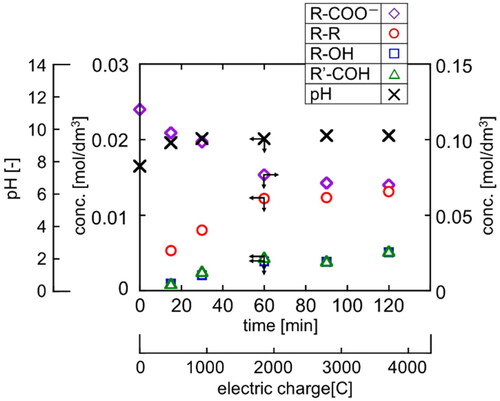
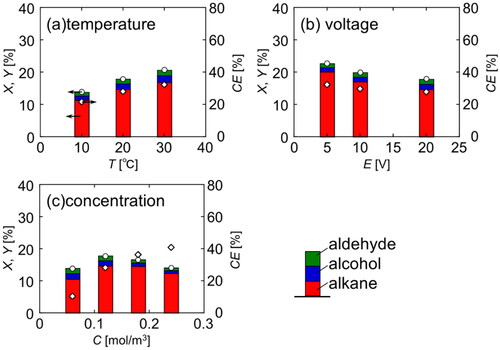
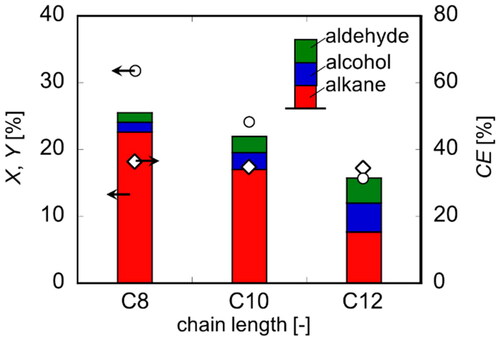
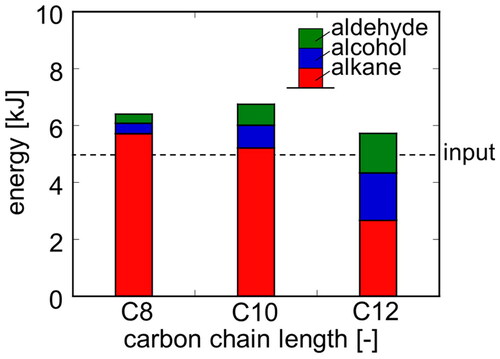
Figure 7. Conversion, yield and faradaic efficiency in electrolysis under various conditions at Q = 1000 C (Basic condition: T = 20 °C, E = 20 V, C = 0.12 mol/dm3).