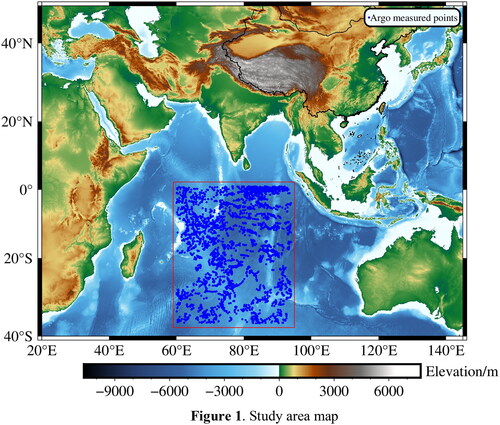
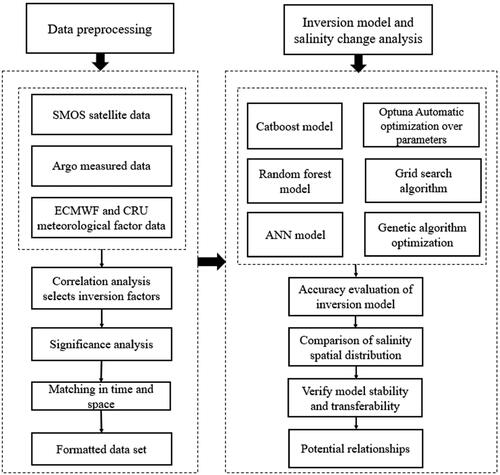
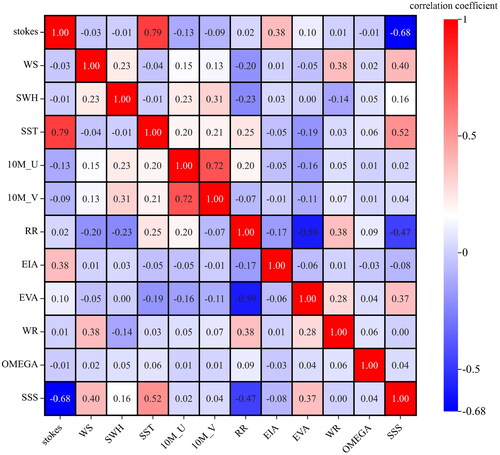
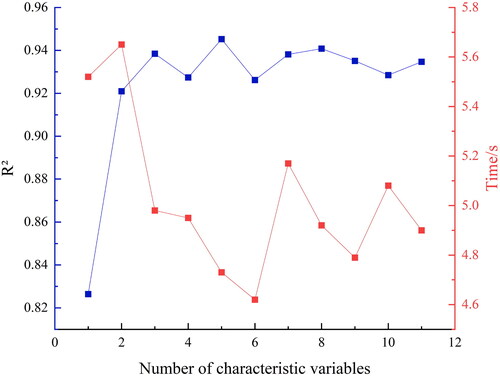
Figures & data
Table 1. Parameter optimization results for the three models.
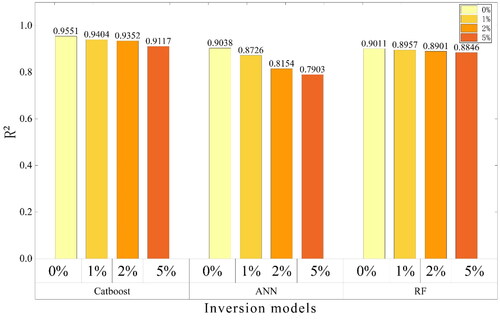
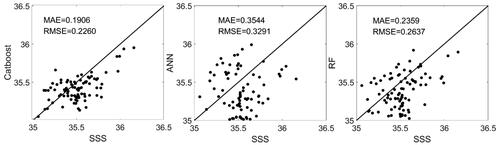
Table 2. Evaluation indicators results of the training set and test set.
Figure 7. Histogram of the error between the salinity inverted by the model and the salinity measured by Argo.
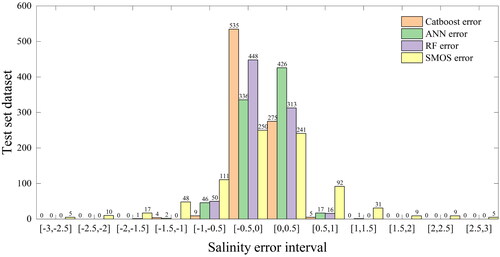
Table 3. RMSE and MAE of the random error model.
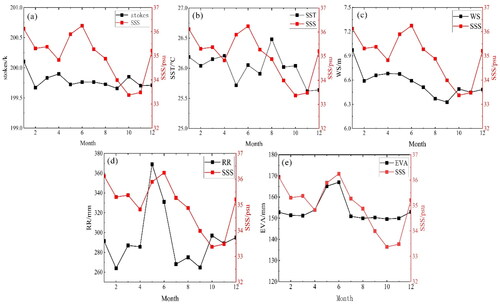
Table 4. The measured buoy site in South China sea.