Figures & data
Figure 1. Effect of HFD on mouse physiology
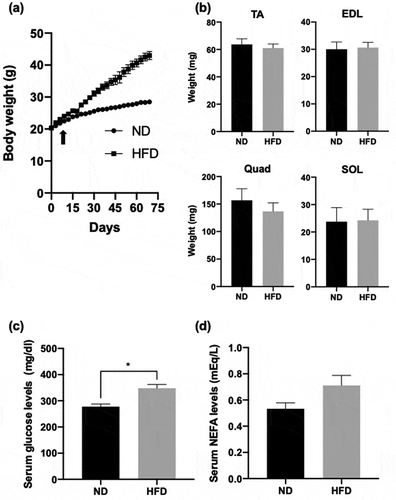
Figure 2. Effect of HFD on CXCL10 expression and secretion in mouse skeletal muscles
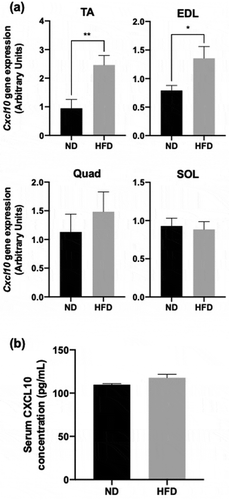
Figure 3. Effect of glucose on CXCL10 expression and secretion in C2C12 myotubes
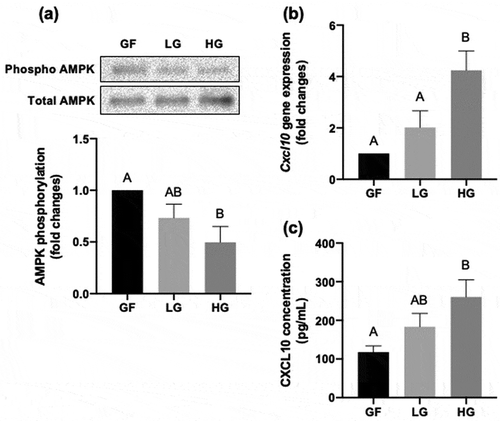
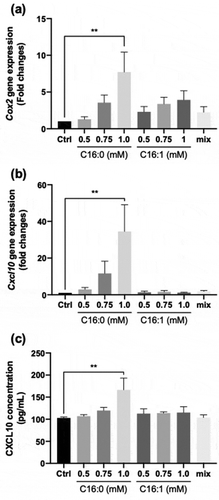
Figure 4. Effect of palmitic and/or palmitoleic acid on CXCL10 secretion and expression in C2C12 myotubes