Figures & data
Table 1. Pesticides tested against Lecanicillium muscarium in this study.
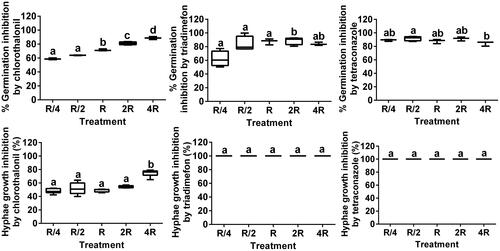
Figure 1. Inhibition of Lecanicillium muscarium conidial germination and hyphal growth by pyridalyl at different concentrations. R, R/4, R/2, 2R, and 4R indicate recommended concentration for use, a quarter of the recommended concentration, half of the recommended concentration, double the recommended concentration, and four times the recommended concentration, respectively. Colony morphology of L. muscarium grown on potato dextrose agar (PDA) containing pyridalyl at different concentrations at 5 d after inoculation (A). The plates were 9 cm in diameter. Control (PDA medium) did not contain any pesticides (A). Conidial germination inhibition rate and hyphal growth inhibition rate were determined relative to that in the control (see Materials and Methods) (B). In the box chart, uppermost point, lowest point, upper box edge, lower box edge, and line within the box represent the maximum, minimum, upper quartile, lower quartile, and median of three or four replicates, respectively. A single line in the box chart indicates 100% inhibition rate in all replicates. Data were arcsine square-root transformed before one-way analysis of variance. Means were compared using Turkey’s multiple range test. Different letters indicate significant differences among treatments (p < 0.05).
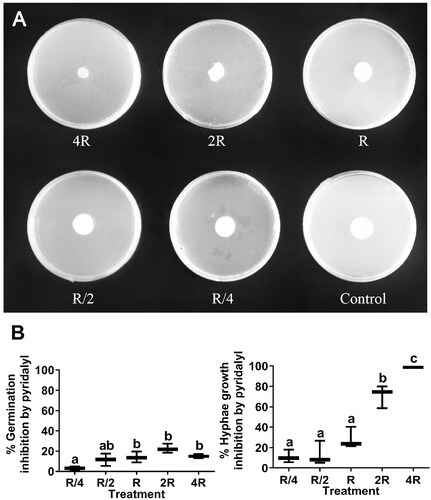
Figure 2. Inhibition of Lecanicillium muscarium conidial germination and hyphal growth by difenoconazole, thiamethoxam, and dimethomorph at different concentrations. Colony morphology of L. muscarium grown on potato dextrose agar (PDA) containing difenoconazole (A) and thiamethoxam (B) at different concentrations at 5 d after inoculation.The plates were 9 cm in diameter. Different letters indicate significant differences among treatments (p < 0.05) (C). The meanings of R, R/4, R/2, 2R, 4R and box chart, as well as data processing methods are all the same as .
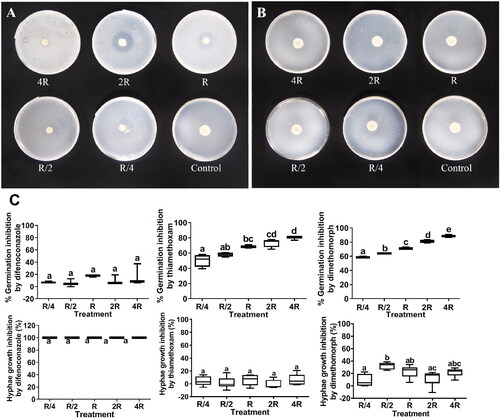
Figure 3. Inhibition of L. muscarium conidial germination and hyphal growth by phoxim at different concentrations. Colony morphology of L. muscarium grown on potato dextrose agar (PDA) containing phoxim at different concentrations at 5 d after inoculation (A). The plates were 9 cm in diameter. Different letters indicate significant differences among treatments (p < 0.05) (B). The meanings of R, R/4, R/2, 2 R, 4 R and box chart, as well as data processing methods are all the same as .
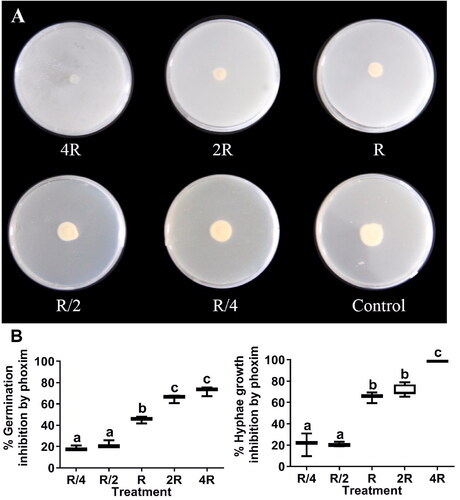
Figure 4. Inhibition of Lecanicillium muscarium conidial germination and hyphal growth by chlorothalonil, triadimefon, and tetraconazole at different concentrations. The meanings of R, R/4, R/2, 2 R, 4 R and box chart, as well as data processing methods are all the same as . Different letters indicate significant differences among treatments (p < 0.05).