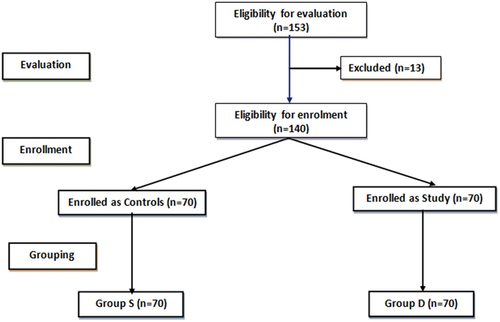
Figures & data
Table 1. Baseline data of patients from both groups.
Table 2. The finding detected during surgery for patients from both groups.
Table 3. Hemodynamic and pain data reported during postoperative course for patients from both groups.
Table 4. The reported postoperative adverse events affected patients from both groups.
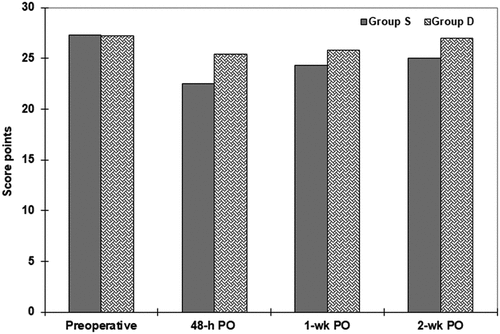
Table 5. Postoperative findings on Montreal Cognitive Assessment for patients from both groups.
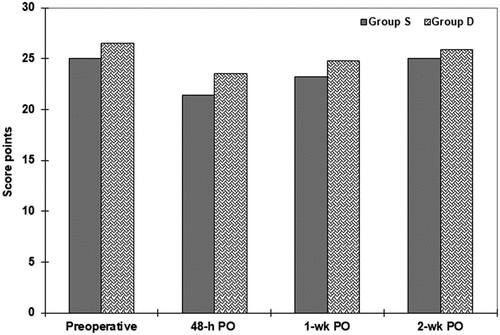
Table 6. Mini-mental state examination findings of patients from both groups.
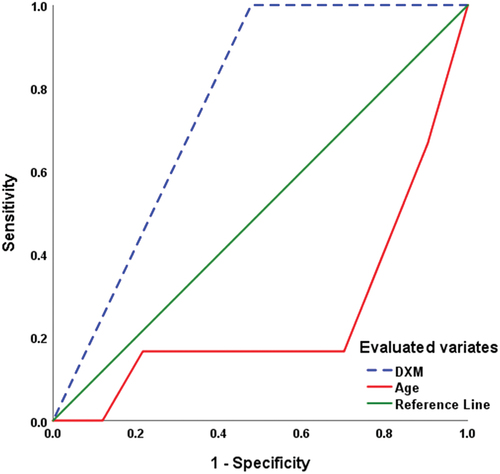
Table 7. Correlation analysis of the relation between cognitive function scorings and perioperative data.
Table 8. Regression analysis for the correlated perioperative data with CF scorings.