Figures & data
Figure 1. Overview of the complement cascade and its activation. Three different activation pathways (classical, alternative and lectin) mediate the immune response through a series of protein–protein interactions in a cascade that leads to cleavage of C3. The cleaved components go on to perform multiple roles; C3a acts as an anaphylatoxin, effecting inflammation and chemotaxin, while C3b can either cause phagocytosis of foreign species through opsonization or combine with other complement components to form C5 convertase, which cleaves C5 into C5a and C5b, initiating the terminal complement pathway. C5a, like C3a, is an anaphylatoxin, causing amplification of the inflammatory signal. C5b undergoes a series of interactions with further complement components to form the membrane attack complex (MAC), a cytolytic pore which then destroys pathogens.
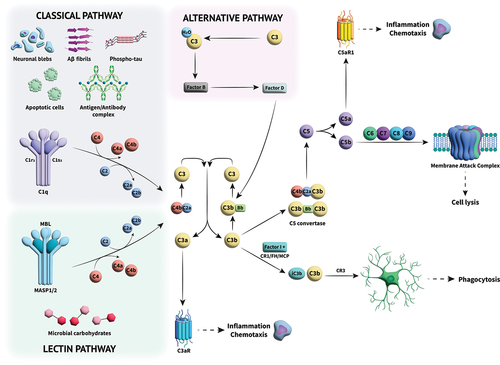
Figure 2. Structure of C5 with C5a residues highlighted in blue, in complex with a small molecule ligand (PDB:6I2X) [Citation36].
![Figure 2. Structure of C5 with C5a residues highlighted in blue, in complex with a small molecule ligand (PDB:6I2X) [Citation36].](/cms/asset/429d313d-2a38-41b3-9453-a40f6de00085/iett_a_2177532_f0002_oc.jpg)
Figure 3. Diagram of C5 with the residues forming C5a on cleavage highlighted in light blue, the biologic eculizumab (PDB ID: 5I5K) in Orange [Citation110], small molecule inhibitor H1H (PDB ID: 6I2X) in grey [Citation36], and allosteric modulator knob peptide (PDB ID: 7AD6) in green [Citation154]. The interaction site for cobra venom factor (CVF) is also indicated in light grey.
![Figure 3. Diagram of C5 with the residues forming C5a on cleavage highlighted in light blue, the biologic eculizumab (PDB ID: 5I5K) in Orange [Citation110], small molecule inhibitor H1H (PDB ID: 6I2X) in grey [Citation36], and allosteric modulator knob peptide (PDB ID: 7AD6) in green [Citation154]. The interaction site for cobra venom factor (CVF) is also indicated in light grey.](/cms/asset/7593edbc-6913-473a-bae6-71b046cc0cd8/iett_a_2177532_f0003_oc.jpg)
Figure 4. Development of small molecule C5 modulators [Citation36].
![Figure 4. Development of small molecule C5 modulators [Citation36].](/cms/asset/58a6f3f5-dd15-4850-b7c5-09f977caa781/iett_a_2177532_f0004_oc.jpg)
