Figures & data
Figure 1. Mitochondria exert an influence on the hallmarks of aging, while the hallmarks, in turn, reciprocally impact mitochondria, shaping the aging process. Trees symbolize the diverse ways we experience aging, and they are intricately linked to mitochondrial function. Mitochondrial function, in turn, is influenced by the hallmarks of aging, which can also be influenced by mitochondria. The hallmarks of aging are categorized into three groups: primary (genomic instability, telomere attrition, epigenetic alterations, loss of proteostasis, and disabled macroautophagy), antagonistic (deregulated nutrient-sensing), and integrative (cellular senescence, stem cell exhaustion, altered intercellular communication, chronic inflammation, and dysbiosis). The hallmarks of aging, much like soil, can be differently enriched, leading to changes in mitochondrial function. Created with BioRender.com.
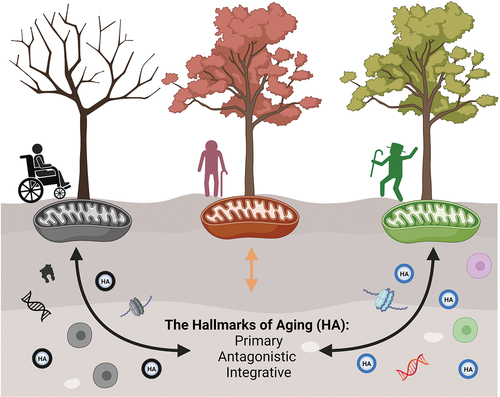
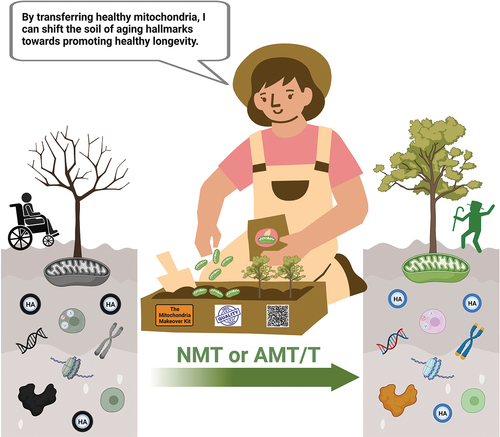
Figure 2. Mitochondria, playing critical roles in molecular, cellular, and systemic aspects of aging, have the potential to profoundly impact the hallmarks of aging (HA) through both natural mitochondrial transfer (NMT) and artificial mitochondrial transfer/transplant (AMT/T). Mitochondria play a pivotal role in governing the molecular, cellular, and systemic processes associated with aging, both in accelerating and potentially reversing the aging process for healthy longevity. In addition to their vital intracellular functions, both NMT and AMT/T hold promise as tools for gaining deeper insights into the hallmarks of aging and for the development of therapeutic interventions. Created with BioRender.com.