Figures & data
Table 1. Characteristics of routine and new routine tests for TBI diagnosis.
Table 2. New strategies for M. tuberculosis DNA detection.
Table 3. New strategies for M. tuberculosis antigens detection.
Table 4. New strategies for detection of anti-M. tuberculosis antibodies.
Table 5. Host blood transcriptomic signatures for incipient TB diagnosis.
Figure 1. Routine and research tests for TBI diagnosis. Diagnosis of TBI may be based on the detection of either host responses to Mtb antigens or of the pathogen itself. The routine immune-based tests currently used are the TST, new versions of EC-based skin tests, IGRA and its new developments. Other possible strategies are based on the detection of host factors such as the serological approach, for the detection of mycobacterial-specific antibodies, and the transcriptomic approach, which characterizes the host response in unstimulated blood, reflecting changes in gene expression between different disease states. On the other hand, microbiological tests able to identify Mtb itself are based on the detection of Mtb DNA or antigens from blood circulation. EC: ESAT-6/CFP-10; IGRA: interferon (IFN)-γ release assays; Mtb: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; NK: natural killer; TBI: tuberculosis infection; TST: tuberculin skin test. Created with BioRender.com.
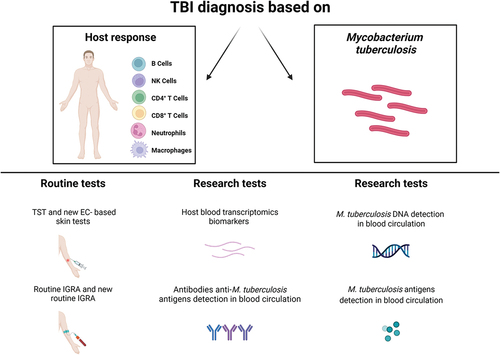
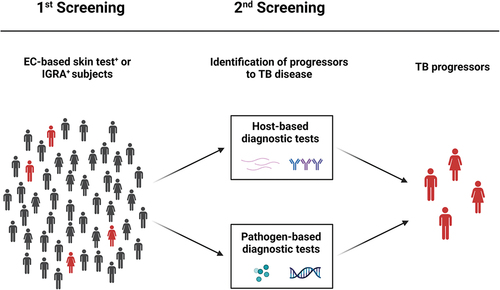
Figure 2. Routine and research tests for the identification of TB progressors. TBI individuals are routinely screened by EC-based skin tests or IGRA that reveal host immune responses to Mtb, in absence of clinically and/or microbiological manifestations of TB disease. The 5–10% of TBI individuals can develop TB disease in their life span, and half of those develop the disease within the first 2 years from infection. Progressors from TBI to TB disease may be identified by host-based or pathogen-based diagnostic tests. EC: ESAT-6/CFP-10; IGRA: interferon (IFN)-γ release assays; Mtb: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; TBI: tuberculosis infection; TST: tuberculin skin test. Created with BioRender.com.