Figures & data
Figure 1. The tissue Doppler curve showed the calculation of the MPI index. MPI: myocardial performance index; ICT: isovolumetric contraction time; IRT: isovolumic relaxation time; ET: ejection time; LV: left ventricle; LA: left atria; RV, right ventricle; RA, right atria; DAO: descending aorta.
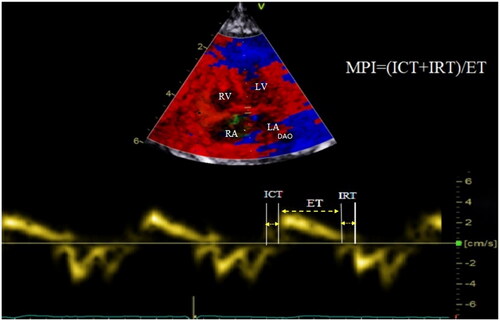
Figure 2. The right ventricular global longitudinal strain curve. LS: longitudinal strain; LV: left ventricle; LA: left atria; RV: right ventricle; RA: right atria; DAO, descending aorta.
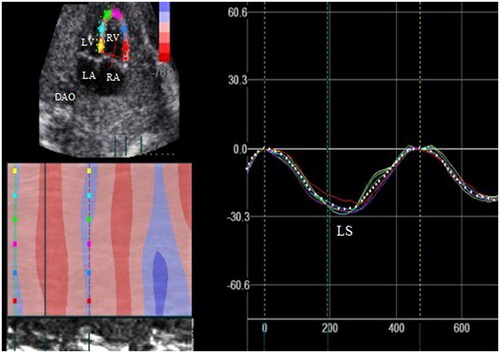
Figure 3. The right ventricular global longitudinal strain rate curve. SRs: systolic wave; SRe: early diastolic wave; SRa: late diastolic wave; LV: left ventricle; LA: left atria; RV: right ventricle; RA: right atria; DAO: descending aorta.
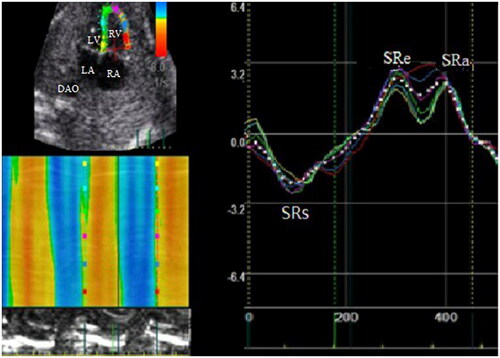
Table 1. Diagnosis of congenital heart disease with left or right outflow obstruction.
Table 2. The comparison of parameters between LVA and control group.
Table 3. The comparison of parameters between RVA and control group.
Table 4. Inter-observer and intra-observer variability.
