Figures & data
Table 1. Group demographics for children with normal sound detection and children with sensorineural hearing loss including anthropometric correlates, hearing levels and proportion of normal peripheral vestibular structures (expressed as a percentage).
Table 2. Hearing loss aetiology, proportion of normal vestibular responses, and amplification type for children with sensorineural hearing loss.
Table 3. Group comparisons for all measures of peripheral vestibular function (vHIT, cVEMP and oVEMP).
Figure 1. Mean path velocity across the four standing conditions for children with normal sound detection and children with SNHL. Children with SNHL showed reduced postural stability, as indicated by increased path velocities, in conditions where somatosensory information was modified (FEO and FEC conditions). Additionally, large variability in standing balance was observed in children with SNHL across all conditions when compared to children with normal sound detection. *Denotes p < 0.05.
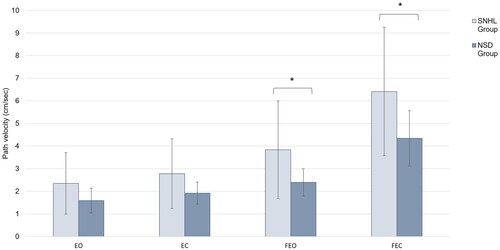
Table 4. Group comparisons for DWT bandwidth velocity across frequency bands for all standing balance conditions.
