Figures & data
Figure 1. Flowchart of the selection process for the case reports and case series studies included in this study.
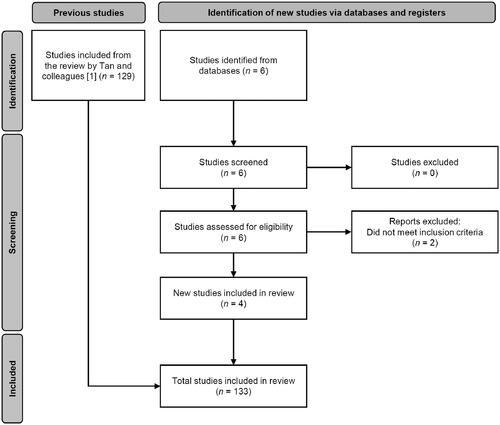
Table 1. Clinical laboratory values and patient properties of the whole population (n = 1,119).
Table 2. Clinical laboratory values and characteristics of the patients treated with or without activated charcoal from the whole population (n = 1,119).
Figure 2. Effect of activated charcoal on survival outcomes of patients with amatoxin poisonings. (A) whole database. Patients treated without activated charcoal (control, n = 452) and with activated charcoal (n = 667). (B) subgroup analysis of reasonably certain cases. Patients treated without activated charcoal (control, n = 329) and with activated charcoal (n = 667). Percentage of patients with treatment success (white) and treatment failure (black). ***P < 0.001 compared to control.
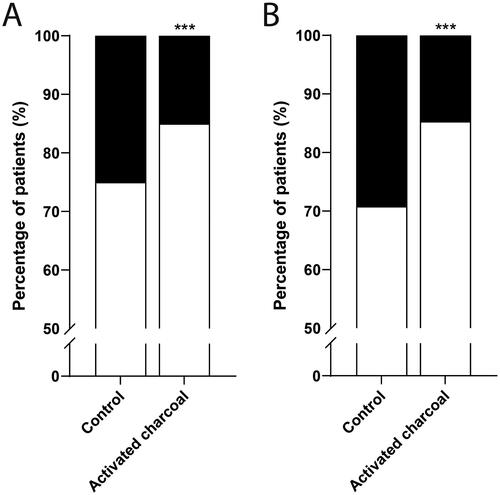
Figure 3. Clinical laboratory peak values of important liver markers in 1,119 patients divided in treated without activated charcoal (control) and with activated charcoal. (A) Aspartate aminotransferase activity, (B) Alanine aminotransferase activity, (C) Total serum bilirubin concentration, and (D) International normalized ratio. *P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 compared to the control.
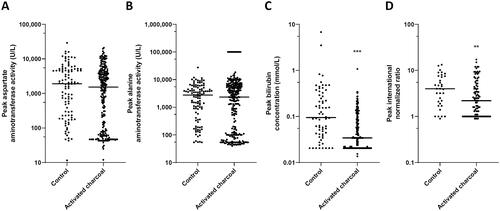
Table 3. Association of potential confounders on treatment outcome.
Supplemental Material
Download MS Word (27.5 KB)Data sharing statement
Upon reasonable request, and subject to review, the authors will provide the data that support the findings of this study.
