Figures & data
Figure 1. Overview of the multi-country, multi-method TIMCI evaluation – study design and main outcomes. Abbreviations: CDSA: clinical decision support algorithm; RCT: randomised controlled trial; KII: key informant interviews; HMIS: health management information system; DALY: disease-adjusted life years.
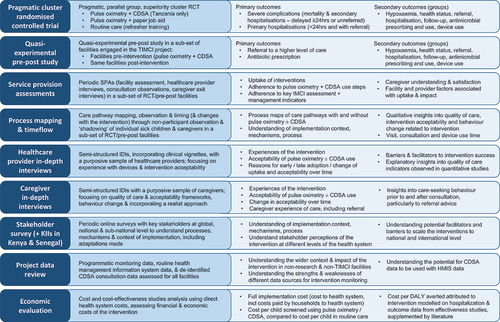
Table 1. Overview of the study setting and intervention according by country.
Figure 2. Pulse oximetry criteria for Senegal and Tanzania. In India and Kenya, Ministries opted to recommend pulse oximetry for all sick young infants and children.
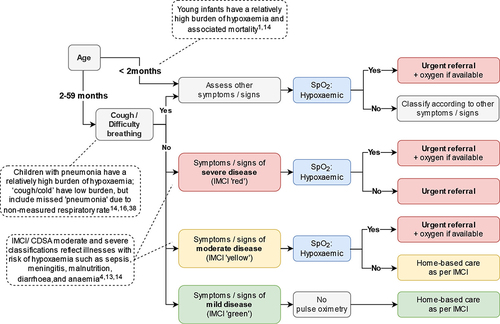
Figure 3. Study flowcharts of the pragmatic cluster RCT and quasi-experimental pre-post study, with interconnections with the embedded mixed-methods studies involving caregivers and children. (1) Location refers to urban/rural for Tanzania and to districts in India. (2) Data collected after consultations include caregiver responses at consultation exit and clinical records. (3) In all countries other than Kenya, data are collected from hospital (or primary care admission area) records for all children reported to have attended a hospital/admission facility (4) If children return to their enrolment facility (or attend any other study facility) during the follow-up period, data about the visit is collected, which includes the same information as gathered on Day 0.
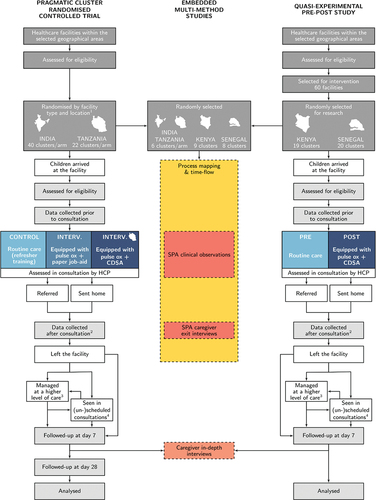
Table 2. Estimated sample sizes for each of the TIMCI sub-studies.
