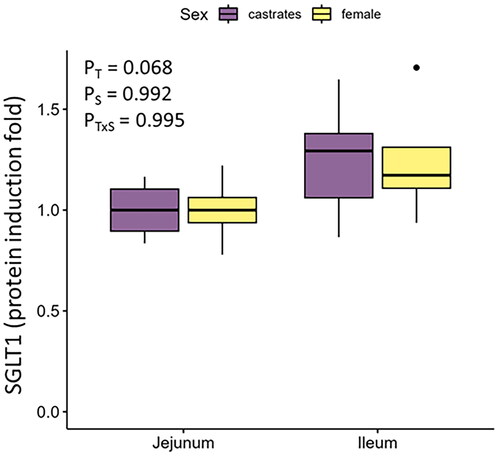
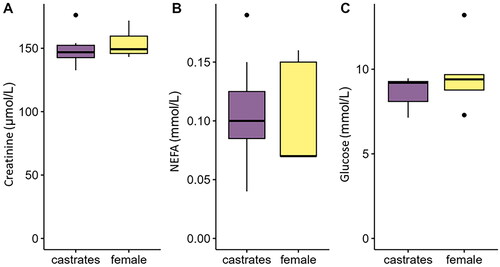
Figures & data
Table 1. Dietary ingredients and analysed composition (g or MJ/kg as-fed) of the grower and finisher diets.Table Footnote1
Table 2. Mean values with their standard error of the overall period feed intake, protein intake, carcase protein, average daily gain and feed conversion ratio in female and castrated pigs.
Figure 1. Trans-epithelial electrical resistance (TEER; Ω × cm2) in the jejunum and ileum of female and castrated finishing pigs. T: tissue; S: sex.
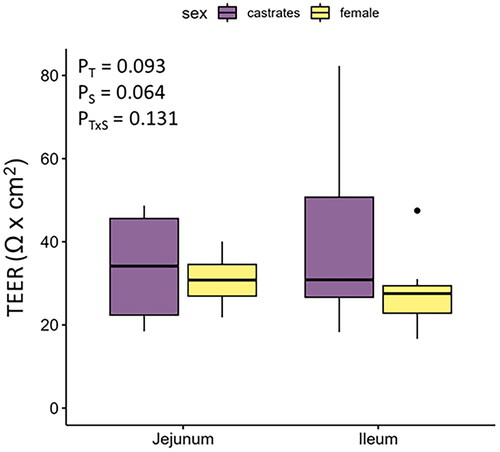
Table 3. Change in short-circuit current induced by L-glutammate, L-arginine, L-methionine and D-glucose in the jejunum and ileum of female and castrated finishing pigs.
Data availability statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, [T.M.], upon reasonable request.