Figures & data
Table 1. Demographic characteristics of the study sample.
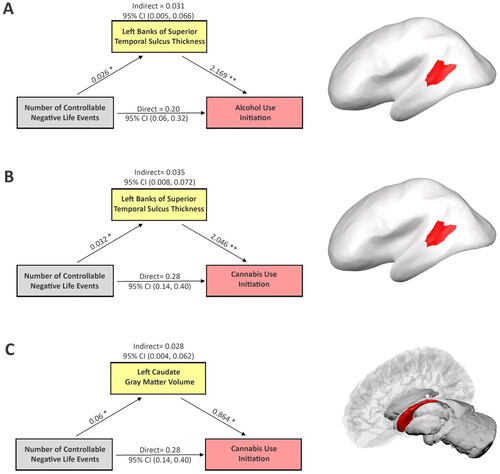
Figure 1. Mediation analysis shows how brain features explain relationships between controllable NLEs and initiation of alcohol and cannabis, respectively. Potential confounding effects due to age, gender, race/ethnicity, parental highest education level, pubertal stage, scanner type, and estimated intracrine volume were controlled in the mediation analyses. Cortical thickness of the left banks of the superior temporal sulcus mediates the effects of controllable NLEs on initiations of alcohol (A) and cannabis (B) use, respectively, (C) left caudate gray-matter volume mediates the effect of controllable NLEs on initiation of cannabis use. The figure includes the following regression coefficients: (1) the effects of controllable NLEs on each brain mediator; (2) the effects of brain mediators on initiation of alcohol and cannabis first use when adjusting for controllable NLEs; (3) the direct and indirect associations along with the 95%CIs between controllable NLEs and the onset of alcohol or cannabis use, respectively. *p < 0.05. **p < 0.001. The right column shows the location of each corresponding brain region. Note, NLEs and substance initiation data were collected at the same visit. While brain feature measures were collected at the visit before substance initiation, therefore, brain immaturity should be regarded as a pre-existing condition in the mediation analyses.
Data availability statement
The data used in this paper was retrieved on 21 October 2021, from Sage Bionetworks Synapse (https://doi.org/10.7303/syn22213272).
