Figures & data
Table 1. Pandemic-related and clinical characteristics (N = 15,169).
Table 2. Health-related characteristics (N = 15,169).
Table 3. Pandemic-related stressors (N = 15,169).
Figure 1. Effect estimates of the linear mixed regression analysis.
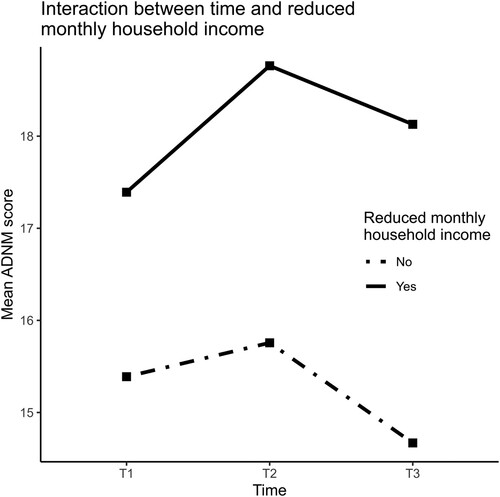
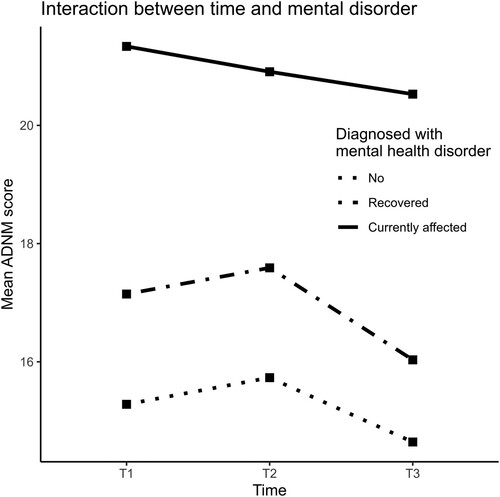
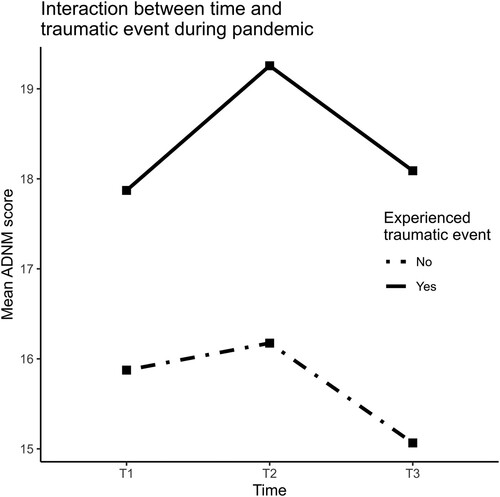
Notes. ≥10 years = 10 or more years of schooling. Reduced income = Reduced monthly household income due to the coronavirus. Financial support = Receiving financial support from the government. Maintenance/repair/etc. = Maintenance, repair, construction. More at home = Spent more time at home due to the coronavirus pandemic. Social dist. = Spent more time at home as a precautionary measure (social distancing). Self-isolation = Stayed at home in self-isolation because of self-infection. Quarantine = Stayed at home due to contact with infected people or being in risk areas. Face contact = Face-to-face contact with loved ones or friends. Face contact at work = Work involves (almost) daily face-to-face contact with other people. Digital contact = Digital contact with loved ones or friends, e.g. by phone, Skype, or Zoom. News = Hours a day watching, reading, or listening to the news or other information about the coronavirus pandemic. COVID-19 inf. = Infected (i.e. tested positive) with the coronavirus.
Reference categories: aMale. bLess than 10 years of schooling. cVery low. dNo. eOther. fNo. gI have no personal contact with other people. hI have no contact by phone, skype, etc. iI do not watch, read or listen to news about the coronavirus pandemic. jVery good. kNo.

Table 4. Effect estimates of risk factors and stressors on symptoms of adjustment disorder (N = 15,169).
Data availability
The detailed sociodemographic information of the dataset does not fully protect the anonymity of the respondents. For this reason, the entire dataset cannot be made publicly available. However, excerpts of the data on a higher aggregation level can be provided upon justified request by the first author.