Figures & data
Figure 1. Schematic procedure of the study. MALDI-TOF/MS, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry; BALF, Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid; hvKP, hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae; E. coli, Escherichia coli; E. aerogenes, Enterobacter aerogenes; WGS, whole-genome sequencing.
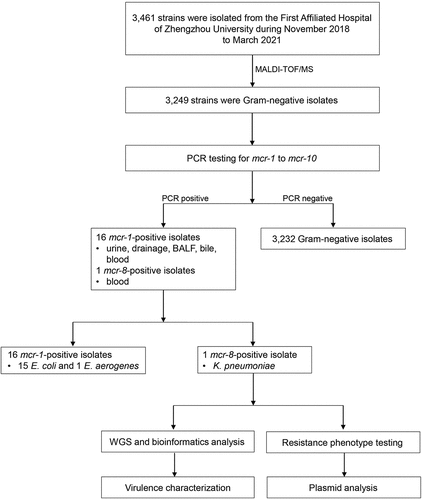
Table 1. MIC values of antimicrobials for K. pneumoniae FAHZZU2591, transconjugant FAHZZU2591-E. coli 600 and recipient strain E. coli C600.
Table 2. Antibiotic resistance genes of K. pneumoniae FAHZZU2591.
Table 3. The detection of virulence genes in K. pneumoniae FAHZZU2591 based on whole-genome sequence.
Figure 2. Plasmid profiles of K. pneumoniae FAHZZU2591, transconjugant FAHZZU2591-E. coli 600 and recipient strain E. coli 600. Plasmid size determination by S1-PFGE, with Salmonella enterica serotype Braenderup H9812 as the size marker. The names of the isolates are shown in the first line. The arrows in indicated the locations of mcr-8, rmpA or rmpA2 harbouring plasmids according to the Southern blotting experiment. .
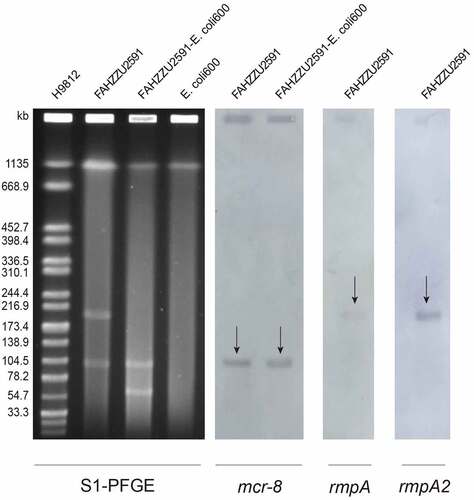
Figure 3. The genomic analysis of K. pneumoniae FAHZZU2591. (a) Comparison between plasmid pFAHZZU2591 and other pLVPK-like virulence plasmids based on BLASTn analyses (GenBank accession numbers from inside to outside are AY378100, CP034776, MN200128, and CP083752). Plasmid pLVPK (the outer circle) was used as the reference. (b) Comparison between plasmid pFahzzu2591mcr-8 and four similar plasmids in NCBI nr/nt database (accession numbers: CP074185.1, MK262711.1, CP076032.1 and LC549807.1). pFahzzu2591mcr-8 (the outer circle) was used as the reference. The different colours indicate different plasmids and are listed in the colour key. (c) a linear demonstration of main structural features of plasmid pFahzzu2591mcr-8 compared with plasmids pKP32558-2-mcr8 (CP076032) and pJBIWA001_3 (CP074185). Open reading frames (ORFs) are indicated as arrows that show the orientation of coding sequence with the gene name. Yellow indicates genes related to mobile elements, red indicates genes related to drug resistance, blue indicates genes involved in conjugation and pink represents other functional genes. Hypothetical protein encoded genes are coloured by grey. Regions with a high degree of homology are indicated by pale blue shading.
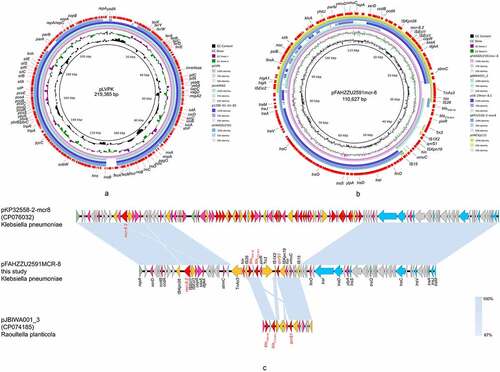
Figure 4. Virulence assessment of strain FAHZZU2591. (A) Serum-killing assay. Survival in a serum-killing assay of FAHZZU2591 and ATCC700603. The survival is denoted in percentage. The bars denote the means and standard errors of the mean. **P <0.01 (unpaired t test). (B) Galleria mellonella infection assay. Survival at 176 h in a G. mellonella assay of isolates FAHZZU2591, ATCC700603, transconjugant FAHZZU2591-E. coli 600 and recipient strain E. coli 600. Thirty larvae were used per strain. G. mellonella larvae were inoculated with 20 µl of each strain at doses of 1 × 106 and incubated at 37°C; the viability was assessed over 164 h. The Kaplan-Meier estimator method was used to plot a survival curve for G. mellonella. The survival is denoted in percentage. Survival curves were compared with the log-rank (Mantel – cox) test. **P <0.01. (C) Haematoxylin and eosin staining of ileum and lung tissues at seven days post infection. NS: normal saline. (D) Homology analysis of K. pneumoniae strains isolated from faeces of mice by XbaI-PFGE. (E) Time diagram of mouse infection model assay. D represents the days of isolation, and M stands for mouse number.
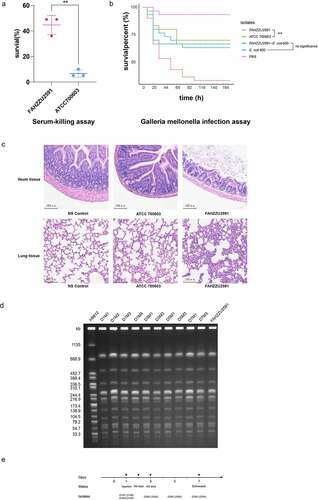
Figure 5. Phylogenetic analysis. (a) a phylogenetic analysis of mcr-8-producing K. pneumoniae strains based on core genomes. The drug resistance genes, collection years, locations, isolation sources, and ST types are shown. The annotation denotes the isolation sources. Different classes of resistance genes were divided into different coloured squares. (b) Phylogenetic tree of ST412 K. pneumoniae from NCBI database and this study. The locations, isolation sources, and collection years are shown. K. pneumoniae FAHZZU2591 is indicated by red.


