Figures & data
Figure 1. Schematic overview of Markov structure – ZOster ecoNomic Analysis (ZONA) model. HZ: Herpes Zoster; PHN: postherpetic neuralgia. Figure originally published in D. Curran et al. 2017.Citation20
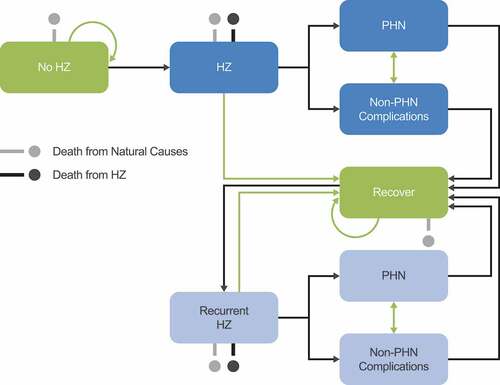
Table 1. Demographic, epidemiological and vaccine efficacy input values (base case)
Table 2. Health outcomes and healthcare resource utilization in individuals ≥50 YOA (base case)
Table 3. Cases avoided with RZV vaccination vs. no vaccination by age cohort, in the mass vaccination setting (base case)
Figure 2. HZ cases avoided with RZV vaccination per one million people over the respective age cohorts’ lifetime, compared with no vaccination, in the mass vaccination setting (base case). HZ: herpes zoster; RZV: recombinant zoster vaccine; YOA: years of age. Step increases over time (particularly pronounced in the 50–59 YOA cohort) are due to incidence being included as an age-specific step function
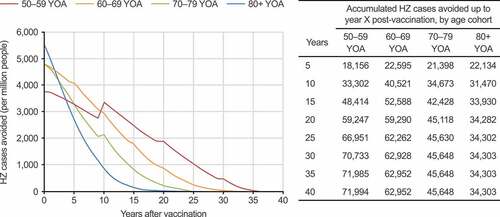
Figure 3. NNV to avoid one case of HZ and one case of PHN by age cohort (base case). HZ: herpes zoster; NNV: number needed to vaccinate; PHN: postherpetic neuralgia; YOA: years of age. NNV results are not affected by the vaccination coverage level, and thus do not differ between the private market and mass vaccination settings
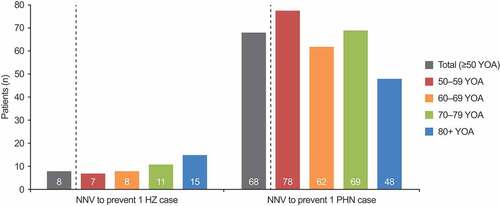
Figure 4. Deterministic one-way sensitivity analysis: HZ cases avoided with RZV vaccination, compared with no vaccination. HZ: herpes zoster; RZV: recombinant zoster vaccine; YOA: years of age. Lower bound estimates are in blue and upper bound estimates are in green, with lower and upper ranges for inputs in brackets; refer to Supplementary Table 1 for details of inputs which varied by age group
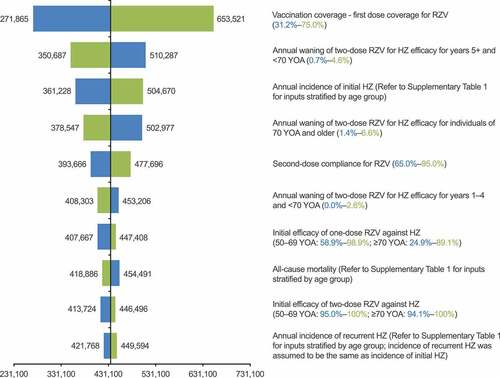
Figure 5. Probabilistic sensitivity analysis: HZ cases avoided with RZV vaccination, compared with no vaccination. HZ: herpes zoster. The blue line shows the percentage of simulations averting at least the number of HZ cases shown on the x-axis
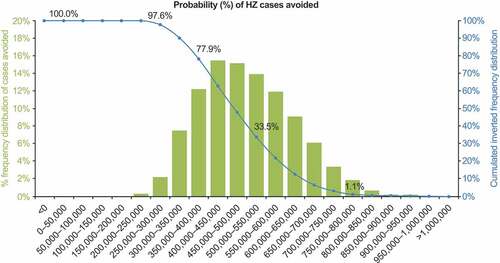
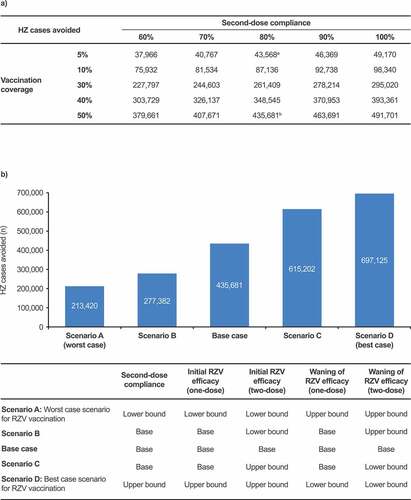
Figure 6. Scenario analysis assumptions and results comparing RZV vaccination with no vaccination, targeting individuals 50 YOA and older, estimating the number of HZ cases avoided (a) with increasing vaccination coverage and second-dose compliance; (b) with varying second-dose compliance, RZV efficacy, and its waning. aBase-case outcome for the private market setting analysis. bBase-case outcome for the mass vaccination setting analysis. Values for lower and upper bounds can be found in Supplementary Table 1. HZ: herpes zoster; PHN: postherpetic neuralgia; RZV: recombinant zoster vaccine; YOA: years of age