Figures & data
Table 1. Advantages and disadvantages of exosome isolation methods.
Figure 1. The common exosome characterization techniques.
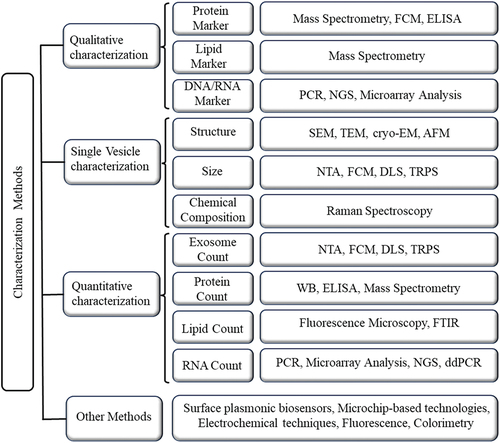
Table 2. Advantages and disadvantages of vaccine types.
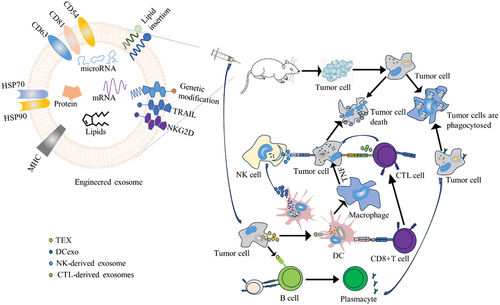
Figure 2. The mechanism of action of tumor-derived exosomes and immune cell-derived exosomes on tumor cells.
Data availability statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
