Figures & data
Figure 1. Characterization of DMA2017. (A) Characterization of the binding ability of DMA2017 with A, B1, B2 and C subgenotypes of CA16. (B) SDS-PAGE analysis of CA16 and Western blotting of CA16 bound with DMA2017.
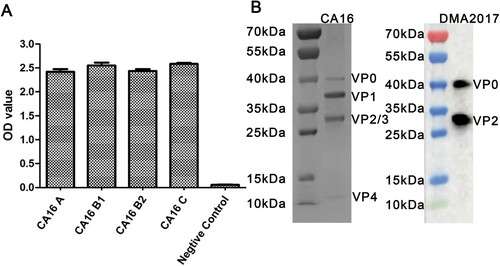
Table 1. Neutralization titers of DMA2017 against four CA16 subgenotypes and EV71. Note: NA11F12 is a known CA16-neutralizing antibody.
Figure 2. Protection efficacy of DMA2017 against CA16 challenge in suckling mice. (A) Groups of mice (n = 5) were infected with 54 CCID50 BJCA08/CA16. One day post-challenge, the mice were treated with different doses of DMA2017 (10, 2, 0.4, 0.08 and 0.016 μg/g) via intraperitoneal route. The asterisk indicates significant differences at **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001. (B) Clinical symptoms of mice were monitored and recorded for 21 days.
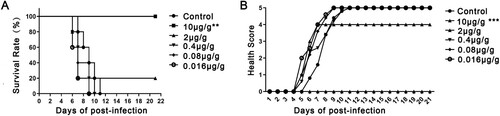
Figure 3. Histological examination results. In the group of health control and DMA2017 treated, no histological change was observed in the heart, brain and limb muscle. (d) In the MEM-treated group of mice, myocardial cell necrosis occurred in the heart. (e) MEM-treated mice exhibited severe muscle fiber necrosis in the limb muscle (arrow). (f) In the brain of mice, eosinophilic neuronal necrosis was observed occasionally. All the pathological changes are indicated by arrow. Representative images are shown at a magnification of 200×. Scale bar: 200 μm.
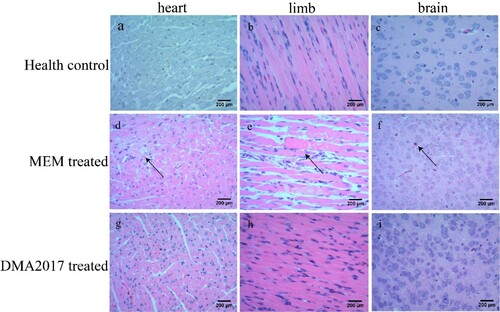
Figure 4. Immunohistochemical results. An anti-CA16 VP1 antibody was used to detect CA16 antigen. Numerous viral antigen positive reactions were observed in the heart, limb muscle and brain (arrows) in the MEM-treated mice. In contrast, no viral antigen was observed in the heart, limb muscle and brain of the health control and DMA2017-treated mice. Representative images are shown at a magnification of 200×. Scale bar: 200 μm.
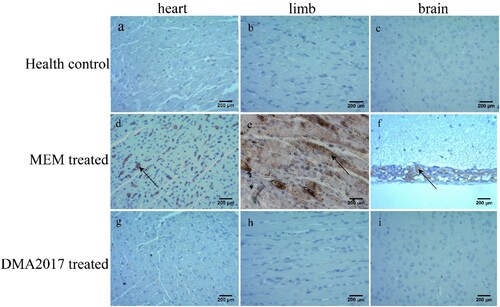
Figure 5. The Fc fragment is essential for DMA2017 against CA16 infection. (A) SDS-PAGE of Fab and F(ab’)2. Groups of mice (n = 6) were infected with 54 CCID50 BJCA08/CA16. The mice were treated with 10 μg/g of DMA2017, Fab, F(ab’)2 or PBS via intraperitoneal route. (B)The survivorship curve of each group. (C) Clinical symptoms of mice were monitored and recorded for 21 days. (D) Weight change of each group. (E) DMA2017 mediated the ADCC between Murine FcγRIII Jurkat cell and CA16 P1 expressing 293 T. The asterisk indicates significant differences at **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001.
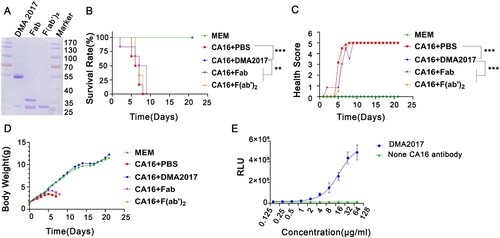
Figure 6. NSHPPY is the minimal epitope recognized by DMA2017. (A) DMA2017 could bind the peptide 139TGNENSHPPYATT151 located on the capsid protein VP2. (B) Assessing the interaction of individual peptides with DMA2017 by ELISA. (C)Alignment of VP2 amino acid sequence (143-148) of the different CA16 and EV71 subgenotypes. (D)An enlarged protomer of the mature CVA16 particle. Different parts of the capsid are colored as follows - VP1, blue; VP2, green; VP3, red; VP4, yellow. The epitope is shown in hot pink. (E) VP2 EF-loop, BC-loop and HI loop are signed (black arrows) [Citation16]. The epitope of DMA2017 is located in EF-loop (red arrow).
![Figure 6. NSHPPY is the minimal epitope recognized by DMA2017. (A) DMA2017 could bind the peptide 139TGNENSHPPYATT151 located on the capsid protein VP2. (B) Assessing the interaction of individual peptides with DMA2017 by ELISA. (C)Alignment of VP2 amino acid sequence (143-148) of the different CA16 and EV71 subgenotypes. (D)An enlarged protomer of the mature CVA16 particle. Different parts of the capsid are colored as follows - VP1, blue; VP2, green; VP3, red; VP4, yellow. The epitope is shown in hot pink. (E) VP2 EF-loop, BC-loop and HI loop are signed (black arrows) [Citation16]. The epitope of DMA2017 is located in EF-loop (red arrow).](/cms/asset/ce98dba3-3b67-46d3-aed6-6f3275e1da9e/temi_a_2149352_f0006_oc.jpg)
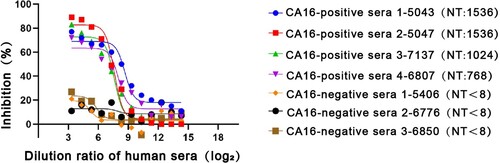
Figure 7. Competitive ELISA of DMA2017 against human sera. The DMA2017 competed with four sera from convalescent children after CA16 natural infection with NT titers 1536, 1024, 1536 and 768, respectively. Three CA16-negative human sera were used as control with NT titer <8. NT represents the neutralization titer of human sera.