Figures & data
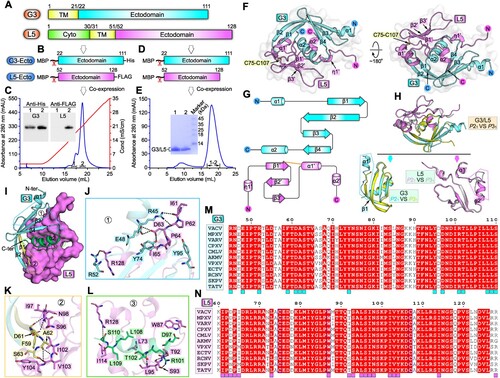
Figure 1. Structure of VACV G3/L5 sub-complex. A schematic view of the protein-engineering strategy used to yield VACV G3-Ecto-His/L5-Ecto-FLAG sub-complex (A, B) or tag-free VACV G3-Ecto/L5-Ecto sub-complex (A, D). The transmembrane domain (TM), the ectodomain, and the cytoplasmic domain (Cyto) are individually marked with the boundary-residue numbers. (C) Identification of G3-Ecto-His/L5-Ecto-FLAG hetero-complex using ion-exchange chromatography and western blot assay. (E) Solution behaviour of G3-Ecto/L5-Ecto sub-complex on a Superdex 200 Increase 10/300 GL column. (F) Overall structure of the heterodimer (P21 space group) formed between G3 (cyan) and L5 (violet). (G) Topology plots of G3 and L5 proteins. (H) Structural comparison of G3/L5 complexes from two space groups (P21 and P31). Those elements exhibiting variant conformations are highlighted by dotted box. (I-L) The atomic binding details between G3 and L5. Residues providing ≥10 contacts are shown and labelled. Dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds. (M) Multiple sequence alignment of the G3 homologues from orthopoxviruses. Key residues on VACV G3 that interact with L5 are marked with cyan squares. (N) Multiple sequence alignment of the L5 homologues from orthopoxviruses. Key residues on VACV L5 that interact with G3 are marked with violet squares.
Supplemental Material
Download MS Word (3.4 MB)Data availability statement
The datasets used and/or analysed during this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. Atomic coordinates and structure factors for the reported crystal structures have been deposited into the Protein Data Bank under accession numbers 7YTT and 7YTU.
