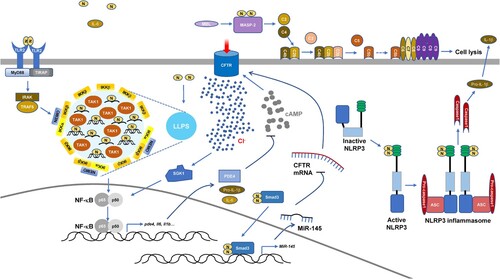
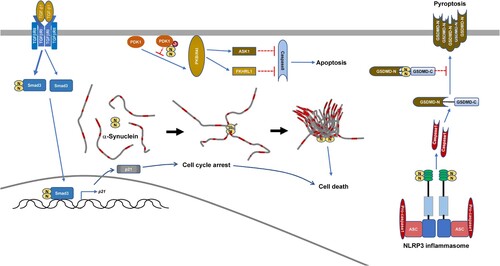
Figures & data
Table 1. Effects of different human-infecting coronavirus N-proteins on host cell signaling.
Table 2. SARS-CoV-2-N-based vaccines under development.
![Figure 1. The structure of SARS-CoV-2 N-protein. (A). Model of SARS-CoV-2 N-protein dimer. (B). Topology diagram for SARS-CoV-2 N-protein N-terminal RNA-binding domain. (C). Superimposed structures in ribbon representation of N-protein N-terminal RNA-binding domain from SARS-CoV-2 (green), SARS-CoV (cyan), HCoV-OC43 (pink), MERS-CoV (orange), and HCoV-NL63 (blue) [Citation6]. The loops that show significant differences are highlighted by dotted circles. The AMP ligand in the HCoV-OC43 N-protein N-terminal RNA-binding domain-AMP complex is shown as a stick structure. D. Topology diagram for SARS-CoV-2 N-protein C-terminal dimerization domain. E. Superimposed structures in ribbon representation of N-protein C-terminal dimerization domain from SARS-CoV-2 (pink), SARS-CoV (cyan), MERS-CoV (orange) and HCoV-NL63 (blue). Figure adapted from [Citation6].](/cms/asset/491d999c-575a-4717-ba83-c3d1747359f8/temi_a_2164219_f0001_oc.jpg)