Figures & data
Figure 1. Number of (A) positive COVID-19 cases, (B) hospitalizations, (C) intensive care unit visits, and (D) deaths that have been recorded within the University of Texas Medical Branch network during July 01, 2021, and October 31, 2021, characterized by the predominance of the Delta variant. The horizontal line represents the total number of individuals for each category and the dotted arrows represent the percentage decrease compared to the NoI group. NoI: No known induced immunity from reportedly naïve patients who have not been vaccinated and have not experienced a COVID-19 infection prior to the current infection; VaxI: Vaccine-induced immunity prior to first infection; InfI: Infection-acquired immunity without vaccination but having recovered from a known previous infection prior to reinfection; HybrI: Hybrid immunity from both vaccination and a known previous infection prior to reinfection.
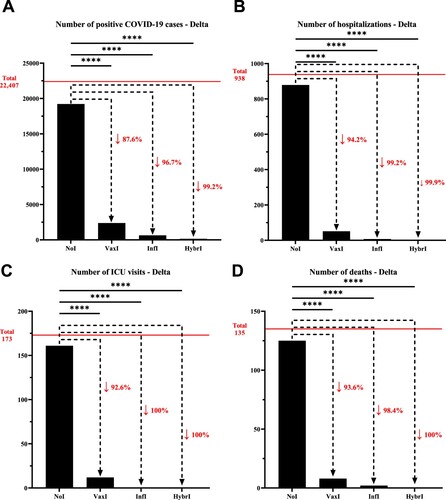
Figure 2. Number of (A) positive COVID-19 cases, (B) hospitalizations, (C) intensive care unit visits, and (D) deaths that have been recorded within the University of Texas Medical Branch network during December 10, 2021, and February 28, 2022, characterized by the predominance of the Omicron variant. The horizontal line represents the total number of individuals for each category and the dotted arrows represent the percentage decrease compared to the NoI group. NoI: No known induced immunity from reportedly naïve patients who have not been vaccinated and have not experienced a COVID-19 infection prior to the current infection; VaxI: Vaccine-induced immunity prior to first infection; InfI: Infection-acquired immunity without vaccination but having recovered from a known previous infection prior to reinfection; HybrI: Hybrid immunity from both vaccination and a known previous infection prior to reinfection.
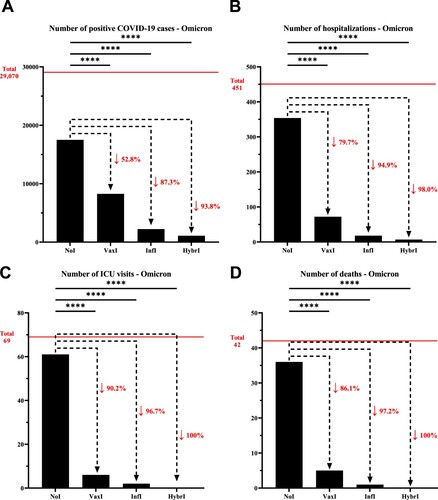
Figure 3. NL63 infected mice produced cross-reactive IgG against HCoV-229E and SARS-CoV-2 antigens. (A) Overview of Ad5-hACE2 transduction and NL63 infection of BALB/c mice. (B, C) The ELISA plates were coated with N or S. The sera were collected from the Ad-PBS group (n = 5) and Ad-NL63 infected groups (n = 6). HRP-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG Ab was used as secondary antibody. The absorbance was read at 450 nm after terminating reaction. Statistical significance was determined by the two-tailed t-test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01).
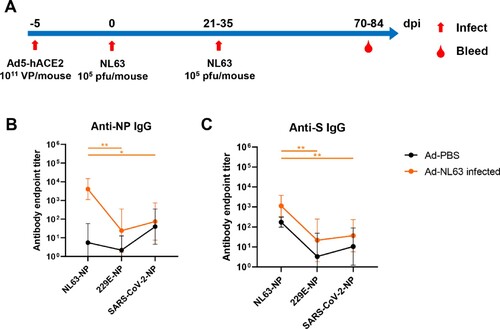
Table 1. Cross-reactivity of pre-COVID-19 sera to the spike (S) and nucleocapsid (N) of SARS-CoV-2.
Supplementary_Tables.docx
Download MS Word (24.4 KB)Data availability statement
The data files used in the current study can be made available upon reasonable request to the corresponding author. It should be noted that the human data will be made available with consideration of a regulated process that oversees human data management at the University of Texas Medical Branch.
