Figures & data
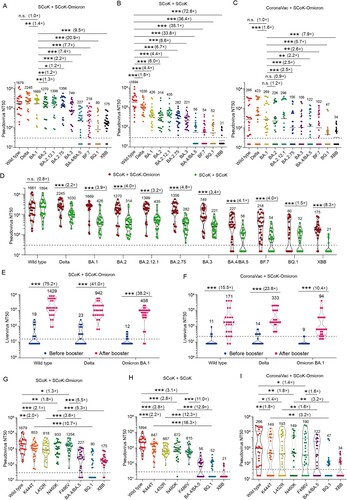
Figure 1. Neutralizing antibodies elicited by an Omicron BA.1–based updated RBD-Fc fusion protein vaccine booster against SARS-CoV-2 variants in adults. A-E, The 50% neutralizing titers (NT50) against SARS-CoV-2 Wild type, Delta, and Omicron subvariants VSV-based pseudoviruses. (A), Individuals who received three doses of RBD-Fc fusion protein vaccine (SCoK) and a booster Omicron BA.1–based updated RBD-Fc fusion protein vaccine (SCoK-Omicron) (n = 25). (B), Individuals who received three doses of RBD-Fc fusion protein vaccine (SCoK) and a booster RBD-Fc fusion protein vaccine (SCoK) (n = 25). (C), Individuals who received two doses of inactivated vaccine (CoronaVac) and a booster Omicron BA.1–based updated RBD-Fc fusion protein vaccine (SCoK) (n = 25). (D), Comparison of two immunization groups that received a booster of the original or updated vaccine (SCoK + SCoK-Omicron vs. SCoK + SCoK). (E, F), The NT50 of two immunization groups (E, SCoK + SCoK-Omicron; F, CoronaVac + SCoK-Omicron) against SARS-CoV-2 Wild type, Delta, and Omicron BA.1 live viruses before and after the booster. (G, I), The NT50 of three immunization groups (G, SCoK + SCoK-Omicron; H, SCoK + SCoK; I, CoronaVac + SCoK-Omicron) against SARS-CoV-2 Wild type, Omicron BA.4/BA.5, and two single-point mutation variants (L452R or F486V) VSV-based pseudoviruses. Data were analyzed by Student's t-test (normal distribution) or one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple comparison test. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; n.s., not significant, P > 0.05. Geometric mean titers (GMT) and positive rates are labelled and annotated above each group of points. The horizontal dotted line indicates the positive seroconversion threshold of NT50 (30 in pseudovirus assay, 16 in live virus assay).
Supplemental Material
Download MS Word (630 KB)Data availability statement
All data are available in this article, supplementary materials, or available from the corresponding authors.

