Figures & data
Figure 1. Minimum spanning tree of all Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates. We defined genetic distances within 12 SNPs isolates were clusters, only clustered isolates were retained. Each circle represents a cluster. The size of the circle represents the number of isolates in the cluster. The colour of each circle represents the surveillance site of the isolates. Isolates isolated from the same county within a cluster were coloured by white but not mean all white colour isolates isolated from same site.

Table 1. The risk/protective factors associated with the likelihood of clustering.
Figure 2. WGS-clusters of multidrug resistant or rifampin-resistant isolates with rifampin-sensitive isolates. 98 multidrug resistant (MDR) isolates, 23 rifampin-resistant (RR) isolates and 28 rifampin-sensitive (RS) isolates clustered in 50 WGS – clusters.
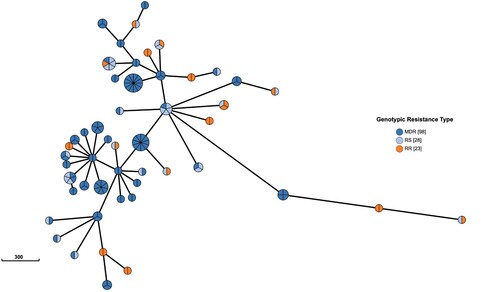
Figure 3. Classification of MDR/RR-TB based on treatment history and genomic analysis. MDR/RR-TB: multidrug resistant or rifampin-resistant tuberculosis.
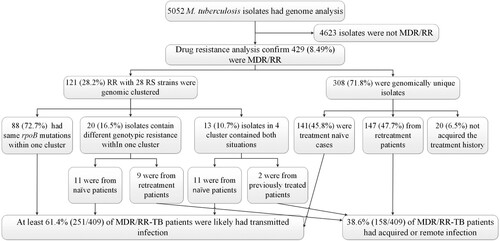
Table 2. Univariable analysis of risk factors associated with multidrug-resistance in genomic clusters.
