Figures & data
Figure 1. Agro-ecological suitability map for rain-fed rice production of Ethiopia (MoA, Citation2010; MoARD, Citation2010).
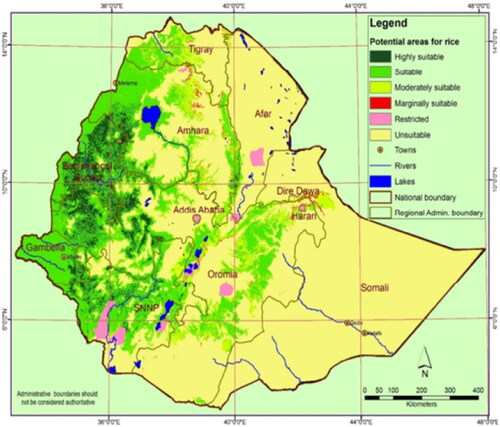
Figure 2. Different stages of rice stem borer identified from rice in Ethiopia (Bewket, Citation2018).
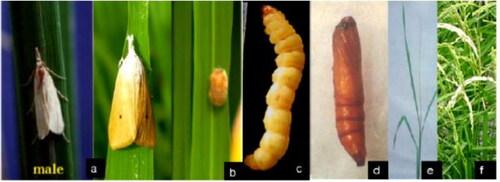
Figure 3. Distribution of rice diseases in Pawi and Jawi districts during 2020 main cropping season (Gudisa, Citation2020).
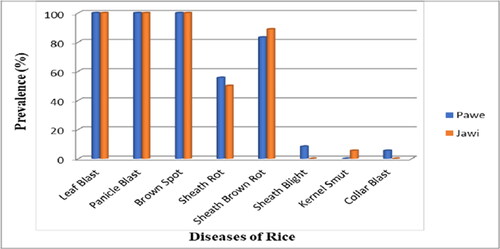
Table 1. The overall disease prevalence, incidence, and severity of rice diseases in different administrative districts of Ethiopia.
Figure 4. The disease severity level in vegetative and heading growth stages of rice at Pawe district (Wubneh & Bayu, Citation2016). Where: veg: vegetative growth stage; head: head setting growth stage; PB: panicle blast; LB: leaf blast; BS: brown spot; SB: sheath blight; BPB: bacterial panicle blight; SS: sheath rot; BLS: bacterial leaf strike.
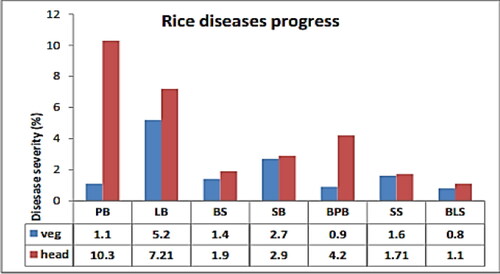
Figure 5. Symptoms of sheath rot (a), sheath brown (b), and brown spot (c) disease in a rice field in Ethiopia. Source: Zeleke et al. (Citation2019).

Figure 6. Symptoms of panicle blast (A), neck blast (B), node blast (C), and leaf blast (D) diseases in rice field in Ethiopia. Source: Zeleke et al. (Citation2019).

Figure 7. Symptoms of sheath blight (a) and rice yellow motile viruses (b) diseases in rice filed. Source: Zeleke et al. (Citation2019).

Figure 8. Few medicinal plants [Kulkual (Euphorbia abyssinica) J. Gmel] (a), Eret (Aloe sp.) (b), Nechbahirzaf (Eucalyptus globulus Labill.) (c), and Nechshinkuret (Allium sativum L.) (d) are used to treat different diseases, including rice, in Ethiopia. Source: Mekonnen et al. (Citation2022).
![Figure 8. Few medicinal plants [Kulkual (Euphorbia abyssinica) J. Gmel] (a), Eret (Aloe sp.) (b), Nechbahirzaf (Eucalyptus globulus Labill.) (c), and Nechshinkuret (Allium sativum L.) (d) are used to treat different diseases, including rice, in Ethiopia. Source: Mekonnen et al. (Citation2022).](/cms/asset/6479bfed-5119-4de2-8fe7-634cae933faa/oafa_a_2300558_f0008_c.jpg)
