Figures & data
Table 1. Characteristic of study population: qualifying conditions, comorbidity burden, and demographics.
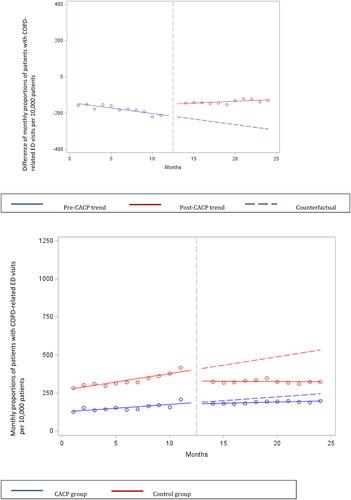
Figure 1. Difference and overall trend in mean monthly COPD-related hospitalizations per 10,000 patients in CACP group compared to Control group. Abbreviations: CACP, comprehensive annual care plan; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
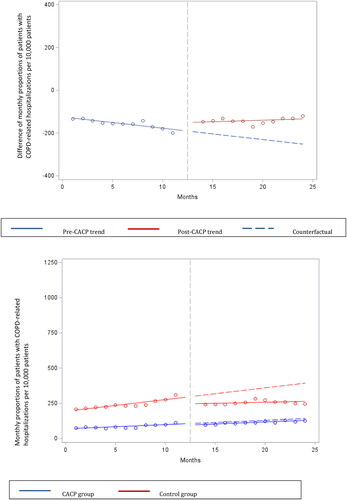
Table 2. Interrupted time series analysis of healthcare utilization before and after CACP in COPD patients (1 year pre- and post-CACP index date) per 10,000 patients.
Supplemental Material
Download MS Word (564.8 KB)Data availability statement
The dataset from this study is held securely in coded form at the School of Public Health, University of Alberta. Access may be granted to those who meet pre-specified criteria for confidential access.